简介: 手写实现redux基础api
createStore( )和store相关方法
api回顾:
createStore(reducer, [preloadedState], enhancer)
创建一个 Redux store 来以存放应用中所有的 state
reducer (Function): 接收两个参数,当前的 state 树/要处理的 action,返回新的 state 树
preloadedState: 初始时的 state
enhancer (Function): store creator 的高阶函数,返回一个新的强化过的 store creator
Store 方法
getState() 返回应用当前的 state 树
dispatch(action) 分发 action。这是触发 state 变化的惟一途径
subscribe(listener) 添加一个变化监听器。每当 dispatch action 的时候就会执行,state 树中的一部分可能已经变化
replaceReducer(nextReducer) 替换 store 当前用来计算 state 的 reducer(高级不常用,不作实现)实现 Redux 热加载机制会用到源码实现:
./self-redux.js
export function createStore(reducer, enhancer) {
if(enhancer) {
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer)
}
let currentState = {}
let currentListeners = []
function getState() {
return currentState
}
function subscribe(listeners) {
currentListeners.push(listener)
}
function dispatch(action) {
currentState = reducer(currentState, action)
currentListeners.forEach(v => v())
return action
}
dispatch({ type: '@rainie/init-store' })
return {
getState,
subscribe,
dispatch
}
}demo:验证正确性
// import { createStore } from 'redux'
// 将redux文件替换成自己实现的redux文件
import { createStore } from './self-redux.js'
// 这就是reducer处理函数,参数是状态和新的action
function counter(state=0, action) {
// let state = state||0
switch (action.type) {
case '加机关枪':
return state + 1
case '减机关枪':
return state - 1
default:
return 10
}
}
// 新建store
const store = createStore(counter)
const init = store.getState()
console.log(`一开始有机枪${init}把`)
function listener(){
const current = store.getState()
console.log(`现在有机枪${current}把`)
}
// 订阅,每次state修改,都会执行listener
store.subscribe(listener)
// 提交状态变更的申请
store.dispatch({ type: '加机关枪' })combineReducers(reducers)
api简介
把一个由多个不同 reducer 函数作为 value 的 object,合并成一个最终的 reducer 函数
实现 Redux 热加载机制会用到
import { combineReducers } from 'redux'
import todos from './todos'
import counter from './counter'
export default combineReducers({
todos,
counter
})实现:
实质就是返回一个大的function 接受state,action,然后根据key用不同的reducer
注:combinedReducer的key跟state的key一样
const reducer = combineReducers({
a: doSomethingWithA,
b: processB,
c: c
})
function reducer(state = {}, action) {
return {
a: doSomethingWithA(state.a, action),
b: processB(state.b, action),
c: c(state.c, action)
}
}
function combindReducer(reducers) {
// 第一个只是先过滤一遍 把非function的reducer过滤掉
const reducerKeys = Object.keys(reducers)
const finalReducers = {}
reducerKeys.forEach((key) => {
if(typeof reducers[key] === 'function') {
finalReducers[key] = reducers[key]
}
})
const finalReducersKeys = Object.keys(finalReducers)
// 第二步比较重要 就是将所有reducer合在一起
// 根据key调用每个reducer,将他们的值合并在一起
let hasChange = false;
const nextState = {};
return function combind(state={}, action) {
finalReducersKeys.forEach((key) => {
const previousValue = state[key];
const nextValue = reducers[key](previousValue, action);
nextState[key] = nextValue;
hasChange = hasChange || previousValue !== nextValue
})
return hasChange ? nextState : state;
}
}applyMiddleware(...middleware)
使用包含自定义功能的 middleware 来扩展 Redux 是
...middleware (arguments): 遵循 Redux middleware API 的函数。
每个 middleware 接受 Store 的 dispatch 和 getState 函数作为命名参数,并返回一个函数。
该函数会被传入 被称为 next 的下一个 middleware 的 dispatch 方法,并返回一个接收 action 的新函数,这个函数可以直接调用 next(action),或者在其他需要的时刻调用,甚至根本不去调用它。
调用链中最后一个 middleware 会接受真实的 store 的 dispatch 方法作为 next 参数,并借此结束调用链。
所以,middleware 的函数签名是 ({ getState, dispatch }) => next => action
import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import * as reducers from './reducers'
let reducer = combineReducers(reducers)
// applyMiddleware 为 createStore 注入了 middleware:
let store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))中间件机制applyMiddleware的实现
中间件机制图
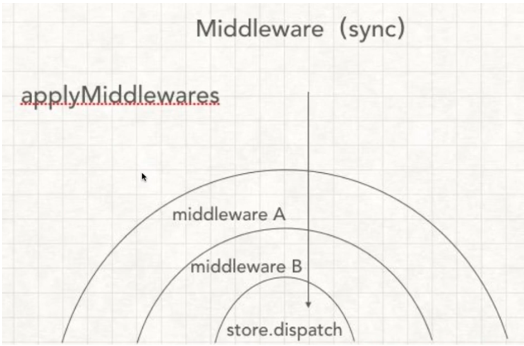
实现步骤
1.扩展createStore,使其接受第二个参数(中间件其实就是对createStore方法的一次扩展)
2.实现applyMiddleware,对store的disptach进行处理
3.实现一个中间件
正常调用
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
// import { createStore, applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import { createStore, applyMiddleware} from './self-redux'
// import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import thunk from './self-redux-thunk'
import { counter } from './index.redux'
import { Provider } from './self-react-redux';
import App from './App'
const store = createStore(counter, applyMiddleware(thunk))
ReactDOM.render(
(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
),
document.getElementById('root'))
// 便于理解:函数柯利化例子
function add(x) {
return function(y) {
return x+y
}
}
add(1)(2) //3applymiddleware
// ehancer(createStore)(reducer)
// createStore(counter, applyMiddleware(thunk))
// applyMiddleware(thunk)(createStore)(reducer)
// 写法函数柯利化
export function applyMiddleware(middleware) {
return function (createStore) {
return function(...args) {
// ...
}
}
}
// 只处理一个 middleware 时
export function applyMiddleware(middleware) {
return createStore => (...args) => {
const store = createStore(...args)
let dispatch = store.dispatch
const midApi = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (...args) => dispatch(...args)
}
// 经过中间件处理,返回新的dispatch覆盖旧的
dispatch = middleware(midApi)(store.dispatch)
// 正常中间件调用:middleware(midApi)(store.dispatch)(action)
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}
}
// 处理多个middleware时
// 多个 compose
export function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return createStore => (...args) => {
const store = createStore(...args)
let dispatch = store.dispatch
const midApi = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (...args) => dispatch(...args)
}
const middlewareChain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(midApi))
dispatch => compose(...middlewareChain(store.dispatch))
// dispatch = middleware(midApi)(store.dispatch)
// middleware(midApi)(store.dispatch)(action)
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}
}
手写redux-thunk异步中间件实现
// middleware(midApi)(store.dispatch)(action)
const thunk = ({ dispatch, getState }) => next => action => {
// next就是store.dispatch函数
// 如果是函数,执行以下,参数dispatch和getState
if (typeof action == 'function') {
return action(dispatch, getState)
}
// 默认 什么都不干
return next(action)
}
export default thunk
处理异步action
export function addGunAsync() {
// thunk插件作用,这里可以返回函数
return dispatch => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 异步结束后,手动执行dispatch
dispatch(addGun())
}, 2000)
}
}趁热打铁,再实现一个中间件: dispatch接受一个数组,一次处理多个action
export arrayThunk = ({ dispatch, getState }) => next => action => {
if(Array.isArray(action)) {
return action.forEach(v => dispatch(v))
}
return next(action)
}
这类action会被处理
export function addTimes() {
return [{ type: ADD_GUN },{ type: ADD_GUN },{ type: ADD_GUN }]
}bindActionCreators的实现
在react-redux connect mapDispatchToProps中使用到了该方法,可以去看那篇blog,有详解~
api: bindActionCreators(actionCreators, dispatch)
把 action creators 转成拥有同名 keys 的对象,但使用 dispatch 把每个 action creator 包围起来,这样可以直接调用它们
实现:
function bindActionCreator(creator, dispatch) {
return (...args) => dispatch(creator(...args))
}
export function bindActionCreators(creators, dispatch) {
let bound = {}
Object.keys(creators).forEach( v => {
let creator = creators[v]
bound[v] = bindActionCreator(creator, dispatch)
})
return bound
}
// 简写
export function bindActionCreators(creators, dispatch) {
return Object.keys(creators).reduce((ret, item) => {
ret[item] = bindActionCreator(creators[item], dispatch)
return ret
}, {})
}compose的实现
api: compose(...functions)
从右到左来组合多个函数。
当需要把多个 store 增强器 依次执行的时候,需要用到它
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import DevTools from './containers/DevTools'
import reducer from '../reducers'
const store = createStore(
reducer,
compose(
applyMiddleware(thunk),
DevTools.instrument()
)
)实现:
compose(fn1, fn2, fn3)
fn1(fn2(fn3))
export function compose(...funcs) {
if(funcs.length == 0) {
return arg => arg
}
if(funcs.length == 1) {
return funcs[0]
}
return funcs.reduce((ret,item) => (...args) => ret(item(...args)))
}原文地址: