继上次开发完Maven插件开发:根据库表生成实体类&根据实体类生成库表之后,博主对开发maven插件喜爱得一塌糊涂。这不,今天给大家带来了《自定义maven插件:自动生成API的word文档》。
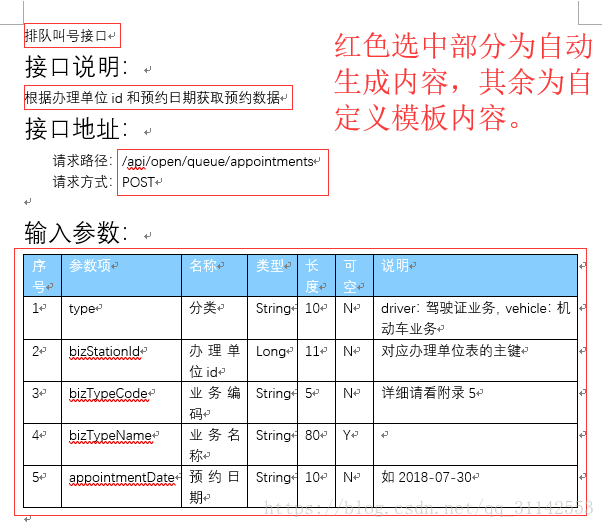
老规矩,先上镇楼图。(读者们也可以研究下Swagger2生成doc文档)
开门见山,直接上开发教程!首先是插件配置:
<plugin>
<groupId>cn.zhh</groupId>
<artifactId>apidoc-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<configuration>
<!-- 项目class文件根路径,以"\"结尾 -->
<classFolderPath>D:\eclipse_workspace\cgs4-queue\target\classes\</classFolderPath>
<!-- maven本地仓库根路径,以"\"结尾 -->
<repositoryPath>D:\repository\</repositoryPath>
<!-- 模板文件全路径 -->
<templateFilePath>C:\Users\dell\Desktop\template.docx</templateFilePath>
<!-- 输出文件全路径 -->
<outputFilePath>C:\Users\dell\Desktop\result.docx</outputFilePath>
<!-- 接口所在类全类名 -->
<apiClassName>com.hauxsoft.controller.open.AppointmentQueueCallController</apiClassName>
<!-- 接口方法名,避免一个类里面存在相同方法名 -->
<apiMethodName>list</apiMethodName>
<!-- 参数的类型全类名 -->
<apiParamClassName>com.hauxsoft.data.BizAppointmentFormDTO</apiParamClassName>
</configuration>
</plugin>思路:根据配置里面的接口类和接口方法,使用自定义类加载器找到它们,然后通过反射拿到它们上面的自定义注解,获取里面的值生成接口说明和访问地址,然后使用类似的方法去处理配置里面的参数类,得到输入参数列表。之后,使用第三方基于Apache POI的Word模板引擎将模板文件里面的相关内容替换,在输出路径得到最终文档。
开发步骤
一、关于创建maven插件项目,在上一篇博文中已经做了介绍,不会的童鞋们可以去看一下,链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31142553/article/details/81256516。
二、自定义注解,一共四个,分别用于接口类的类上和方法上、参数类的类上和字段上。
**
* API类注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//@Documented
//@Inherited
public @interface ApiClass {
// 接口类描述
String description();
// 接口根URL
String basePath() default "";
}/**
* API方法注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//@Documented
//@Inherited
public @interface ApiMethod {
// url
String url();
// 请求方式
String requestMethod() default "POST";
// 接口说明
String description();
}/**
* 参数类注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//@Documented
//@Inherited
public @interface ParamClass {
// 仅作标记作用
}/**
* 参数字段注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//@Documented
//@Inherited
public @interface ParamField {
// 字段名
String name() default "";
// 注释
String description();
// 类型
String type() default "";
// 长度
int length() default 0;
// 是否可为空
boolean nullAble() default false;
// 备注
String remark() default "";
}三、Api实体类,表示一个接口该有的东西。
class Api {
// 标题
private String title;
// 介绍
private String explain;
// url
private String url;
// 请求方式
private String method;还有一个List类型的参数,元素是Api的内部类Param
// 参数
private List<Param> params = new ArrayList<>();
static class Param {
// 序号
private int no;
// 名称
private String name;
// 描述
private String description;
// 类型
private String type;
// 长度
private String length;
// 是否可空
private String nullAble;
// 备注
private String remark;四、定义maven插件执行主类。注解”@goal“,表示我们使用命令apidoc-maven-plugin:word的时候,会执行这个类,还有几个成员变量,接收插件配置里面的参数。
/*
* @goal CustomMavenMojo:表示该插件的服务目标
* @phase compile:表示该插件的生效周期阶段
* @requiresProject false:表示是否依托于一个项目才能运行该插件
* @parameter expression="${name}":表示插件参数,使用插件的时候会用得到
* @required:代表该参数不能省略
*/
/**
* @author z_hh
* @date 2018-07-28
*
* @goal word
*
*/
public class WordDocGeneratorMojo extends AbstractMojo {
/**
* path of the classes folder.
* @parameter expression="${classFolderPath}"
* @required
*/
private String classFolderPath;
/**
* all class name of the api.
* @parameter expression="${apiClassName}"
* @required
*/
private String apiClassName;
/**
* method name of the api.
* @parameter expression="${classFolderPath}"
* @required
*/
private String apiMethodName;
/**
* param all class name of the api.
* @parameter expression="${apiParamClassName}"
* @required
*/
private String apiParamClassName;
/**
* path of the maven repository.
* @parameter expression="${repositoryPath}"
* @required
*/
private String repositoryPath;
/**
* path of the template file.
* @parameter expression="${templateFilePath}"
* @required
*/
private String templateFilePath;
/**
* path of the output file.
* @parameter expression="${outputFilePath}"
* @required
*/
private String outputFilePath;
// 类加载器
private URLClassLoader loader;五、参数校验。其实是有点多余,成员变量注释里面使用了@require表示该参数是必需的,没写的话理论上编译不通过,我们校验是为了防止空值的问题。
// 校验参数
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(classFolderPath)) {
throw new MojoFailureException("classFolderPath不能为空!");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(repositoryPath)) {
throw new MojoFailureException("repositoryPath!");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(apiClassName)) {
throw new MojoFailureException("apiClassName不能为空!");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(apiMethodName)) {
throw new MojoFailureException("apiMethodName不能为空!");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(apiParamClassName)) {
throw new MojoFailureException("apiParamClassName不能为空!");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(templateFilePath)) {
throw new MojoFailureException("templateFilePath!");
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(outputFilePath)) {
throw new MojoFailureException("outputFilePath!");
}六、(难点)定义加载项目class文件、maven本地仓库jar包(是为了解决类依赖其它jar包的问题)的URLClassLoader。
// 使用自定义类加载器加载指定目录下的jar包或class文件
// 需要加载当前项目编译后class文件所在根路径和maven本地仓库根目录
try {
getLog().info("加载项目class文件和本地仓库jar包");
// 获取maven本地仓库的所有jar包全路径
List<String> jarPaths = getRepositoryJarPaths();
int size = jarPaths.size() + 1;
URL[] urls = new URL[size];
int i = 0;
// jar包URL
for (; i < size - 1; i++) {
urls[i] = new URL("file:/" + jarPaths.get(i));
}
// 项目class文件URL
urls[size-1] = new URL("file:/" + classFolderPath);
loader = new URLClassLoader(urls);
getLog().info("加载成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
getLog().error(e);
throw new MojoFailureException("初始化类加载器失败!" + e.getClass().getName() + ":" + e.getMessage());
}相关方法代码
/**
* 获取所有jar包全路径集合
* @return List
*/
private List<String> getRepositoryJarPaths() {
List<String> filePaths = new ArrayList<>();
File file = new File(repositoryPath);
return ergodic(file, filePaths);
}
/**
* 递归遍历目录,将jar包路径放进list
* @param file
* @param resultFileName
* @return
*/
private static List<String> ergodic(File file, List<String> resultFileName){
File[] files = file.listFiles();
// 判断目录下是不是空的
if (files == null) {
return resultFileName;
}
for (File f : files) {
// 判断是否文件夹
if (f.isDirectory()) {
// 调用自身,查找子目录
ergodic(f, resultFileName);
} else {
if (f.getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
resultFileName.add(f.getPath());
}
}
}
return resultFileName;
}七、主要逻辑代码入口及异常处理(execute只能抛出MojoFailureException表示执行失败)。(代码接上面片段)
// 执行
try {
run();
} catch (Exception e) {
getLog().error(e);
throw new MojoFailureException("执行失败" + e.getClass().getName() + ":" + e.getMessage());
}
getLog().info("处理完毕!!!");
}
/**
* 业务入口
* @throws Exception
*/
private void run() throws Exception {
// 获得Api对象
getLog().info("开始获取Api对象");
Api api = generateApiObj();
getLog().info("得到Api对象:" + api.toString());
// 生成doc文档
getLog().info("开始生成word文档");
generateWordDoc(api);
getLog().info("得到word文档:" + outputFilePath);
}八、根据插件配置生成Api对象。在这里提供了一个简洁使用方式:有时候参数类字段很多的时候,对每个字段加@ParamField注解也是一个很麻烦的事情。于是为了方便,我们允许用户只在参数类上面使用@ParamClass注解标注,然后,我们就对类里面所有private字段生成参数,但是,因为不处理ParamFidld注解,所以参数只有字段名称和Java类型两个属性。
/**
* 生成Api对象
* @return Api
* @throws Exception
*/
private Api generateApiObj() throws Exception {
/*
* 这里有个大坑:clazz.isAnnotationPresent(ApiClass.class)永远返回false,clazz.getAnnotation(ApiClass.class)永远返回null。
* 具体参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangyufei1107/article/details/79760475
* 大概是不同的类加载器导致的吧!
* 所以需要使用加载项目和仓库的类加载器加载自定义注解得到Class,才是项目里面使用的注解,
* 得到注解后也不能强转为自定义注解,需要使用反射调用获取属性值。
*/
Class clazz = loader.loadClass(apiClassName);
Api api = new Api();
// 处理API类上面的ApiClass注解(可空)
Class apiClazz = loader.loadClass(ApiClass.class.getName());
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(apiClazz)) {
Annotation annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(apiClazz);
String description = (String) apiClazz.getMethod("description").invoke(annotation),
basePath = (String) apiClazz.getMethod("basePath").invoke(annotation);
api.setTitle(description);
api.setUrl(basePath);
}
// 获取API方法
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
Optional<Method> any = Arrays.stream(methods).filter(method -> Objects.equals(method.getName(), apiMethodName)).findAny();
if (!any.isPresent()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("API方法" + apiMethodName + "不存在!");
}
Method method = any.get();
// 处理API方法上面的ApiMethod注解,不能为空
Class apiMetnod = loader.loadClass(ApiMethod.class.getName());
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(apiMetnod)) {
Annotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(apiMetnod);
String url = (String) apiMetnod.getMethod("url").invoke(annotation),
requestMethod = (String) apiMetnod.getMethod("requestMethod").invoke(annotation),
description = (String) apiMetnod.getMethod("description").invoke(annotation);
api.setUrl(api.getUrl() + url);
api.setMethod(requestMethod);
api.setExplain(description);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("API方法" + apiMethodName + "缺少ApiMethod注解!");
}
// 处理ApiParamClass
handleApiParamClass(api);
return api;
}
/**
* 处理参数类
* @param api
* @throws Exception
*/
private void handleApiParamClass(Api api) throws Exception {
Class clazz = loader.loadClass(apiParamClassName);
// 判断是否有ParamClass注解
Class paramClazz = loader.loadClass(ParamClass.class.getName());
boolean exist = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(paramClazz);
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(1);
List<Api.Param> params = new ArrayList<>();
for (Field field : fields) {
// 类存在ParamClass注解,所有private字段都要参与生成文档,但是只有名称和类型
if (exist) {
if (field.getModifiers() == Modifier.PRIVATE) {
Api.Param param = new Api.Param();
param.setNo(i.getAndIncrement());
param.setName(field.getName());
param.setType(field.getType().getSimpleName());
// 空的字段留白
param.setDescription("");
param.setLength("");
param.setNullAble("");
param.setRemark("");
params.add(param);
}
continue;
}
// 类没有ParamClass注解,只处理有ParamField注解的字段
Class paramField = loader.loadClass(ParamField.class.getName());
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(paramField)) {
Api.Param param = new Api.Param();
// 自增序号
param.setNo(i.getAndIncrement());
Annotation annotation = field.getAnnotation(paramField);
// 字段名
String name = (String) paramField.getMethod("name").invoke(annotation);
param.setName(StringUtils.isEmpty(name) ? field.getName() : name);
// 说明
String description = (String) paramField.getMethod("description").invoke(annotation);
param.setDescription(description);
// 类型
String type = (String) paramField.getMethod("type").invoke(annotation);
param.setType(StringUtils.isEmpty(type) ? field.getType().getSimpleName() : type);
// 长度,为零就留空
int length = (int) paramField.getMethod("length").invoke(annotation);
param.setLength(length == 0 ? "" : String.valueOf(length));
// 是否可为空
boolean nullAble = (boolean) paramField.getMethod("nullAble").invoke(annotation);
param.setNullAble(nullAble ? "Y" : "N");
// 备注
String remark = (String) paramField.getMethod("remark").invoke(annotation);
param.setRemark(remark);
params.add(param);
}
}
api.setParams(params);
}九、将Api对象填充模板文件的变量。(这里主要使用了第三方模板引擎的jar包,了解更多:http://deepoove.com/poi-tl/)
word文档模板
数据填充代码
/**
* 根据Api对象生成Word文档
* 使用说明查看官网http://deepoove.com/poi-tl/
* @param api
*/
private void generateWordDoc(Api api) throws Exception {
// 表格的表头
RowRenderData header = new RowRenderData(Arrays.asList(new TextRenderData("FFFFFF", "序号"),
new TextRenderData("FFFFFF", "参数项"),
new TextRenderData("FFFFFF", "名称"),
new TextRenderData("FFFFFF", "类型"),
new TextRenderData("FFFFFF", "长度"),
new TextRenderData("FFFFFF", "可空"),
new TextRenderData("FFFFFF", "说明")),
"87CEFF");
// 表格的数据
List<RowRenderData> tableDatas = api.getParams().parallelStream()
.map(param -> {
return RowRenderData.build(String.valueOf(param.getNo()), param.getName(),
param.getDescription(), param.getType(), param.getLength(),
param.getNullAble(), param.getRemark());
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 替换模板文件的变量
Map<String, Object> datas = new HashMap<String, Object>() {
{
put("title", api.getTitle());
put("url", api.getUrl());
put("method", api.getMethod());
put("explain", api.getExplain());
put("params", new MiniTableRenderData(header, tableDatas, MiniTableRenderData.WIDTH_A4_FULL));
}
};
// 生成文件
XWPFTemplate template = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
template = XWPFTemplate.compile(templateFilePath).render(datas);
out = new FileOutputStream(outputFilePath);
template.write(out);
out.flush();
} finally {
out.close();
template.close();
}
}十、本次教程就先介绍到这里啦,后面有优化的话会更新文章,欢迎网友们订阅。
完整的项目代码和模板文件已上传,前往下载
存在问题及解决意向:插件现在的功能是一次只能生成一个接口的文档,后续考虑通过配置接口类(或者自动扫描所有或者指定路径下带Controller/RestController注解的类),处理它所有带xxxMapping注解的方法,url和method也从这个注解获取,然后参数类型也用Method反射获取(非自定义类型直接生成一个Api.Param对象),一次生成多个接口文档。敬请期待!