- ダークホースプログラマー-JDBCドキュメント(Tencent Weiyun)JDBC notes.pdf:https://share.weiyun.com/Kxy7LmRm
目次
JDBCクラスの詳細な説明_ResultSet_基本的な使用法
Emp.java // Empテーブルデータをカプセル化するJavaBean
JDBC_PreparedStatementの各クラスの詳細な説明
04詳細なResultSetクラス
JDBCクラスの詳細な説明_ResultSet_基本的な使用法
4. ResultSet:結果セットオブジェクト、クエリ結果のカプセル化
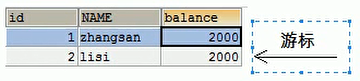
* boolean next():カーソルを1行下に移動して、現在の行が最後の行の終わりかどうか(データがあるかどうか)を判断します。終わりがある場合はfalseを返します。 、そうでない場合は、trueを返します。
* getXxx(パラメーター):データを取得します
* Xxx:次のようなデータ型を表します:int getInt()、String getString()
*パラメーター:1。int :
1から始まる列の番号を表します:getString( 1)
2。文字列:次のように列名を表します:getDouble( "balance")
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
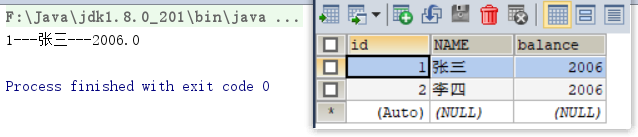
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}詳細なJDBCクラス_ResultSet_トラバーサル
4. ResultSet:クエリ結果をカプセル化した結果セットオブジェクト
* boolean next():カーソルを1行下に移動して、現在の行が最後の行の終わりかどうか(データがあるかどうか)を判断します。終わりがある場合はfalseを返します。 ;そうでない場合は、trueを返します。
* getXxx(パラメーター):データを取得します
* Xxx:次のようなデータ型を表します:int getInt()、String getString()
*パラメーター:1。int :
1から始まる列の番号を表します:getStringなど(1)
2。文字列:列名を表します。例:getDouble( "balance")
*注:
*手順:
1。カーソルを1行下に移動します
2.データがあるかどうかを確認します
3.データを取得します//6.1ループは、カーソルが最後の行の終わりにあるかどうかを判別します。
while(rs.next()){ // 6.2データの取得 int id = rs.getInt(1); String name = rs.getString( "name"); double balance = rs.getDouble(3); System.out。 println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance); }
エラーコード:
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id2 = rs.getInt(1);
String name2 = rs.getString("name");
double balance2 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id2 + "---" + name2 + "---" + balance2);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id3 = rs.getInt(1);
String name3 = rs.getString("name");
double balance3 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id3 + "---" + name3 + "---" + balance3);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
//6.1 循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾。
while (rs.next()) {
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
/* //6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}*/
/* //6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id2 = rs.getInt(1);
String name2 = rs.getString("name");
double balance2 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id2 + "---" + name2 + "---" + balance2);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id3 = rs.getInt(1);
String name3 = rs.getString("name");
double balance3 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id3 + "---" + name3 + "---" + balance3);*/
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}05JDBCログインケースの演習
JDBCプラクティス_selectステートメント
4. ResultSet:クエリ結果をカプセル化した結果セットオブジェクト
* boolean next():カーソルを1行下に移動して、現在の行が最後の行の終わりかどうか(データがあるかどうか)を判断します。終わりがある場合はfalseを返します。 ;そうでない場合は、trueを返します。
* getXxx(パラメーター):データを取得します
* Xxx:次のようなデータ型を表します:int getInt()、String getString()
*パラメーター:1。int :
1から始まる列の番号を表します:getStringなど(1)
2。文字列:列名を表します。例:getDouble( "balance")
*注:
*手順:
1。カーソルを1行下に移動します
2.データがあるかどうかを確認します
3.データを取得します//6.1ループは、カーソルが最後の行の終わりにあるかどうかを判別します。
while(rs.next()){ // 6.2データの取得 int id = rs.getInt(1); String name = rs.getString( "name"); double balance = rs.getDouble(3); System.out。 println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance); }*演習:
*メソッドを定義し、empテーブルのデータをクエリしてオブジェクトとしてカプセル化し、コレクションをロードして返します。
1.Empクラスを定義します
。2。メソッドを定義します。publicList<Emp> findAll(){}
3。メソッドselect * fromemp;を実装します。
Emp.java // Empテーブルデータをカプセル化するJavaBean
package cn.itcast.domain;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 封装Emp表数据的JavaBean
*/
public class Emp {
private int id;
private String ename;
private int job_id;
private int mgr;
private Date joindate;
private double salary;
private double bonus;
private int dept_id;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getEname() {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public int getJob_id() {
return job_id;
}
public void setJob_id(int job_id) {
this.job_id = job_id;
}
public int getMgr() {
return mgr;
}
public void setMgr(int mgr) {
this.mgr = mgr;
}
public Date getJoindate() {
return joindate;
}
public void setJoindate(Date joindate) {
this.joindate = joindate;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getDept_id() {
return dept_id;
}
public void setDept_id(int dept_id) {
this.dept_id = dept_id;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", ename='" + ename + '\'' +
", job_id=" + job_id +
", mgr=" + mgr +
", joindate=" + joindate +
", salary=" + salary +
", bonus=" + bonus +
", dept_id=" + dept_id +
'}';
}
}JDBCDemo8.java
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.domain.Emp;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* * 定义一个方法,查询emp表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合,返回。
*/
public class JDBCDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Emp> list = new JDBCDemo8().findAll();
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.size());
for (Emp x : list) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
/**
* 查询所有emp对象
*
* @return
*/
public List<Emp> findAll() {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<Emp> list = null;
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from emp";
//4.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.遍历结果集,封装对象,装载集合
Emp emp = null;
list = new ArrayList<Emp>();
while (rs.next()) {
//获取数据
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String ename = rs.getString("ename");
int job_id = rs.getInt("job_id");
int mgr = rs.getInt("mgr");
Date joindate = rs.getDate("joindate");
double salary = rs.getDouble("salary");
double bonus = rs.getDouble("bonus");
int dept_id = rs.getInt("dept_id");
// 创建emp对象,并赋值
emp = new Emp();
emp.setId(id);
emp.setEname(ename);
emp.setJob_id(job_id);
emp.setMgr(mgr);
emp.setJoindate(joindate);
emp.setSalary(salary);
emp.setBonus(bonus);
emp.setDept_id(dept_id);
//装载集合
list.add(emp);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
}JDBCツール
JDBCツールクラスを抽出します:JDBCUtils
*目的:書き込みを簡素化
*分析:
1。ドライバーも抽出を登録します
2.接続オブジェクトを取得するためのメソッドを抽出します
*要件:パラメーター(トラブル)を渡したくないだけでなく、ツールの普遍性を確保します。
*解決策:構成ファイル
jdbc.properties
url = ...
user = ...
password = .. ..3.リソースを解放するメソッドを抽出します
*コードの実装:...

Java19-day10 [標準入出力ストリーム、バイト文字印刷ストリーム、オブジェクトのシリアル化-逆シリアル化ストリーム、serialVersionUID&transient、プロパティ]
前書き
- Mapシステムのコレクションクラスです。
- プロパティは、ストリームに保存することも、ストリームからロードすることもできます。
- 属性リスト内の各キーとそれに対応する値は文字列です。

package cn.itcast.util;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* JDBC工具类
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String driver;
/**
* 文件的读取,只需要读取一次即可拿到这些值。使用静态代码块
* 静态代码块,随着类的加载而执行(只会执行一次)
*/
static {
//读取资源文件,获取值。
try {
//1. 创建Properties集合类。
Properties pro = new Properties();
//获取src路径下的文件的方式--->ClassLoader 类加载器:加载字节码文件进内存、获取src下资源文件的路径
//获取ClassLoader要先获取其对应的字节码文件对象
ClassLoader classLoader = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader();
//以src为相对的根路径 统一资源定位符URL
URL res = classLoader.getResource("jdbc.properties"); // 传文件名,获取resource资源
String path = res.getPath();
// System.out.println(path);///D:/IdeaProjects/itcast/out/production/day04_jdbc/jdbc.properties
//2. 加载文件
// pro.load(new FileReader("D:\\IdeaProjects\\itcast\\day04_jdbc\\src\\jdbc.properties"));
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
//3. 获取数据,赋值
url = pro.getProperty("url");
user = pro.getProperty("user");
password = pro.getProperty("password");
driver = pro.getProperty("driver");
//4. 注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
*
* @return 连接对象
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
}
/**
* 释放资源
*
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}JDBCpractice_loginケース
*演習:
*要件:
1
。キーボードからユーザー名とパスワードを入力します。2。ユーザーが正常にログインしたかどうかを確認します。
* select * from user where username = "" and password = "";
* SQLにクエリ結果、成功します、そうでなければ失敗します*手順:
1。データベーステーブルユーザー
CREATE TABLE USER(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT、
username VARCHAR(32)、
PASSWORD VARCHAR(32)
);を作成します。INSERT INTO USER VALUES(NULL、 'zhangsan'、 '123');
INSERT INTO USER VALUES(NULL、 'lisi'、 '234');2.コードの実装:..。
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 练习:
* * 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class JDBCDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//2.调用方法 非静态方法,需要创建对象来调用
boolean flag = new JDBCDemo9().login(username, password);
//3.判断结果,输出不同语句
if (flag) {
//登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
/**
* 登录方法
*/
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = '" + username + "' and password = '" + password + "' ";
System.out.println(sql);
//3.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.执行查询
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, stmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
}06PreparedStatementクラスの詳細な説明
JDBC_PreparedStatementの各クラスの詳細な説明
5. PreparedStatement:SQL
1を実行するオブジェクト。SQLインジェクションの問題: SQLをスプライシングする場合、SQLのいくつかの特別なキーワードが文字列のスプライシングに関与するため、セキュリティ上の問題が発生します。
1.ユーザーを気軽に入力し、パスワードを入力します:
a 'または' a ' =' a 2. sql:select * from user where username = 'fhdsjkf' and password = 'a' or'a '=' a '2. SQLインジェクションの問題を解決し
ます: PreparedStatementオブジェクトを使用して解決します3.プリコンパイル済みSQL:パラメーターをプレースホルダーとして使用します
4.手順:
1。ドライバーjarパッケージmysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jarをインポートします2.
登録しますドライバー
3.データベース接続オブジェクトの取得接続
4.SQLの定義
*注:SQLのパラメーターは何ですか?次のようなプレースホルダーとして:select * from user where username =?and password = ?;
5.sqlステートメントを実行するためのオブジェクトPreparedStatementConnection.prepareStatement(String sql)を取得します。6。Give
?割り当て:
*メソッド:setXxx(パラメーター1、パラメーター2)
*パラメーター1:?位置番号は1から始まります
*パラメータ2 :?値
7。sqlを実行し、返された結果を受け入れ
ます。sqlステートメントを渡す必要はありません。8 。結果を処理します。9 。
リソースを解放します。5.注: PreparedStatementは、追加、削除、変更、およびチェックのすべての操作を完了するために後の期間に使用され
ます1.SQLインジェクションを防ぐことができます
2.より効率的
ログインケース-SQLインジェクションの問題を解決する
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 练习:
* * 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class JDBCDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//2.调用方法 非静态方法,需要创建对象来调用
boolean flag = new JDBCDemo9().login(username, password);
//3.判断结果,输出不同语句
if (flag) {
//登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
/**
* 登录方法
*/
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = '" + username + "' and password = '" + password + "' ";
System.out.println(sql);
//3.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.执行查询
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, stmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 登录方法,使用PreparedStatement实现
*/
public boolean login2(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
//3.获取执行sql的对象
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给?赋值
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
//4.执行查询,不需要传递sql
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, pstmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
}さあ、さあ、さあ、私は壊すよりも死にたいです~~~