写在前面
继续开始刷题了,加油哦~
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
解题方法
顺序访问+反转
递归遍历链表,把结果放在list里,然后反转该链表
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
list.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 反转list
Collections.reverse(list);
// 使用stream语法转为int数组
return list.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
}
}
辅助栈
先入后出的顺序适合使用栈数据结构,遍历链表,把值放到栈中,依次出栈放到数组中即可。
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = head;
// 顺序放在栈中
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
int size = stack.size();
int[] arr = new int[size];
// 遍历栈
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = stack.pop();
}
return arr;
}
}
递归
利用递归: 先走至链表末端,回溯时依次将节点值加入列表 ,这样就可以实现链表值的倒序输出。
递推阶段,走到尾部的空指针
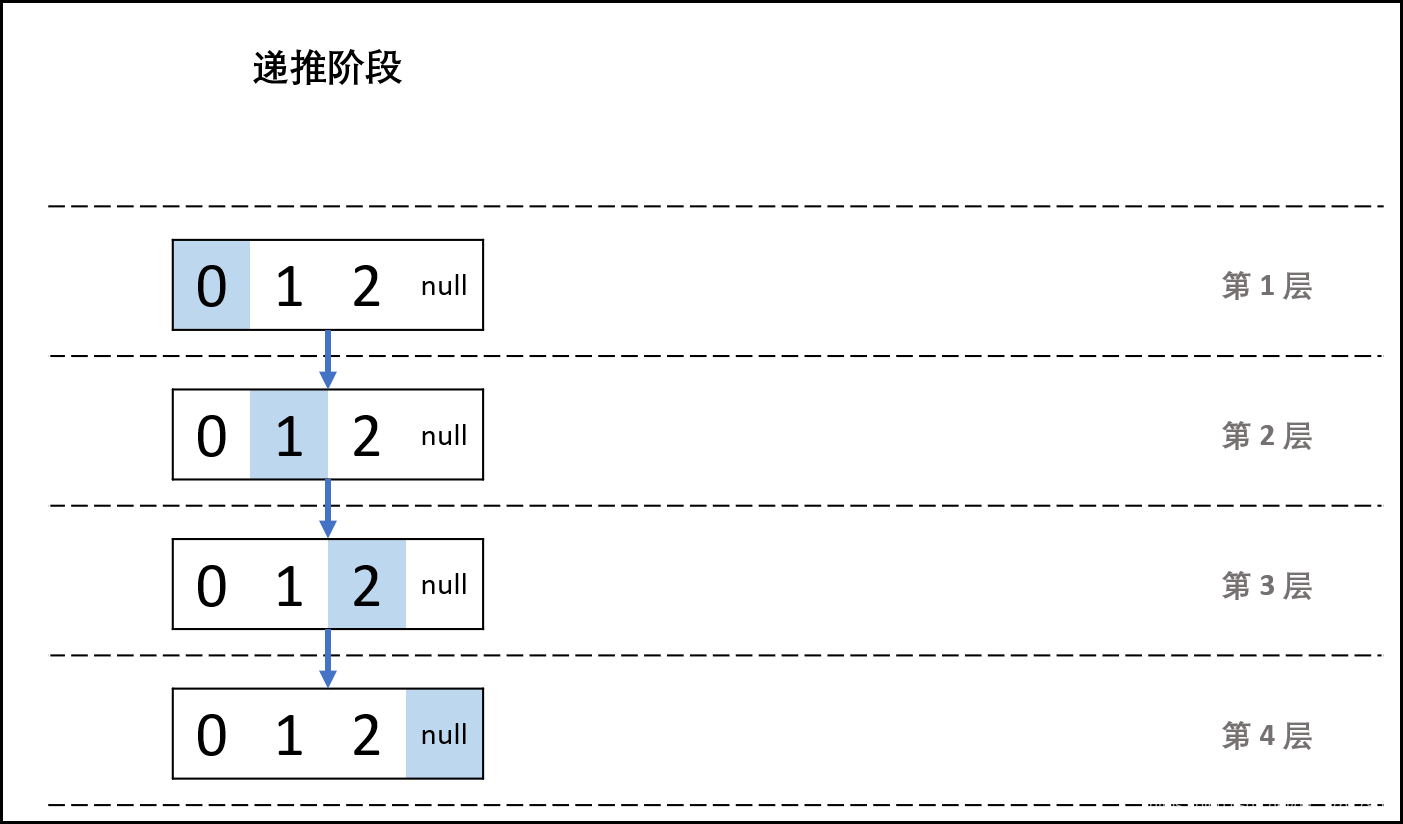
回溯阶段,回溯的过程中添加元素

递推阶段: 每次传入 head.next ,以 head == null(即走过链表尾部节点)为递归终止条件,此时直接返回。
回溯阶段: 层层回溯时,将当前节点值加入列表,即tmp.add(head.val)。
最终,将列表 tmp 转化为数组 res ,并返回即可。
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
recur(head);
return list.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
}
public void recur(ListNode head) {
// 递归退出条件
if (head == null) {
return;
}
// 递归下一个节点
recur(head.next);
// 回退函数将元素加到list中
list.add(head.val);
}
}
反转链表
先反转链表,再遍历链表
关于链表的反转其实解法也比较多,这里先列出简单的两种,一个是递归的,一个是非递归的。
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ListNode reversed = reverseList(head);
// ListNode reversed = reverseListRecur(head);
ListNode cur = reversed;
int count = 0;
// 获取链表节点个数
while (cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
// 遍历链表
cur = reversed;
int[] arr = new int[count];
int i = 0;
while (cur != null) {
arr[i++] = cur.val;
cur = cur.next;
}
return arr;
}
// 非递归反转链表
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
// 三个指针 pre head next不断移动 最后head为空 pre为真正的头指针 return pre
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next; // 记录next节点
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 递归反转链表
public ListNode reverseListRecur(ListNode head) {
// 如果链表为空或者为尾节点 返回节点
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// tempList为反转后的头指针 需要返回
ListNode tempList = reverseListRecur(head.next);
// 调转最后的head指针 并置尾指针为空
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return tempList;
}
}
反转链表 II
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
解题方法
头插法
思路:1、我们定义两个指针,分别称之为g(guard 守卫)和p(point)。
我们首先根据方法的参数m确定g和p的位置。将g移动到第一个要反转的节点的前面,将p移动到第一个要反转的节点的位置上。我们以m=2,n=4为例。

2、将p后面的元素删除,然后添加到g的后面。也即头插法。

3、根据m和n重复步骤(2)
4、返回dummyHead.next
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode guard = dummyHead;
ListNode pointer = dummyHead.next;
// 前进m-1步
int tempM = m;
while ((--tempM) != 0) {
guard = guard.next;
pointer = pointer.next;
}
// 头插法将后面的节点插到对头 不断的把pointer后面的节点插到guard后面
for (int i = 0; i < n - m; i++) {
// 记住要插到前面去的节点
ListNode removed = pointer.next;
// 删掉该节点
pointer.next = pointer.next.next;
// 插到前头去
removed.next = guard.next;
guard.next = removed;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
递归
public class Solution {
boolean stop;
ListNode left;
public void recurseAndReverse(ListNode right, int m, int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return;
}
right = right.next;
if (m > 1) {
left = left.next;
}
recurseAndReverse(right, m - 1, n - 1);
if (left == right || right.next == left) {
stop = true;
}
if (!stop) {
int t = left.val;
left.val = right.val;
right.val = t;
left = left.next;
}
}
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
left = head;
stop = false;
recurseAndReverse(head, m, n);
return head;
}
}