继承关系对比


从JDK API中可知二者都实现了 List 接口,故此二者都会有add,cantains等方法。
对于List接口的实现类,都有以下特点:
- 允许重复的元素
- 允许null值。至少ArrayList和LinkedList都允许有null值,并且null也是可以重复的,添加多个null,list的长度也会增加
- 删除操作时,如果是根据对象删除的话,会删除第一个出现的元素。(这样如果数组内有多个重复元素的时候也不会混淆)
底层数据结构对比
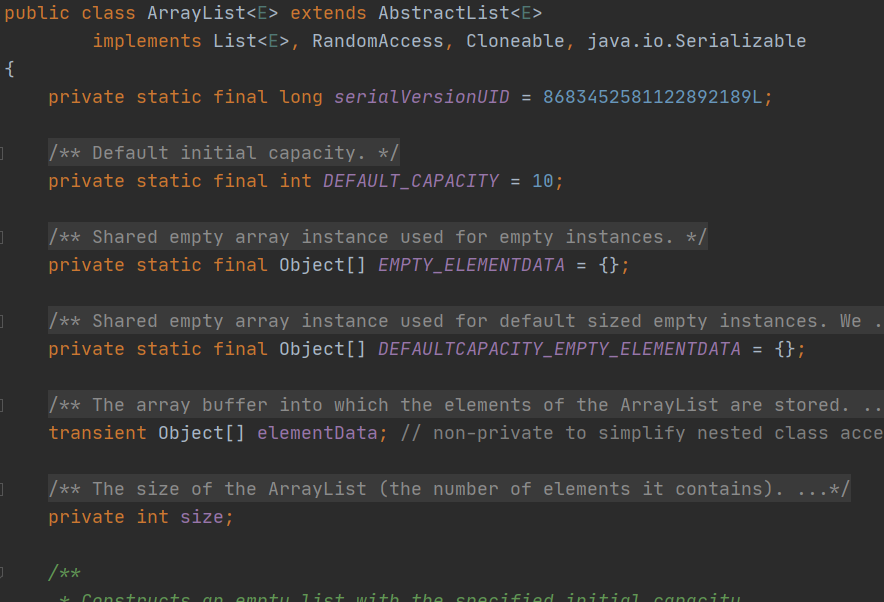
ArrayList底层数据结构是 数组
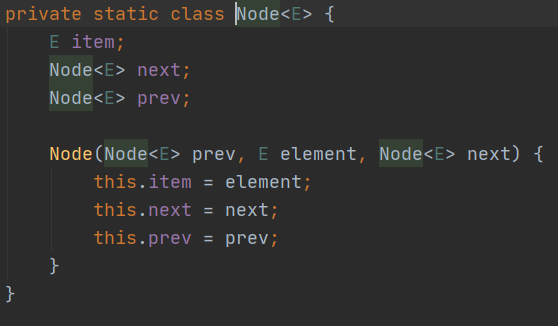
LinkedList底层数据结构是双向链表
操作性能对比
ArrayList,查找快,因为是连续的内存空间,方便寻址,但删除,插入慢,因为需要发生数据迁移
LinkedList,查找慢,因为需要通过指针一个个寻找,但删除,插入块,因为只要改变前后节点的指针指向即可。
具体分析,贴源码
查找
ArrayList,下标直接访问,时间复杂度O(1)
public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); }
LinkedList,挨个遍历,时间复杂度O(n),可以用加索引的方式优化查询时间复杂度为O(logn),这时候叫做跳表
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
添加
ArrayList,添加到尾部O(1),添加到中间O(n),数据迁移耗时
public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 判断数组大小是否足够 elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
LinkedList添加为O(1)
public void add(E e) { checkForComodification(); lastReturned = null; if (next == null) linkLast(e); else linkBefore(e, next); nextIndex++; expectedModCount++; }
删除
ArrayList 涉及数据迁移 O(n)
public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
LinkedList 改变尾节点的next即可 O(1)
public void remove() { checkForComodification(); if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; unlink(lastReturned); if (next == lastReturned) next = lastNext; else nextIndex--; lastReturned = null; expectedModCount++; }