一、二叉树的定义
1. 树的基本概念
树是二叉树是由n(n≥0)个结点所构成的有限集合。当n=0时,称为空树;当n>0时,n个结点满足以下条件:
1)有且仅有一个称为根的结点;
2)其余结点可分为m(m≥0)个互不相交的有限集合,且每一个集合又构成一棵树,这棵树称为根结点的子树。
2. 二叉树的基本概念
二叉树是一种特殊的树,它的每个结点最多只有两棵子树,并且这两棵子树也是二叉树。
二、二叉树的性质
1. 二叉树中第i(i≥0)层上的结点数最多为2^i。
2. 深度为h(h≥1)的二叉树中最多有2^h-1个结点。
3. 对于任何一棵二叉树,若其叶结点的个数为n0,度为2的结点个数为n2,则有n2=n0+1。
4. 具有n个结点的完全二叉树,其深度为或者
。
5. 对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,若从根结点开始自上到下并且按照层次由左向右对结点从0开始进行编号,则对于任意一个编号为i(0≤i≤n)的结点有:
1)若i=0,则编号为i的结点是二叉树的根结点,它没有双亲;若i>1,则编号为i的结点其双亲的编号为(i-1)/2。
2)若2i+1≥n,则编号为i的结点无左孩子,否则编号为2i+1的结点就是其左孩子。
3)若2i+2≥n,则编号为i的结点无右孩子,否则编号2i+2的结点就是其右孩子。
三、二叉树的遍历
//使用泛型构造二叉树结点类
public class BitTreeNode<E> {
public E data; //存放数据值
public BitTreeNode<E> lchild,rchild; //左、右孩子域
//构造一个空节点
public BitTreeNode() {
this(null);
}
//构造一棵左右孩子域为空的二叉树
public BitTreeNode(E data) {
this(data,null,null);
}
//构造医科数据域和左右孩子域都不为空的二叉树
public BitTreeNode(E data,BitTreeNode<E> lchild,BitTreeNode<E> rchild) {
this.data = data;
this.lchild = lchild;
this.rchild = rchild;
}
}//二叉树
public class BinaryTree<E> {
public BitTreeNode<E> root;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//测试
BitTreeNode<String> d = new BitTreeNode<String>("D");
BitTreeNode<String> g = new BitTreeNode<String>("G");
BitTreeNode<String> h = new BitTreeNode<String>("H");
BitTreeNode<String> e = new BitTreeNode<String>("E",g,null);
BitTreeNode<String> b = new BitTreeNode<String>("B",d,e);
BitTreeNode<String> f = new BitTreeNode<String>("F",null,h);
BitTreeNode<String> c = new BitTreeNode<String>("C",f,null);
BitTreeNode<String> a = new BitTreeNode<String>("A",b,c); //根结点
BinaryTree<String> bitTree = new BinaryTree<String>();
System.out.print("递归-先根遍历:");
bitTree.preRootTraverse(a);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("非递归-先根遍历:");
bitTree.preRootTraverse1(a);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("递归-中根遍历:");
bitTree.inRootTraverse(a);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("非递归-中根遍历:");
bitTree.inRootTraverse1(a);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("递归-后根遍历:");
bitTree.postRootTraverse(a);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("非递归-后根遍历:");
bitTree.postRootTraverse1(a);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("层次遍历:");
bitTree.levelTraverse(a);
}
}1. 先根遍历
//递归-先根遍历
public void preRootTraverse(BitTreeNode<E> T) {
if(T != null) {
System.out.print(T.data); //访问根结点
preRootTraverse(T.lchild); //递归遍历左子树
preRootTraverse(T.rchild); //递归遍历右子树
}
}//非递归-先根遍历
public void preRootTraverse1(BitTreeNode<E> T) throws Exception {
if(T != null) {
LinkStack<BitTreeNode<E>> S = new LinkStack<BitTreeNode<E>>(); //构造栈
S.push(T); //根结点入栈
while(!S.isEmpty()) {
T = (BitTreeNode<E>) (S.pop()); //移除栈顶结点,并返回其值
System.out.print(T.data); //访问结点
while(T != null) {
if(T.lchild != null) //访问左孩子
System.out.print(T.lchild.data);
if(T.rchild != null) //右孩子非空入栈
S.push(T.rchild);
T = T.lchild;
}
}
}2. 中根遍历
//递归-中根遍历
public void inRootTraverse(BitTreeNode<E> T) {
if(T != null) {
inRootTraverse(T.lchild); //递归遍历左子树
System.out.print(T.data); //访问根结点
inRootTraverse(T.rchild); //递归遍历右子树
}
}//非递归-中根遍历
public void inRootTraverse1(BitTreeNode<E> T) throws Exception{
if(T != null) {
LinkStack<BitTreeNode<E>> S = new LinkStack<BitTreeNode<E>>(); //构造栈
S.push(T); //根结点入栈
while(!S.isEmpty()) {
while(S.peek() != null) //将栈顶结点的左孩子结点相继入栈
S.push((BitTreeNode<E>)(S.peek()).lchild);
S.pop(); //空结点退栈
if(!S.isEmpty()) {
T = (BitTreeNode<E>) S.pop(); //移除栈顶结点,并返回其值
System.out.print(T.data); //访问结点
S.push(T.rchild); //结点的右孩子入栈
}
}
}
}3. 后根遍历
//递归-后根遍历
public void postRootTraverse(BitTreeNode<E> T) {
if(T != null) {
postRootTraverse(T.lchild); //递归遍历左子树
postRootTraverse(T.rchild); //递归遍历右子树
System.out.print(T.data); //访问根结点
}
}//递归-后根遍历
public void postRootTraverse1 (BitTreeNode<E> T) throws Exception{
Boolean flag; //访问标记
BitTreeNode<E> p = null; //p指向刚被访问的结点
if(T != null) {
LinkStack<BitTreeNode<E>> S = new LinkStack<BitTreeNode<E>>(); //构造栈
S.push(T); //根结点入栈
while(!S.isEmpty()) {
while(S.peek() != null)
S.push((BitTreeNode<E>)(S.peek()).lchild); //将栈顶结点的左孩子相继入栈
S.pop(); //空结点退栈
while(!S.isEmpty()) {
T = (BitTreeNode<E>)S.peek(); //查看栈顶元素
if(T.rchild == null || T.rchild == p) {
System.out.print(T.data); //访问结点
S.pop(); //移除栈顶元素
p = T; //p指向刚被访问的结点
flag = true; //设置访问标记
}else {
S.push(T.rchild); //右孩子结点入栈
flag = false; //设置未被访问标记
}
if(!flag)
break;
}
}
}
}4. 层次遍历
//层次遍历
public void levelTraverse(BitTreeNode<E> T) throws Exception {
if(T != null) {
LinkQueue<BitTreeNode<E>> L = new LinkQueue<BitTreeNode<E>>(); //构造队列
L.offer(T); //根结点图队列
while(!L.isEmpty()) {
T = (BitTreeNode<E>)L.poll();
System.out.print(T.data); //访问结点
if(T.lchild != null) //左孩子非空,入队列
L.offer(T.lchild);
if(T.rchild != null) //右孩子非空,入队列
L.offer(T.rchild);
}
}
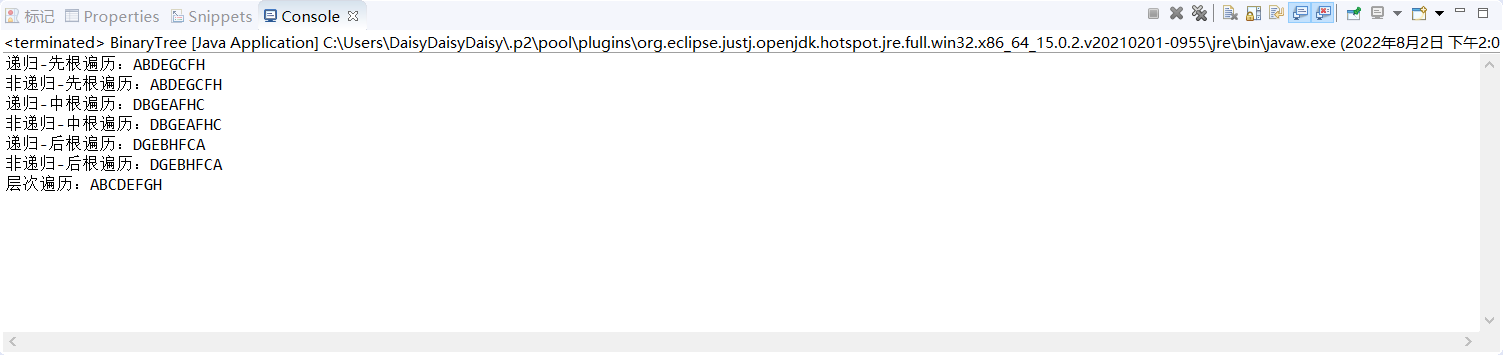
}5. 测试结果
四、二叉树的构建
//二叉树的结点类
public class TreeNode {
int val; //数据值
TreeNode left; //左孩子
TreeNode right; //右孩子
//无参构造方法
TreeNode() {}
//左右孩子为空的构造方法
TreeNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
//左右孩子不为空的构造方法
TreeNode(int val,TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}1. 由先根和中根遍历序列建立一棵二叉树
public class buildTree01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] preorder = {3,9,20,15,7}; //前序遍历序列
int[] inorder = {9,3,15,20,7}; //中序遍历序列
System.out.println(buildTree(preorder,inorder).val);
}
static HashMap<Integer,Integer> map;
//将中序遍历的结点按下标顺序暂存在哈希表中,方便后续取用
public static TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++) map.put(inorder[i],i);
return dfs(preorder,inorder,0,preorder.length-1,0,inorder.length-1);
}
//由前序与中序遍历构造二叉树 == 对中序遍历由根节点结点开始进行深度遍历
public static TreeNode dfs(int[] pre,int[] in,int pf,int pr,int nf,int nr) {
if(pf > pr) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[pf]); //前序遍历的第一位数即为根结点
int pos = map.get(root.val); //中序遍历中根结点的下标(比如:前序遍历中的3,位于后序遍历中下标为1的位置所以第一轮递归pos = 1)
int cnt = pos - nf; //中序遍历中由根节点向左递归结点数
//递归
root.left = dfs(pre,in,pf+1,pf+cnt,nf,pos-1); //左递归
root.right = dfs(pre,in,pf+cnt+1,pr,pos+1,nr); //右递归
return root;
}
}2. 由中根和后根遍历序列建立一棵二叉树
public class buildTree02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] inorder = {9,3,15,20,7};
int[] postorder = {9,15,7,20,3};
System.out.println(buildTree(inorder,postorder).val);
}
static HashMap<Integer,Integer> map;
public static TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder,int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++) map.put(inorder[i],i);
return dfs(inorder,postorder,0,inorder.length-1,0,postorder.length-1);
}
public static TreeNode dfs(int[] in,int[] post,int nf,int nr,int pf,int pr) {
if(pf > pr) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(post[pr]);
int pos = map.get(root.val);
int cnt = pos - nf;
root.left = dfs(in,post,nf,pos-1,pf,pf+cnt-1);
root.right = dfs(in,post,pos+1,nr,pf+cnt,pr-1);
return root;
}
}3. 由先根和后根遍历序列建立一棵二叉树
public class buildTree03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] preorder = {1,2,4,5,3,6,7};
int[] postorder = {4,5,2,6,7,3,1};
System.out.println(constructFromPrePost(preorder,postorder).val);
}
public static TreeNode constructFromPrePost(int[] pre,int[] post) {
int N = pre.length;
//长度为0,返回空
if(N == 0) return null;
//长度为1,返回根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
if(N == 1) return root;
//使用L来区分左右子树
int L = 0;
for(int i=1;i<N-1;i++) {
if(post[i] == pre[1]) {
L = i+1;
}
}
root.left = constructFromPrePost(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, L+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(post,0,L)); //向左递归
root.right = constructFromPrePost(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, L+1, N),Arrays.copyOfRange(post,L,N-1)); //向右递归
return root;
}
}五、二叉树的应用
/* 二叉树的应用 */
//1. 二叉树上的查找算法
public BitTreeNode<E> searchNode(BitTreeNode<E> T,E x) {
if(T != null) {
if(T.data.equals(x)) //对根结点进行判断
return T;
else {
BitTreeNode<E> lresult = searchNode(T.lchild,x); //查找左子树
return lresult != null ? lresult : searchNode(T.rchild,x); //左子树若为空,则查找右子树
}
}
return null; //未找到,返回空值
}
//2. 统计二叉树中结点个数的算法-先根遍历
public int countNode(BitTreeNode<E> T) {
int count = 0; //计数器
if(T != null) {
++count; //根结点加1
count += countNode(T.lchild); //加上左子树上的结点数
count += countNode(T.rchild); //加上右子树上的结点数
}
return count;
}
//3. 统计二叉树中结点个数的算法-层次遍历
public int countNode1(BitTreeNode<E> T) throws Exception{
int count = 0; //计数器
if(T != null) {
LinkQueue<BitTreeNode<E>> L = new LinkQueue<BitTreeNode<E>>(); //构造队列
L.offer(T); //根结点入队
while(!L.isEmpty()) {
T = (BitTreeNode<E>)L.poll();
++count; //结点数目加1
if(T.lchild != null) //左孩子非空入队
L.offer(T.lchild);
if(T.rchild != null) //右孩子非空入队
L.offer(T.rchild);
}
}
return count;
}
//4. 统计二叉树中结点个数的算法-递归模型
public int countNode2(BitTreeNode<E> T) {
if(T == null)
return 0;
else
return countNode2(T.lchild) + countNode2(T.rchild) + 1;
}
//5. 求二叉树深度的算法
public int getDepth(BitTreeNode<E> T) {
if(T != null) {
int lDepth = getDepth(T.lchild);
int rDepth = getDepth(T.rchild);
return 1 + (lDepth > rDepth ? lDepth : rDepth);
}
return 0;
}
//6. 求二叉树深度的算法-递归模型
public int getDepth1(BitTreeNode<E> T) {
if(T == null)
return 0;
else if(T.lchild==null && T.rchild==null)
return 1;
else
return 1 + (getDepth1(T.lchild) > getDepth1(T.rchild) ? getDepth1(T.lchild) : getDepth1(T.rchild));
}
//7. 判断两棵二叉树是否相等的算法
public boolean isEqual(BitTreeNode<E> T1,BitTreeNode<E> T2) {
if(T1==null && T2==null) //同时为空
return true;
if(T1!=null && T2!=null) //同时非空,则进行比较
if(T1.data.equals(T2.data)) //根结点的值是否相等
if(isEqual(T1.lchild,T2.lchild)) //左子树是否相等
if(isEqual(T1.rchild,T2.rchild)) //右子树是否相等
return true;
return false;
}
//8. 判断两棵二叉树是否相等的算法-递归模型
public boolean isEqual1(BitTreeNode<E> T1,BitTreeNode<E> T2) {
if(T1==null && T2==null) //同时为空
return true;
else if(T1!=null && T2!=null) //同时非空,则进行比较
return (T1.data.equals(T2.data)) && (isEqual(T1.lchild,T2.lchild)) && (isEqual(T1.rchild,T2.rchild)); //递归判断
else
return false;
}