- Dark horse 프로그래머 -JDBC 문서 (Tencent Weiyun) JDBC notes.pdf : https://share.weiyun.com/Kxy7LmRm
목차
JDBC 클래스 _ResultSet_ 기본 사용에 대한 자세한 설명
상세한 JDBC 클래스 _ResultSet_ traversal
Emp.java // Emp 테이블 데이터를 캡슐화하는 JavaBean
06 PreparedStatement 클래스 상세 설명
JDBC_PreparedStatement의 각 클래스에 대한 자세한 설명
04 세부 ResultSet 클래스
JDBC 클래스 _ResultSet_ 기본 사용에 대한 자세한 설명
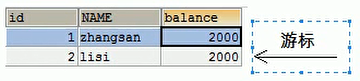
4. ResultSet : 결과 집합 객체, 질의 결과 캡슐화
* boolean next () : 커서를 한 줄 아래로 이동하여 현재 줄이 마지막 줄의 끝인지 확인 (데이터가 있는지 여부), 있으면 false 반환 , 그렇지 않은 경우 true를 반환합니다.
* getXxx (매개 변수) : 데이터 가져 오기
* Xxx : 다음과 같은 데이터 유형을 나타냅니다. int getInt (), String getString ()
* 매개 변수 :
1. int : 다음과 같이 1부터 시작하는 열 번호를 나타냅니다. getString ( 1)
2. 문자열 : 다음과 같은 열 이름을 나타냅니다. getDouble ( "balance")
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
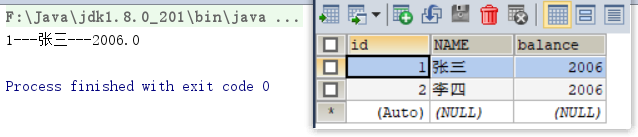
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}상세한 JDBC 클래스 _ResultSet_ traversal
4. ResultSet : 쿼리 결과를 캡슐화하는 결과 집합 객체
* boolean next () : 커서를 한 줄 아래로 이동하여 현재 줄이 마지막 줄의 끝인지 (데이터가 있는지 여부) 확인하고, 있으면 false를 반환합니다. ; 그렇지 않은 경우 true를 반환합니다.
* getXxx (매개 변수) : 데이터 가져 오기
* Xxx : 다음과 같은 데이터 유형을 나타냅니다. int getInt (), String getString ()
* 매개 변수 :
1. int : 다음과 같이 1부터 시작하는 열 번호를 나타냅니다. getString (1)
2. 문자열 : 열 이름을 나타냅니다. 예 : getDouble ( "balance")
* 참고 :
* 단계 :
1. 커서를 한 줄 아래로 이동
2. 데이터가 있는지 확인
3. 데이터 가져 오기//6.1 루프는 커서가 마지막 줄의 끝에 있는지 여부를 결정합니다.
while (rs.next ()) { //6.2 데이터 가져 오기 int id = rs.getInt (1); String name = rs.getString ( "name"); double balance = rs.getDouble (3); System.out. println (id + "---"+ 이름 + "---"+ 잔액); }
에러 코드:
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id2 = rs.getInt(1);
String name2 = rs.getString("name");
double balance2 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id2 + "---" + name2 + "---" + balance2);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id3 = rs.getInt(1);
String name3 = rs.getString("name");
double balance3 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id3 + "---" + name3 + "---" + balance3);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
//6.1 循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾。
while (rs.next()) {
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
/* //6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}*/
/* //6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id2 = rs.getInt(1);
String name2 = rs.getString("name");
double balance2 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id2 + "---" + name2 + "---" + balance2);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id3 = rs.getInt(1);
String name3 = rs.getString("name");
double balance3 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id3 + "---" + name3 + "---" + balance3);*/
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}05 JDBC 로그인 사례 실습
JDBC 연습 _select 문
4. ResultSet : 쿼리 결과를 캡슐화하는 결과 집합 객체
* boolean next () : 커서를 한 줄 아래로 이동하여 현재 줄이 마지막 줄의 끝인지 (데이터가 있는지 여부) 확인하고, 있으면 false를 반환합니다. ; 그렇지 않은 경우 true를 반환합니다.
* getXxx (매개 변수) : 데이터 가져 오기
* Xxx : 다음과 같은 데이터 유형을 나타냅니다. int getInt (), String getString ()
* 매개 변수 :
1. int : 다음과 같이 1부터 시작하는 열 번호를 나타냅니다. getString (1)
2. 문자열 : 열 이름을 나타냅니다. 예 : getDouble ( "balance")
* 참고 :
* 단계 :
1. 커서를 한 줄 아래로 이동
2. 데이터가 있는지 확인
3. 데이터 가져 오기//6.1 루프는 커서가 마지막 줄의 끝에 있는지 여부를 결정합니다.
while (rs.next ()) { //6.2 데이터 가져 오기 int id = rs.getInt (1); String name = rs.getString ( "name"); double balance = rs.getDouble (3); System.out. println (id + "---"+ 이름 + "---"+ 잔액); }* 연습 :
* 메소드를 정의하고 emp 테이블의 데이터를 쿼리하고 객체로 캡슐화 한 다음 컬렉션을로드하고 반환합니다.
1. Emp 클래스
정의 2. 메소드 정의 public List <Emp> findAll () {}
3. 메소드 select * from emp;
Emp.java // Emp 테이블 데이터를 캡슐화하는 JavaBean
package cn.itcast.domain;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 封装Emp表数据的JavaBean
*/
public class Emp {
private int id;
private String ename;
private int job_id;
private int mgr;
private Date joindate;
private double salary;
private double bonus;
private int dept_id;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getEname() {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public int getJob_id() {
return job_id;
}
public void setJob_id(int job_id) {
this.job_id = job_id;
}
public int getMgr() {
return mgr;
}
public void setMgr(int mgr) {
this.mgr = mgr;
}
public Date getJoindate() {
return joindate;
}
public void setJoindate(Date joindate) {
this.joindate = joindate;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getDept_id() {
return dept_id;
}
public void setDept_id(int dept_id) {
this.dept_id = dept_id;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", ename='" + ename + '\'' +
", job_id=" + job_id +
", mgr=" + mgr +
", joindate=" + joindate +
", salary=" + salary +
", bonus=" + bonus +
", dept_id=" + dept_id +
'}';
}
}JDBCDemo8.java
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.domain.Emp;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* * 定义一个方法,查询emp表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合,返回。
*/
public class JDBCDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Emp> list = new JDBCDemo8().findAll();
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.size());
for (Emp x : list) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
/**
* 查询所有emp对象
*
* @return
*/
public List<Emp> findAll() {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<Emp> list = null;
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from emp";
//4.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.遍历结果集,封装对象,装载集合
Emp emp = null;
list = new ArrayList<Emp>();
while (rs.next()) {
//获取数据
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String ename = rs.getString("ename");
int job_id = rs.getInt("job_id");
int mgr = rs.getInt("mgr");
Date joindate = rs.getDate("joindate");
double salary = rs.getDouble("salary");
double bonus = rs.getDouble("bonus");
int dept_id = rs.getInt("dept_id");
// 创建emp对象,并赋值
emp = new Emp();
emp.setId(id);
emp.setEname(ename);
emp.setJob_id(job_id);
emp.setMgr(mgr);
emp.setJoindate(joindate);
emp.setSalary(salary);
emp.setBonus(bonus);
emp.setDept_id(dept_id);
//装载集合
list.add(emp);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
}JDBC 도구
JDBC 도구 클래스를 추출하십시오. JDBCUtils
* 목적 : 쓰기 단순화
* 분석 :
1. 드라이버 등록도 추출
2. 연결 개체를 얻기위한 방법 추출
* 요구 사항 : 매개 변수 (문제)를 전달하고 싶지 않지만 도구의 보편성을 보장합니다.
* 솔루션 : 구성 파일
jdbc.properties
url = ...
user = ...
password = ...3. 리소스 해제 방법 추출
* 코드 구현 : ...

Java19-day10 [표준 입력 및 출력 스트림, 바이트 문자 인쇄 스트림, 객체 직렬화-역 직렬화 스트림, serialVersionUID & transient, 속성]
소개
- Map 시스템의 컬렉션 클래스입니다.
- 속성은 스트림에 저장하거나 스트림에서로드 할 수 있습니다.
- 속성 목록의 각 키와 해당 값은 문자열입니다.

package cn.itcast.util;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* JDBC工具类
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String driver;
/**
* 文件的读取,只需要读取一次即可拿到这些值。使用静态代码块
* 静态代码块,随着类的加载而执行(只会执行一次)
*/
static {
//读取资源文件,获取值。
try {
//1. 创建Properties集合类。
Properties pro = new Properties();
//获取src路径下的文件的方式--->ClassLoader 类加载器:加载字节码文件进内存、获取src下资源文件的路径
//获取ClassLoader要先获取其对应的字节码文件对象
ClassLoader classLoader = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader();
//以src为相对的根路径 统一资源定位符URL
URL res = classLoader.getResource("jdbc.properties"); // 传文件名,获取resource资源
String path = res.getPath();
// System.out.println(path);///D:/IdeaProjects/itcast/out/production/day04_jdbc/jdbc.properties
//2. 加载文件
// pro.load(new FileReader("D:\\IdeaProjects\\itcast\\day04_jdbc\\src\\jdbc.properties"));
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
//3. 获取数据,赋值
url = pro.getProperty("url");
user = pro.getProperty("user");
password = pro.getProperty("password");
driver = pro.getProperty("driver");
//4. 注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
*
* @return 连接对象
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
}
/**
* 释放资源
*
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}JDBC practice_login 사례
* 연습 :
* 요구 사항 :
1. 키보드를 통해 사용자 이름과 암호를 입력합니다
. 2. 사용자가 성공적으로 로그인했는지 확인합니다.
* select * from user where username = ""and password = "";
* SQL에있는 경우 쿼리 결과, 성공, 그렇지 않으면 실패* 단계 :
1. 데이터베이스 테이블 생성 사용자
CREATE TABLE USER (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
사용자 이름 VARCHAR (32),
PASSWORD VARCHAR (32)
);사용자 값에 삽입 (NULL, 'zhangsan', '123');
사용자 값에 삽입 (NULL, 'lisi', '234');2. 코드 구현 : ...
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 练习:
* * 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class JDBCDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//2.调用方法 非静态方法,需要创建对象来调用
boolean flag = new JDBCDemo9().login(username, password);
//3.判断结果,输出不同语句
if (flag) {
//登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
/**
* 登录方法
*/
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = '" + username + "' and password = '" + password + "' ";
System.out.println(sql);
//3.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.执行查询
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, stmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
}06 PreparedStatement 클래스 상세 설명
JDBC_PreparedStatement의 각 클래스에 대한 자세한 설명
5. PreparedStatement : SQL을 실행하는 객체
1. SQL 인젝션 문제 : SQL 스 플라이 싱시 SQL의 일부 특수 키워드가 문자열 스 플라이 싱에 참여하여 보안 문제가 발생합니다.
1. 사용자를
아무렇게나 입력하고 암호를 입력하십시오 : a'or'a ' ='a 2. sql : 사용자 이름 = 'fhdsjkf'및 암호 = 'a'또는 ' a'= 'a'에서 * 선택2. SQL 주입 문제 해결 : PreparedStatement 객체를 사용하여 해결
3. 미리 컴파일 된 SQL : 매개 변수 사용?을 자리 표시 자로 사용
4. 단계 :
1. 드라이버 jar 패키지 mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar 가져 오기
2. 등록 드라이버
3. 데이터베이스 연결 개체 연결 가져
오기 4. SQL 정의
* 참고 : SQL의 매개 변수는 무엇입니까? 다음과 같은 자리 표시 자 : select * from user where username =? 및 password =
?; 5. SQL 문 실행을위한 PreparedStatement Connection.prepareStatement (String sql) 개체를 가져옵니다.
6. Give? 할당 :
* 방법 : setXxx (매개 변수 1, 매개 변수 2)
* 매개 변수 1 :? 위치 번호는 1
* 매개 변수 2 :? 값
7. sql 실행, 반환 된 결과 수락, sql 문을 전달할 필요 없음
8. 결과 처리
9. 리소스 해제5. 참고 : PreparedStatement는 추후 추가, 삭제, 수정 및 확인 작업을 모두 완료하기 위해 사용됩니다
. 1. SQL 주입 방지 가능
2.보다 효율적
로그인 케이스-SQL 주입 문제 해결
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 练习:
* * 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class JDBCDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//2.调用方法 非静态方法,需要创建对象来调用
boolean flag = new JDBCDemo9().login(username, password);
//3.判断结果,输出不同语句
if (flag) {
//登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
/**
* 登录方法
*/
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = '" + username + "' and password = '" + password + "' ";
System.out.println(sql);
//3.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.执行查询
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, stmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 登录方法,使用PreparedStatement实现
*/
public boolean login2(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
//3.获取执行sql的对象
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给?赋值
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
//4.执行查询,不需要传递sql
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, pstmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
}어서, 어서, 어서, 난 깨기 보단 죽을 래 ~~~