With the development of domestic Internet + and innovation economy, the external business environment factors of enterprises are changing more and more rapidly, and enterprise projectization is an inevitable trend to further reduce transaction costs.
The project will replace the enterprise as the smallest unit to deliver customer value, and this is true for the collaboration between enterprises, business lines within an enterprise, and departments within a business line.
There are countless successful and failed project cases, and the reasons are also different. Here is a summary of the research on enterprise project management, which draws out our thoughts on the construction of organizational-level project management through research.
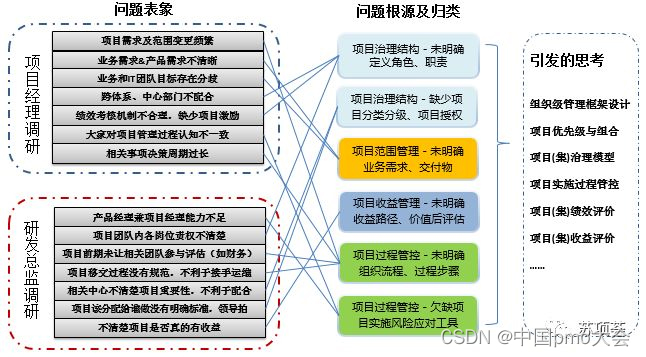
- What are the difficulties in organizational-level project management in your organization?
- Does your project performance evaluation include an assessment of the value of project benefits?
- From which areas of competence and methods are you cultivating project talents?
1. Elements and design of organizational project management framework
1. First of all, we need to understand the four elements of the organization-level project management framework, namely the operating organization (multi-level PMO), the project under control, the shared project information, and the undertaking team. Establishing a PMO organization that can adapt to corporate environmental factors is a key step in our project management work.

2. Secondly, we need to clarify the functional positioning and maturity of the localized PMO. The construction of PMO is a systematic project. The development stages of enterprises are different, and the industries in which enterprises are located are different. The construction paths and phased functions are also different.
From establishment to maturity, through theoretical induction and practical analysis, three stages of PMO function evolution can be roughly summarized: the initial stage of establishment, the growth stage, and the mature stage.
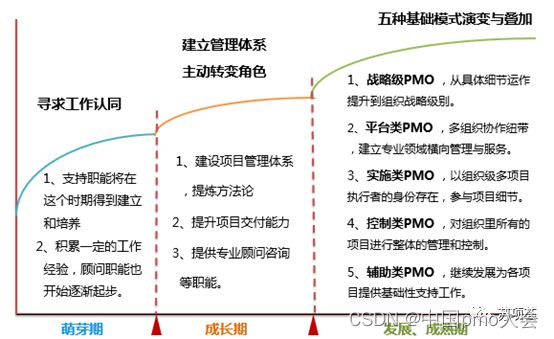
(1) In the initial stage of establishment, the positioning at this time is very important, and the most urgent task is to seek recognition. The main responsibility of the PMO at this stage is to assist the project manager and functional managers in handling some project-related activities, so as to quickly open up the work situation, and help the project managers and functional managers to do supportive work with a relatively low profile and seek their approval. During this period, the project management system is established and cultivated.
(2) In the growth period, after being approved, on the one hand, we must continue to provide support work, and we can transition to a model that focuses on project consultants and supplemented by project assistants; on the other hand, we must strengthen collaboration with functional managers, manage multiple projects well, form reproducible project management practices and experiences, improve the project management system, and establish and implement a project management talent training system.
(3) In the mature stage, due to the adaptability of positioning and functions, there will be differentiation or evolution of the four basic models, and it may also be the superposition of one or several basic models.
The first category is to undertake the functions related to strategy formulation. The focus of PMO’s work has been upgraded from the implementation of specific details to the guidance of organizational strategy, and activities such as strategic planning, strategic decomposition, strategy implementation and tracking of the enterprise have been carried out.
The second category is to undertake the multi-organization collaboration link. In the professional management fields of business demonstration, project implementation, operation and revenue management, it not only exists as an organization-level multi-project executor, but also conducts organization-level management and services horizontally.
The third category is mainly responsible for the success or failure of all projects in the entire organization, carries out specific project implementation details, and exists as an organization-level multi-project executor.
The fourth category, jumping out of specific project implementation, is not directly responsible for the success or failure of each project. On behalf of the company's management, it conducts overall management and control of all projects in the organization to ensure the smooth progress of all projects, forming a control PMO.
The fifth category, continue to develop support functions, provide basic support, consulting and other related work for various projects, and form a supportive and auxiliary PMO.
3. After clarifying the status quo, how can we build or improve an organization-level project management system in line with our own enterprise? Peter Drucker said: What the company assesses, the employees will do. Combining the organizational strategy and KPI, formulate the corresponding management and control process, and implement the process through the way, method, technique, device, and momentum.

Tao: that is, evangelism, the concept and awareness conveyed to enterprises, organizations, and employees;
Law: that is, rules and regulations, combined with enterprise environmental factors, formulate relevant rules and regulations for enterprise-level project management;
Technique: that is, the routine, the relevant process of implementation, without technique, it cannot be advanced in an orderly manner;
Tool: that is, the tool, the requirements for specific work execution, without the tool, the work cannot be completed simply and efficiently;
Potential: That is to borrow strength, make use of momentum, create a good momentum, meet the east wind, and raise the sails to borrow the wind.
2. Application of enterprise organization-level project management framework
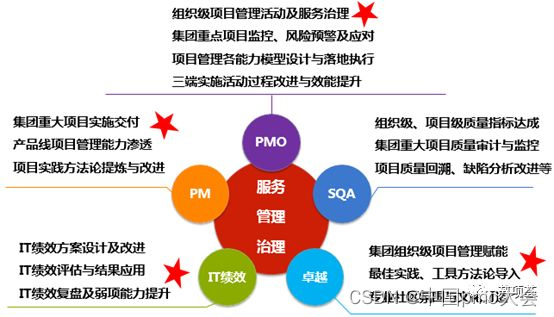
1. First of all, let me introduce the core functions of the PMO organization where the author works, mainly including the implementation and delivery of major projects (PM), organizational project management (OPM), organizational and project-level R&D quality management (SQA), IT system performance management (ITPM), and the creation of project management communities and cultural atmospheres.
2. Based on organizational positioning and maturity, establish OPM management ideas to strengthen three-terminal contractual delivery and improve revenue-oriented project life cycle management, carry out work such as demand governance, R&D implementation governance, and post-evaluation governance of value and revenue, and use special project teams to promote integrated management of project portfolio + project (collection) implementation.
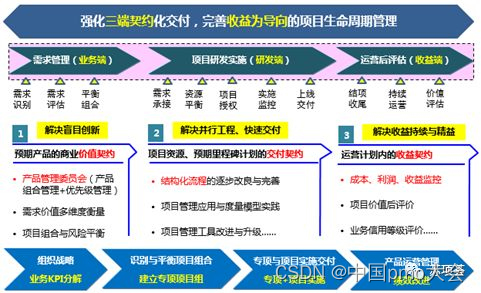
★ Demand management (business side): Anticipate the commercial value contract of the product and solve the problem of blind innovation. Establish a three-level management mechanism for demand decision-making, and clarify the priority of demand at the center level, system level, and group level (cross-system).

★ Project R&D implementation (R&D end): project resources, delivery contract of expected milestone plan, solving problems of concurrent engineering and rapid delivery. Establish a project classification and grading management mechanism, a comprehensive project information view and Kanban, and clearly implement the project management talent training system.

★ Post-operation evaluation (revenue side): operate the revenue contract in the plan to solve the problems of continuous revenue and lean. In the project establishment stage, data quantification is carried out on the demand value, and the revenue achievement plan is decomposed, and the periodic (for example: the evaluation period is one year, quarterly evaluation) cycle evaluation mode is used to track the operation effect and achieve evaluation, establish a business credit rating, and incorporate it into the performance evaluation system.

3. Some examples of excellent project management practices in enterprises
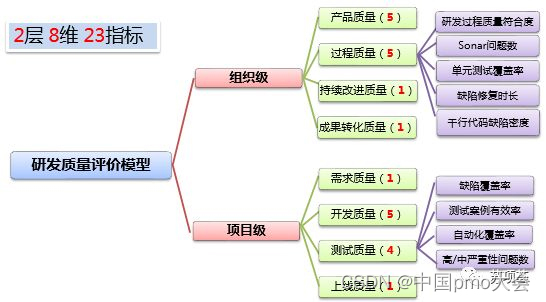
(1) Organization-level and project-level quality evaluation models
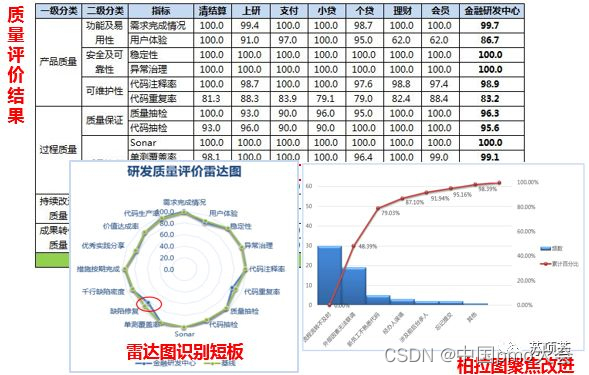
The model has 2 layers, 10 dimensions and 24 indicators, to identify the shortcomings of the center's capabilities horizontally, and to improve the organizational quality vertically.
(2) Project manager capability assessment model
From 4 major categories, 9 subcategories, and 34 dimensions, the model conducts a comprehensive sampling of the project manager's ability, completes the evaluation in 10 minutes, quickly identifies the strengths and weaknesses of the ability, and helps provide targeted counseling and follow-up to promote the successful delivery of the project.

Model application:
•Ability self-assessment at the individual level, which can identify its shortcomings and promote targeted self-improvement;
•Horizontal comparison at the team level is conducive to the analysis of gaps between departments and general improvement;
• Establishment of resource pool at the organizational level, rational allocation of resource use, and risk reduction.

Application effect of the model: Establish a resource pool of financial service project managers (including part-time product managers), identify and evaluate common problems in project management, implement organizational improvement and introduce capacity-enhancing countermeasures, and recommend and appoint project managers that match their capabilities according to project priorities, effectively preventing project risks from occurring.
(3) Project health evaluation model
From the 7Key dimensions of project scope, schedule, cost, quality, team (resources) and risk, the model realizes the visualization of project health status in the form of traffic lights, helps organizations quickly focus, locate project problems, and give real-time warnings to promote successful project delivery.
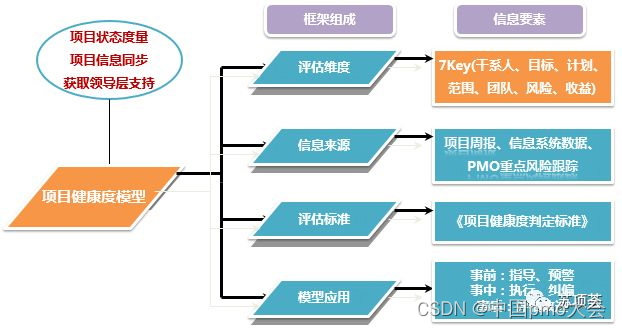
Model application: Generate a standard project health status report on a weekly basis, support project process monitoring, achieve advance reminders, implement corrections during the event, and evaluate and improve afterwards.

Application effect of the model: After one year of application, the project risk early warning resolution rate increased to 30% within three days, and the project cost early warning rate was greatly reduced, providing a good foundation for financial service project cost accounting management and control.
(4) Post-evaluation model of project value
In the project approval stage, data quantification is carried out on the value of demand, the profit achievement plan is decomposed, and the periodic cycle evaluation model is used to track and evaluate the operation effect, establish a business credit rating, incorporate it into the performance evaluation system, and focus on R&D resources.
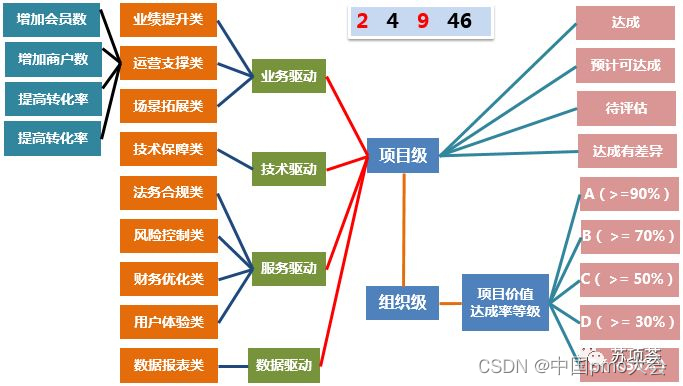
Model application: Generate a standard project health status report on a weekly basis, support project process monitoring, achieve advance reminders, implement corrections during the event, and evaluate and improve afterwards.
Application effect of the model: The standard project within two years has been evaluated on a quarterly basis with corresponding rules, and its value achievement rate (achieved, excluding expected achievable and pending evaluation) has increased by about 10% year-on-year. Classify unrealized value items, conduct root cause analysis, analyze resource and cost usage data, effectively monitor product operation value achievement, and adjust corresponding resource allocation.
conclusion
Organization-level project management depends on the environmental factors of the enterprise and exists because of the improvement of efficiency. Organizational change is used as the means. It requires joint construction and win-win in the large environment, and it also requires perseverance and adaptability in the small environment. (Source: Su Xianghui and Wang Lin)