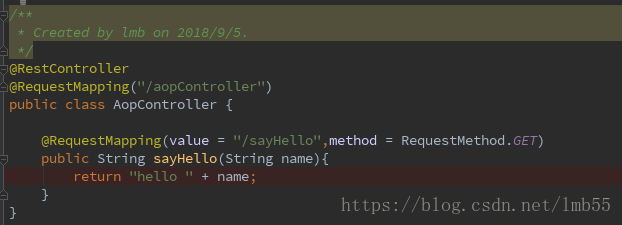
看完正文之后再来理解这个表达式 艘EZ
先看完下面的文章再来看这一部分
首先我说一下切入点表达式,然后你在去看下面的文章
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.skxx.vrxmty.modules.*.*.controller.*.*(..))")
public void before(){}匹配modules下的所有controller下的所有方法,不包含controlelr中方法调用其他的方法
先看此处----------------------正文---------------------------------------------------
以下转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/lmb55/article/details/82470388
一、示例应用场景:对所有的web请求做切面来记录日志。
1、pom中引入SpringBoot的web模块和使用AOP相关的依赖:
<!--10.springboot aop-->
<!-- start of aop-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- end of aop-->其中:
cglib包是用来动态代理用的,基于类的代理;
aspectjrt和aspectjweaver是与aspectj相关的包,用来支持切面编程的;
aspectjrt包是aspectj的runtime包;
aspectjweaver是aspectj的织入包;
2、实现一个简单的web请求入口(实现传入name参数,返回“hello xxx”的功能):
注意:在完成了引入AOP依赖包后,一般来说并不需要去做其他配置。使用过Spring注解配置方式的人会问是否需要在程序主类中增加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy来启用,实际并不需要。
因为在AOP的默认配置属性中,spring.aop.auto属性默认是开启的,也就是说只要引入了AOP依赖后,默认已经增加了@EnableAspectJAutoProxy。
3、定义切面类,实现web层的日志切面
要想把一个类变成切面类,需要两步,
① 在类上使用 @Component 注解 把切面类加入到IOC容器中
② 在类上使用 @Aspect 注解 使之成为切面类
package com.example.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by lmb on 2018/9/5.
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class WebLogAcpect {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WebLogAcpect.class);
/**
* 定义切入点,切入点为com.example.aop下的所有函数
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.aop..*.*(..))")
public void webLog(){}
/**
* 前置通知:在连接点之前执行的通知
* @param joinPoint
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Before("webLog()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 接收到请求,记录请求内容
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
// 记录下请求内容
logger.info("URL : " + request.getRequestURL().toString());
logger.info("HTTP_METHOD : " + request.getMethod());
logger.info("IP : " + request.getRemoteAddr());
logger.info("CLASS_METHOD : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
logger.info("ARGS : " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
@AfterReturning(returning = "ret",pointcut = "webLog()")
public void doAfterReturning(Object ret) throws Throwable {
// 处理完请求,返回内容
logger.info("RESPONSE : " + ret);
}
}以上的切面类通过 @Pointcut定义的切入点为com.example.aop包下的所有函数做切人,通过 @Before实现切入点的前置通知,通过 @AfterReturning记录请求返回的对象。
访问http://localhost:8004/hello?name=lmb得到控制台输出如下:
详细代码参见本人的Github:SpringBoot整合AOP
二、AOP支持的通知
1、前置通知@Before:在某连接点之前执行的通知,除非抛出一个异常,否则这个通知不能阻止连接点之前的执行流程。
/**
* 前置通知,方法调用前被调用
* @param joinPoint/null
*/
@Before(value = POINT_CUT)
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
logger.info("前置通知");
//获取目标方法的参数信息
Object[] obj = joinPoint.getArgs();
//AOP代理类的信息
joinPoint.getThis();
//代理的目标对象
joinPoint.getTarget();
//用的最多 通知的签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
//代理的是哪一个方法
logger.info("代理的是哪一个方法"+signature.getName());
//AOP代理类的名字
logger.info("AOP代理类的名字"+signature.getDeclaringTypeName());
//AOP代理类的类(class)信息
signature.getDeclaringType();
//获取RequestAttributes
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
//从获取RequestAttributes中获取HttpServletRequest的信息
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestAttributes.resolveReference(RequestAttributes.REFERENCE_REQUEST);
//如果要获取Session信息的话,可以这样写:
//HttpSession session = (HttpSession) requestAttributes.resolveReference(RequestAttributes.REFERENCE_SESSION);
//获取请求参数
Enumeration<String> enumeration = request.getParameterNames();
Map<String,String> parameterMap = Maps.newHashMap();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()){
String parameter = enumeration.nextElement();
parameterMap.put(parameter,request.getParameter(parameter));
}
String str = JSON.toJSONString(parameterMap);
if(obj.length > 0) {
logger.info("请求的参数信息为:"+str);
}
}注意:这里用到了JoinPoint和RequestContextHolder。
1)、通过JoinPoint可以获得通知的签名信息,如目标方法名、目标方法参数信息等;
2)、通过RequestContextHolder来获取请求信息,Session信息;
2、后置通知@AfterReturning:在某连接点之后执行的通知,通常在一个匹配的方法返回的时候执行(可以在后置通知中绑定返回值)。
/**
* 后置返回通知
* 这里需要注意的是:
* 如果参数中的第一个参数为JoinPoint,则第二个参数为返回值的信息
* 如果参数中的第一个参数不为JoinPoint,则第一个参数为returning中对应的参数
* returning:限定了只有目标方法返回值与通知方法相应参数类型时才能执行后置返回通知,否则不执行,
* 对于returning对应的通知方法参数为Object类型将匹配任何目标返回值
* @param joinPoint
* @param keys
*/
@AfterReturning(value = POINT_CUT,returning = "keys")
public void doAfterReturningAdvice1(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object keys){
logger.info("第一个后置返回通知的返回值:"+keys);
}
@AfterReturning(value = POINT_CUT,returning = "keys",argNames = "keys")
public void doAfterReturningAdvice2(String keys){
logger.info("第二个后置返回通知的返回值:"+keys);
}3、后置异常通知@AfterThrowing:在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。
/**
* 后置异常通知
* 定义一个名字,该名字用于匹配通知实现方法的一个参数名,当目标方法抛出异常返回后,将把目标方法抛出的异常传给通知方法;
* throwing:限定了只有目标方法抛出的异常与通知方法相应参数异常类型时才能执行后置异常通知,否则不执行,
* 对于throwing对应的通知方法参数为Throwable类型将匹配任何异常。
* @param joinPoint
* @param exception
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = POINT_CUT,throwing = "exception")
public void doAfterThrowingAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable exception){
//目标方法名:
logger.info(joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
if(exception instanceof NullPointerException){
logger.info("发生了空指针异常!!!!!");
}
} 4、后置最终通知@After:当某连接点退出时执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
/**
* 后置最终通知(目标方法只要执行完了就会执行后置通知方法)
* @param joinPoint
*/
@After(value = POINT_CUT)
public void doAfterAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint){
logger.info("后置最终通知执行了!!!!");
} 5、环绕通知@Around:包围一个连接点的通知,如方法调用等。这是最强大的一种通知类型。环绕通知可以在方法调用前后完成自定义的行为,它也会选择是否继续执行连接点或者直接返回它自己的返回值或抛出异常来结束执行。
环绕通知最强大,也最麻烦,是一个对方法的环绕,具体方法会通过代理传递到切面中去,切面中可选择执行方法与否,执行几次方法等。环绕通知使用一个代理ProceedingJoinPoint类型的对象来管理目标对象,所以此通知的第一个参数必须是ProceedingJoinPoint类型。在通知体内调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法会导致后台的连接点方法执行。proceed()方法也可能会被调用并且传入一个Object[]对象,该数组中的值将被作为方法执行时的入参。
/**
* 环绕通知:
* 环绕通知非常强大,可以决定目标方法是否执行,什么时候执行,执行时是否需要替换方法参数,执行完毕是否需要替换返回值。
* 环绕通知第一个参数必须是org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint类型
*/
@Around(value = POINT_CUT)
public Object doAroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
logger.info("环绕通知的目标方法名:"+proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName());
try {
Object obj = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
return obj;
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
} 6、有时候我们定义切面的时候,切面中需要使用到目标对象的某个参数,如何使切面能得到目标对象的参数呢?可以使用args来绑定。如果在一个args表达式中应该使用类型名字的地方使用一个参数名字,那么当通知执行的时候对象的参数值将会被传递进来。
@Before("execution(* findById*(..)) &&" + "args(id,..)")
public void twiceAsOld1(Long id){
System.err.println ("切面before执行了。。。。id==" + id);
}注意:任何通知方法都可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型(环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型,它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。JoinPoint接口提供了一系列有用的方法,比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、getThis()(返回代理对象)、getTarget()(返回目标)、getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)和 toString()(打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
三、切入点表达式
定义切入点的时候需要一个包含名字和任意参数的签名,还有一个切入点表达式,如execution(public * com.example.aop...(..))
切入点表达式的格式:execution([可见性]返回类型[声明类型].方法名(参数)[异常])
其中[]内的是可选的,其它的还支持通配符的使用:
1) *:匹配所有字符
2) ..:一般用于匹配多个包,多个参数
3) +:表示类及其子类
4)运算符有:&&,||,!
切入点表达式关键词用例:
1)execution:用于匹配子表达式。
//匹配com.cjm.model包及其子包中所有类中的所有方法,返回类型任意,方法参数任意
@Pointcut(“execution(* com.cjm.model...(..))”)
public void before(){}
2)within:用于匹配连接点所在的Java类或者包。
//匹配Person类中的所有方法
@Pointcut(“within(com.cjm.model.Person)”)
public void before(){}
//匹配com.cjm包及其子包中所有类中的所有方法
@Pointcut(“within(com.cjm..*)”)
public void before(){}
3) this:用于向通知方法中传入代理对象的引用。
@Before(“before() && this(proxy)”)
public void beforeAdvide(JoinPoint point, Object proxy){
//处理逻辑
}
4)target:用于向通知方法中传入目标对象的引用。
@Before(“before() && target(target)
public void beforeAdvide(JoinPoint point, Object proxy){
//处理逻辑
}
5)args:用于将参数传入到通知方法中。
@Before(“before() && args(age,username)”)
public void beforeAdvide(JoinPoint point, int age, String username){
//处理逻辑
}
6)@within :用于匹配在类一级使用了参数确定的注解的类,其所有方法都将被匹配。
@Pointcut(“@within(com.cjm.annotation.AdviceAnnotation)”)
- 所有被@AdviceAnnotation标注的类都将匹配
public void before(){}
7)@target :和@within的功能类似,但必须要指定注解接口的保留策略为RUNTIME。
@Pointcut(“@target(com.cjm.annotation.AdviceAnnotation)”)
public void before(){}
8)@args :传入连接点的对象对应的Java类必须被@args指定的Annotation注解标注。
@Before(“@args(com.cjm.annotation.AdviceAnnotation)”)
public void beforeAdvide(JoinPoint point){
//处理逻辑
}
9)@annotation :匹配连接点被它参数指定的Annotation注解的方法。也就是说,所有被指定注解标注的方法都将匹配。
@Pointcut(“@annotation(com.cjm.annotation.AdviceAnnotation)”)
public void before(){}
10)bean:通过受管Bean的名字来限定连接点所在的Bean。该关键词是Spring2.5新增的。
@Pointcut(“bean(person)”)
public void before(){}