web容器在启动的时候,它会为每个web程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表了当前的web应用;
特性如下:
1.共享数据
我在这个Servlet中保存的数据,可以在另外一个servlet中拿到;
放置参数:
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//this.getInitParameter();
//this.getServletConfig();
//this.getServletContext(); 上下文
ServletContext context=this.getServletContext();
String username="杨凯波";
context.setAttribute("username",username);
System.out.println("HELLO");
}
}获取参数:
public class GetServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String username = (String) context.getAttribute("username");
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.getWriter().print("姓名"+username);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}web,xml 配置文件
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.yang.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>getc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.yang.servlet.GetServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>getc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/getc</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
2.获取初始化参数
<context-param>
<param-name>url</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis</param-value>
</context-param>
public class ServletDemo03 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String url = context.getInitParameter("url");
resp.getWriter().print(url);
Properties properties = new Properties();
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
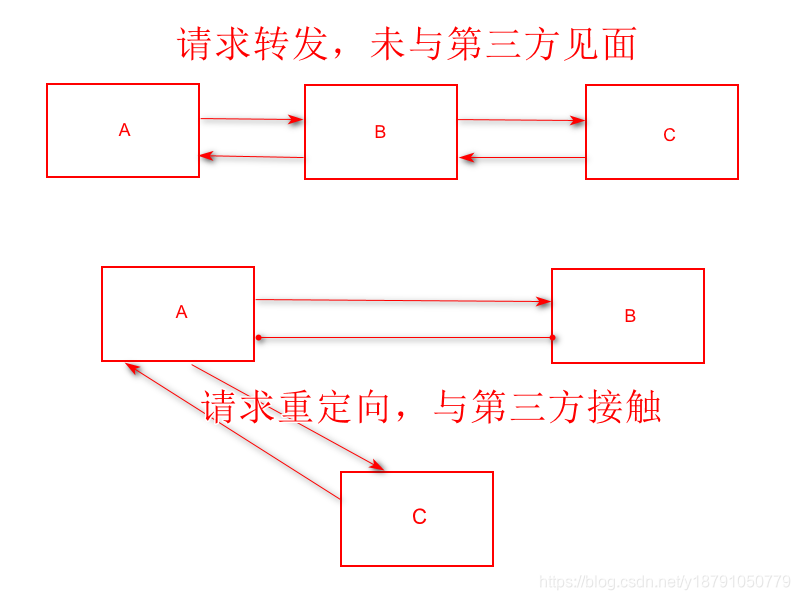
3.请求转发
public class ServletDemo04 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("进入了ServletDemo04");
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
// RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = context.getRequestDispatcher("/gp");
//转发的请求路径
// requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);
//调用forward实现请求转发;
context.getRequestDispatcher("/gp").forward(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
4.读取资源文件
- 新建一个properties文件
username=root password=123456
public class ServerletDemo05 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
InputStream is = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/com/yang/servlet/aa.properties");
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(is);
String user = prop.getProperty("username");
String pwd = prop.getProperty("password");
resp.getWriter().print(user+":"+pwd);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
