目录
1、检查相同字母间的距离

#时间复杂度O(n^2)
class Solution:
def checkDistances(self, s: str, distance: List[int]) -> bool:
n = len(s) #获取字符串长度,为了遍历
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n): #从i的后一个开始
if s[i] == s[j] and distance[ord(s[i]) - ord('a')] != j - i - 1: #关键判断
return False
return True
#时间复杂度O(n)
class Solution:
def checkDistances(self, s: str, distance: List[int]) -> bool:
n = len(s)
firstIndex = [0] * 26; #构造一个26个0的列表
for i in range(n):
idx = ord(s[i]) - ord('a'); #算这个字母在字母表中第几个
if firstIndex[idx] and i - firstIndex[idx] != distance[idx]:
return False #当这个字母已经存在过一次,这个时候去计算间距
firstIndex[idx] = i + 1 #不然则记录下这个字母在字符串s中第几个位置
return True
2、链表中的下一个更大节点

class Solution:
def nextLargerNodes(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> List[int]:
nums = []
while head: #将链表中的值存入数组nums中
nums.append(head.val)
head = head.next
stack = [] #定义一个空的堆栈
n = len(nums)
ans = [0]*n #答案数组
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1): #从右往左遍历整个nums数组,这样方便,因为靠右边的元素它的右边的元素少
while stack and stack[-1] <= nums[i]:
stack.pop()
if stack: #只要栈中的元素没有被清光,就说明有比它大的
ans[i] = stack[-1]
stack.append(nums[i]) #这一步是保证单调栈的
return ans #返回答案3、困于环中的机器人

class Solution:
def isRobotBounded(self,instructions:str) -> bool:
si, dis = 0, 0 #si的0,1,2,3分别代表北,东,南,西;北和东方向dis+=1,南和西方向dis-=1
for i in instructions:
if i == 'G':
if si % 4 < 2: #朝北朝东,两两配对即可,因为我们只要判断它是不是在原点,即看最终的dis是不是0即可
dis += 1
else: #朝南朝西,与朝北朝东相反即可
dis += -1
else:
if i == 'R': #方向向右转了一个
si += 1
else: #方向向左转了一个
si += -1
if dis != 0 and si % 4 == 0: #如果不要陷入循环,则机器人在指令结束以后方向任然朝东,但位置不在原来的地方
return False
else:
return True4、段式回文

class Solution:
def longestDecomposition(self, s: str) -> int:
ans = 0
while s:
i = 1
while i <= len(s)//2 and s[:i] != s[-i:]: #从前往后,从后往前.前面一个判断是为了看是否超过了一半
i += 1
if i > len(s)//2: #超过一半了,不能继续往右走了
ans += 1 #答案加1
break
ans += 2 #还没走到右边,这个时候能分割出s[:i]和s[-i:]
s = s[i:-i] #继续搞剩下来的
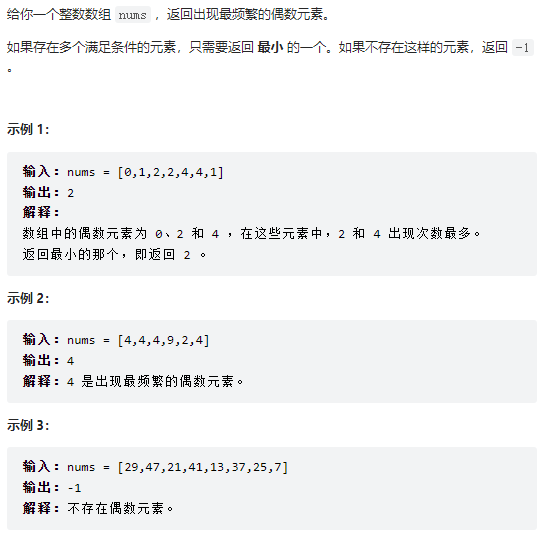
return ans5、出现最频繁的偶数元素
class Solution:
def mostFrequentEven(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
count = {} #定义一个字典记录数组中偶数元素和出现的次数
#统计偶数元素出现的次数
for num in nums:
if num % 2 == 0: #是偶数
count[num] = count.get(num,0) + 1 #个数加一
res = -1 #记录出现最频繁的偶数
max_freq = 0 #最频繁的次数
for num, freq in count.items(): #遍历这个字典
#当前偶数的出现次数大于记录的最频繁次数
#或者等于记录的最频繁次数但当前偶数的值更小
if freq > max_freq or (freq == max_freq and num < res):
res = num
max_freq = freq
return res #返回得到的值6、驼峰式匹配

class Solution:
def camelMatch(self, queries:List[str], pattern:str):
def check(s, t):
m, n = len(s), len(t) #计算两个字符串的长度
i = j = 0 #双指针遍历字符串
while j < n: #j还没有遍历完一整个t字符串
while i < m and s[i] != t[j] and s[i].islower(): #i还没有遍历完整个m字符串,当前两个指针指的不相同,i指针指的是小写字母
i += 1 #满足上面的条件,指针i可以直接向后一步
if i == m or s[i] != t[j]: #t字符串还没有遍历完,s字符串已经遍历完了或者遇到两个不相等
return False
i, j = i + 1, j + 1 #上面条件都不满足,两个指针都向后移动一个
while i < m and s[i].islower(): #s字符串还没有遍历完,如果是小写,则直接看向后一位
i += 1
return i == m #所有事都干完了,如果这个时候刚好遍历完s字符串,就是正确的
return [check(q, pattern) for q in queries] #遍历每一个,返回True或者False