文章目录
一、实验介绍
在深度学习任务中,数据增强是提高模型泛化能力的关键步骤之一。通过对训练集进行变换和扩充,可以有效地增加数据量,引入样本之间的差异,使模型更好地适应不同的输入。
本实验将实现自定义图像数据增强操作,具体包括 Cutout(遮挡)、Random Erasing(随机擦除)和 Mixup(混合)。
二、实验环境
1. 配置虚拟环境
conda create -n Image python=3.9
conda activate Image
conda install pillow numpy
2. 库版本介绍
| 软件包 | 本实验版本 |
|---|---|
| numpy | 1.21.5 |
| python | 3.9.13 |
| pillow | 9.2.0 |
三、实验内容
0. 导入必要的库
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import random
1. PIL基础操作
【深度学习实验】图像处理(一):Python Imaging Library(PIL)库:图像读取、写入、复制、粘贴、几何变换、图像增强、图像滤波
【深度学习实验】图像处理(二):PIL 和 PyTorch(transforms)中的图像处理与随机图片增强
2. Cutout(遮挡)
2.1 原理
Cutout 操作是在图像上随机选择一个或多个方形区域,并将这些区域的像素值设置为零,达到遮挡的效果。该操作有助于模型对于部分区域的缺失具有鲁棒性,使得模型更加关注图像的其他部分。
2.2 实现
class Cutout(object):
def __init__(self, n_holes, length):
self.n_holes = n_holes
self.length = length
def __call__(self, img):
h, w, c = img.shape
mask = np.ones((h, w), np.float32)
for _ in range(self.n_holes):
y = np.random.randint(h)
x = np.random.randint(w)
y1 = np.clip(y - self.length // 2, 0, h)
y2 = np.clip(y + self.length // 2, 0, h)
x1 = np.clip(x - self.length // 2, 0, w)
x2 = np.clip(x + self.length // 2, 0, w)
mask[y1: y2, x1: x2] = 0.
mask = np.expand_dims(mask, axis=2)
mask = np.repeat(mask, c, axis=2)
img = img * mask
return img
- 初始化参数:
- n_holes (int): 每个图像要遮挡的区域数量。
- length (int): 每个正方形区域的边长(以像素为单位)。
- call
- 参数:
- img: 大小为 (h, w, c) 的图像数组。
- 返回
- 从图像中剪切出 n_holes 个边长为 length 的正方形区域后的图像。
- 参数:
2.3 效果展示
img = Image.open('example.jpg').convert('RGB')
# 转换为 NumPy 数组
img = np.array(img)
# 创建 Cutout 实例
cutout = Cutout(3, 64)
# 应用 Cutout 操作
img_cut = cutout(img)
# 将 NumPy 数组转换回 PIL 图像
img_result = Image.fromarray(img_cutout.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
# 保存图像
img_result.save('./cutout_image.jpg')

3. Random Erasing(随机擦除)
3.1 原理
Random Erasing 操作随机选择图像中的一个矩形区域,并将该区域的像素值擦除,用随机值替代。该操作模拟了在现实场景中图像可能被部分遮挡或损坏的情况,从而提高了模型对于不完整图像的适应能力。
3.2 实现
class RandomErasing(object):
def __init__(self, region_w, region_h):
self.region_w = region_w
self.region_h = region_h
def __call__(self, img):
if self.region_w < img.shape[1] and self.region_h < img.shape[0]:
x1 = random.randint(0, img.shape[1] - self.region_w)
y1 = random.randint(0, img.shape[0] - self.region_h)
img[y1:y1+self.region_h, x1:x1+self.region_w, 0] = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(self.region_h, self.region_w))
img[y1:y1+self.region_h, x1:x1+self.region_w, 1] = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(self.region_h, self.region_w))
img[y1:y1+self.region_h, x1:x1+self.region_w, 2] = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(self.region_h, self.region_w))
return img
- 初始化:
- region_w: 擦除区域的宽度
- region_h: 擦除区域的高度
- call
- 参数:
- img: 大小为 (h, w, c) 的图像数组
- 检查擦除区域的宽度和高度是否小于图像的宽度和高度
- 随机选择擦除区域的左上角坐标 ( x 1 , y 1 ) (x_1, y_1) (x1,y1)
- 生成随机像素值并将其应用于图像的擦除区域
- 返回
- 随机擦除后的图像
- 参数:
3.3 效果展示
img = Image.open('example.jpg').convert('RGB')
img = np.array(img)
# 创建 Random Erasing 实例
random_erasing = RandomErasing(region_w=150, region_h=200)
# 应用 Random Erasing 操作
img_erasing = random_erasing(img)
img_result = Image.fromarray(img_erasing.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
img_result.save('./erasing_image.jpg')

4. Mixup(混合)
4.1 原理
Mixup选择两张图像,按照一定的比例进行线性混合,得到一张新的图像。通过引入样本之间的混合,增加了训练集的多样性,有助于模型更好地适应不同的输入。
4.2 实现
class Mixup(object):
def __init__(self, alpha):
self.alpha = alpha
self.lam = np.random.beta(self.alpha, self.alpha)
def __call__(self, img1, img2):
img = self.lam * img1 + (1 - self.lam) * img2
return img
- 初始化参数:
- alpha: 混合参数
- lam: 使用 Beta 分布生成一个随机值
- call
- 参数:
- img1、img2: 大小为 (h, w, c) 的图像数组。
- 使用混合比例将两个图像进行线性混合
- 参数:
4.3 效果展示
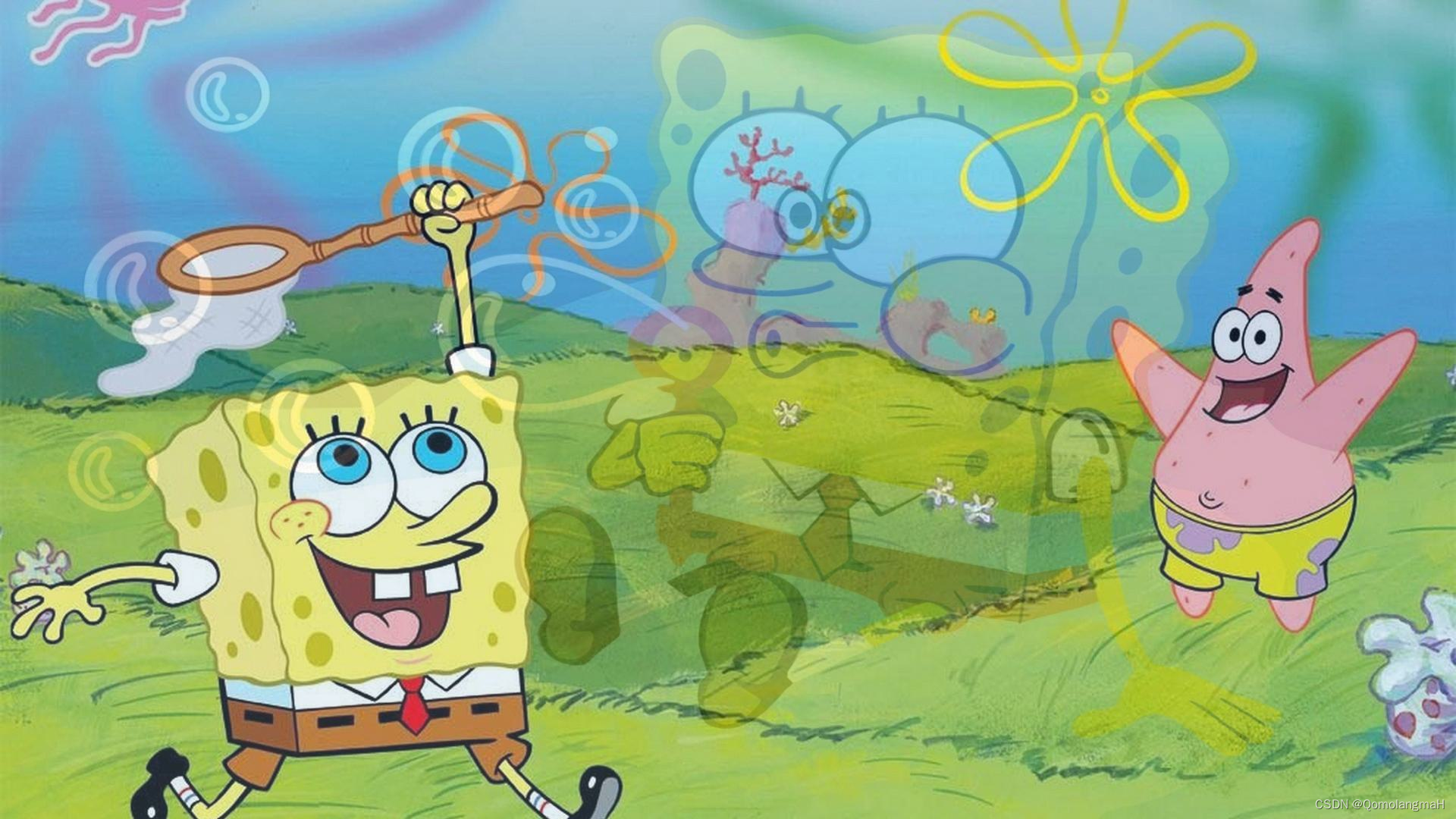
将 Mixup 操作应用于下述两张图像
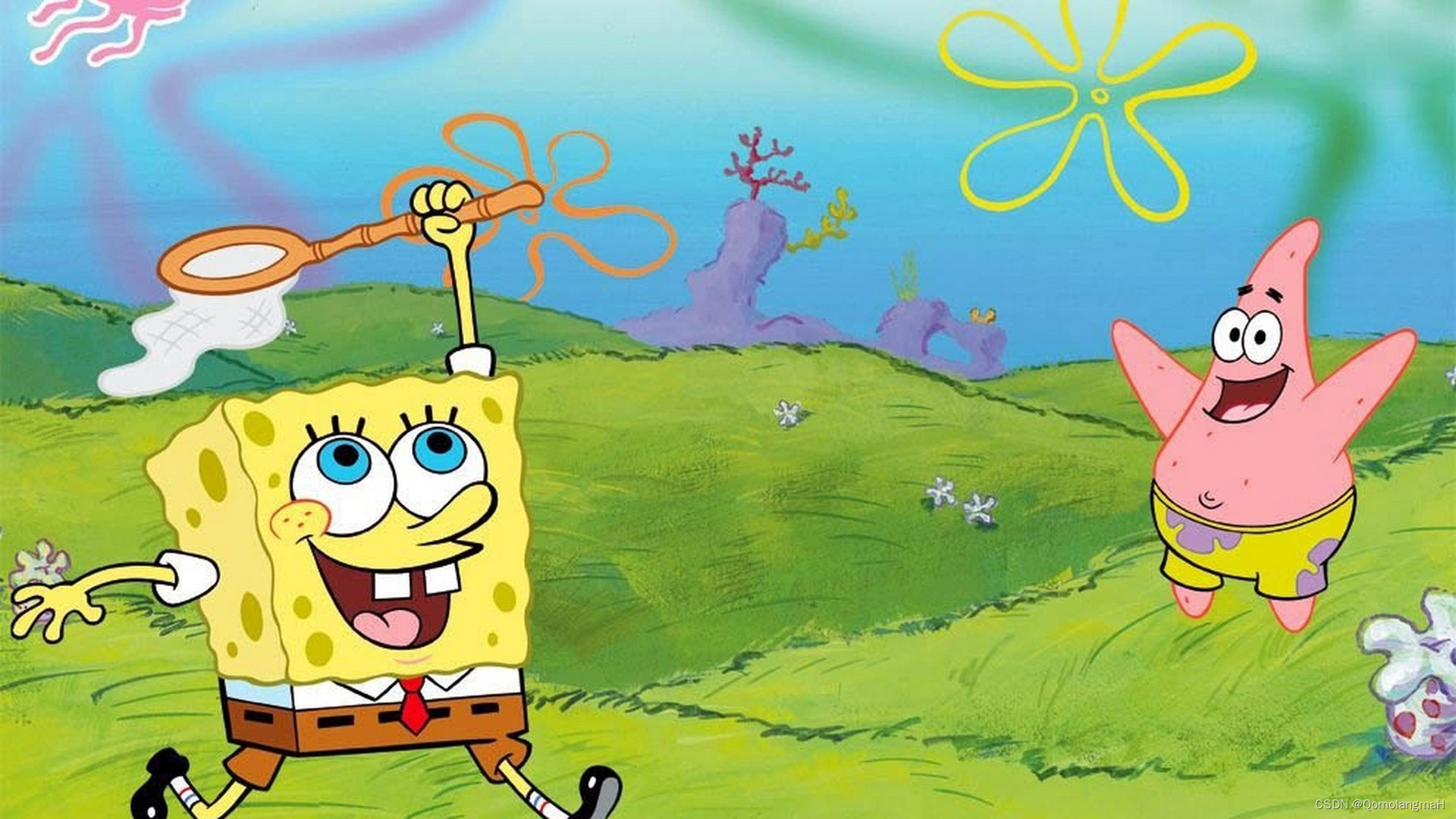

# 读取两张图像
img1 = Image.open('example2.jpg').convert('RGB')
img2 = Image.open('example3.jpg').convert('RGB')
# 调整图像大小
img1 = img1.resize((1920, 1080), Image.Resampling.BICUBIC)
img2 = img2.resize((1920, 1080), Image.Resampling.BICUBIC)
# 转换为 NumPy 数组
img1 = np.array(img1)
img2 = np.array(img2)
# 创建 Mixup 实例
mixup = Mixup(0.6)
# 应用 Mixup 操作
img_mixup = mixup(img1, img2)
# 将 NumPy 数组转换回 PIL 图像
img_result = Image.fromarray(img_mixup.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
# 保存图像
img_result.save('./mixup_image.jpg')
