1.高阶函数F(x)
lisp语言中有高阶函数的概念,即函数可以作为函数的参数,也可以作为函数的返回值。例如:
(define (f n) (lambda (x) (+ x n)))
定义了一个函数f,该函数的返回值是另一个函数,假定称为g即 (lambda (x) (+ x n) 此函数功能是参数为x,返回值为x + n。 于是 ((f 7) 9) 如下执行
(f 7)以参数7调用f, f的返回值是g,n的值为7
((f 7) 9)等价于 (g 9),即以参数9调用g。 因 n = 7, x = 9 ,因此(g 9)返回值为16
编写一个C++的通用函数模板f,使之能完成类似于lisp函数f的功能。 对于下面的程序,输出结果是
16
world hello!
world!
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
// 在此处补充你的代码
int main()
{
cout << f<int,int>(7)(9) << endl; //16
cout << f<string,string> (" hello!")("world") <<endl; // world hello!
cout << f<char,string> ('!')("world") << endl;
return 0; //world!
}
输入
无
输出
16
world hello!
world!
样例输入
无
样例输出
16 world hello! world!
提示
C++函数模板实例化时,也可以通过在<>中指定类型参数所对应的具体类型来实现。
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 // 在此处补充你的代码 4 5 template<class T1, class T2> 6 class f{ 7 public: 8 T1 a; 9 f(T1 a_):a(a_){} 10 T2 operator()(T2 b){ 11 return b+a; 12 } 13 }; 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 cout << f<int,int>(7)(9) << endl; //16 18 cout << f<string,string> (" hello!")("world") <<endl; // world hello! 19 cout << f<char,string> ('!')("world") << endl; 20 21 return 0; //world! 22 }
2.高阶函数Combine
描述
Lisp语言中有高阶函数的概念,即函数可以作为函数的参数,也可以作为函数的返回值。例如:
(define (square x) (* xx)) 定义了一个求x的平方的函数
(define (inc x) (+ x1)) 定义了一个求x+1的函数
(define (combine f g) (lambda (x) (f (+ (fx) (g x)))))
(combine f g) 返回函数k , k(x) = f( f(x)+g(x))
因此 ((combine square inc) 3) 的返回值就是169
此处
f(x) = x*x g(x) = x + 1
k(x) = (x*x+(x+1)) ^2
((combine square inc) 3) 即是 k(3)
因此返回值为169 用C++实现类似的combine函数模板,使得下面的程序输出结果为
169
10.75
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
// 在此处补充你的代码
int main()
{
auto Square = [] (double a) { return a * a; };
auto Inc = [] (double a) { return a + 1; };
cout << combine<decltype(Square),decltype(Inc),int>(Square,Inc)(3) << endl;
cout << combine<decltype(Inc),decltype(Square),double>(Inc,Square)(2.5) << endl;
return 0;
}
输入
无
输出
169
10.75
样例输入
无
样例输出
169 10.75
提示
C++函数模板实例化时,也可以通过在<>中指定类型参数所对应的具体类型来实现。
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 // 在此处补充你的代码 4 template<class T1, class T2, class T3> 5 class combine{ 6 public: 7 T1 a; T2 b; 8 combine(T1 a_, T2 b_):a(a_),b(b_){} 9 T3 operator()(T3 c){ 10 return a(a(c)+b(c)); 11 } 12 }; 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 auto Square = [] (double a) { return a * a; }; 17 auto Inc = [] (double a) { return a + 1; }; 18 cout << combine<decltype(Square),decltype(Inc),int>(Square,Inc)(3) << endl; 19 cout << combine<decltype(Inc),decltype(Square),double>(Inc,Square)(2.5) << endl; 20 21 return 0; 22 }
这个要注意的就是Square和Inc都是函数指针不是变量orz
3.自己实现bitset
描述程序填空,实现一个类似STL bitset的 MyBitset, 输出指定结果
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
template <int bitNum>
struct MyBitset
{
char a[bitNum/8+1];
MyBitset() { memset(a,0,sizeof(a));};
void Set(int i,int v) {
char & c = a[i/8];
int bp = i % 8;
if( v )
c |= (1 << bp);
else
c &= ~(1 << bp);
}
// 在此处补充你的代码
void Print() {
for(int i = 0;i < bitNum; ++i)
cout << (*this) [i];
cout << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
int n;
int i,j,k,v;
while( cin >> n) {
MyBitset<20> bs;
for(int i = 0;i < n; ++i) {
int t;
cin >> t;
bs.Set(t,1);
}
bs.Print();
cin >> i >> j >> k >> v;
bs[k] = v;
bs[i] = bs[j] = bs[k];
bs.Print();
cin >> i >> j >> k >> v;
bs[k] = v;
(bs[i] = bs[j]) = bs[k];
bs.Print();
}
return 0;
}
输入
多组数据
每组数据:
第一行是整数 n , 1 <= n < 20;
第二行是n个整数 k1,k2... kn,均在范围 [0,19]内。
第三行是 四个整数 i1,j1,k1,v1 。 0 <= i1,j1,k1 <= 19, v1值为0或1
第三行是 四个整数 i2,j2,k2,v2 。 0 <= i2,j2,k2 <= 19, v2值为0或1
输出
对每组数据,共输出3行,每行20位,每位为1或者0。最左边称为第0位
第一行: 第 k1,k2 ... kn位为1,其余位为0。
第二行: 将第一行中的第 i1,j1,k1位变为 v1,其余位不变
第三行: 将第二行中的第i2位和k2位变为v2,其余位不变
样例输入
4 0 1 2 8 7 19 0 1 7 2 8 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
样例输出
11100000100000000000 11100001100000000001 11100000000000000001 01000000000000000000 00000000000000000000 01000000000000000000
提示
推荐使用内部类,内部类中使用引用成员。引用成员要在构造函数中初始化。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 template <int bitNum> //函数模板还可以这么用 5 struct MyBitset 6 { 7 char a[bitNum/8+1]; 8 MyBitset() { memset(a,0,sizeof(a));}; 9 void Set(int i,int v) { 10 char & c = a[i/8]; 11 int bp = i % 8; 12 if( v ) 13 c |= (1 << bp); //这里改变的是右数第几位 14 else 15 c &= ~(1 << bp); 16 } 17 // 在此处补充你的代码 18 int bitt[20]; 19 bool flag = false; //用来记录字符串是否已经被转化成数组过 20 void transform(){ 21 memset(bitt,0,sizeof(bitt));//注意清零 22 for(int i = 0; i <= bitNum/8+1;i++){ //将第i个字节转为二进制 23 int temp = i*8; 24 int num = (unsigned char)(a[i]); 25 while(num>0){ //这里就不用逆序了 26 if(num%2) 27 bitt[temp]++; 28 temp++; 29 num/=2; 30 } 31 } 32 flag = true; 33 } 34 int & operator[](int x){ 35 if(!flag) transform(); 36 return bitt[x]; 37 } 38 39 void Print() { 40 for(int i = 0;i < bitNum; ++i) 41 cout << (*this) [i]; 42 cout << endl; 43 } 44 45 }; 46 47 int main() 48 { 49 int n; 50 int i,j,k,v; 51 while( cin >> n) { 52 MyBitset<20> bs; 53 for(int i = 0;i < n; ++i) { 54 int t; 55 cin >> t; 56 bs.Set(t,1); 57 } 58 bs.Print(); 59 cin >> i >> j >> k >> v; 60 bs[k] = v; //重载中括号 61 bs[i] = bs[j] = bs[k]; 62 bs.Print(); 63 cin >> i >> j >> k >> v; 64 bs[k] = v; 65 (bs[i] = bs[j]) = bs[k]; 66 bs.Print(); 67 } 68 return 0; 69 }
嗷我又参考网上题解了,然后我发现像他一样写成那种内部类没有啥意义,就改成了现在这样。要注意的是标黄那一行,要先强转成unsigned char再传给int!要不然就会出现符号位的问题。这是我请教了学弟才明白的结果orz但其实这种方法一看就不是正解,因为相当于用了int数组来存,本来的char数组就废了。
但其实这道题正经的思路是:
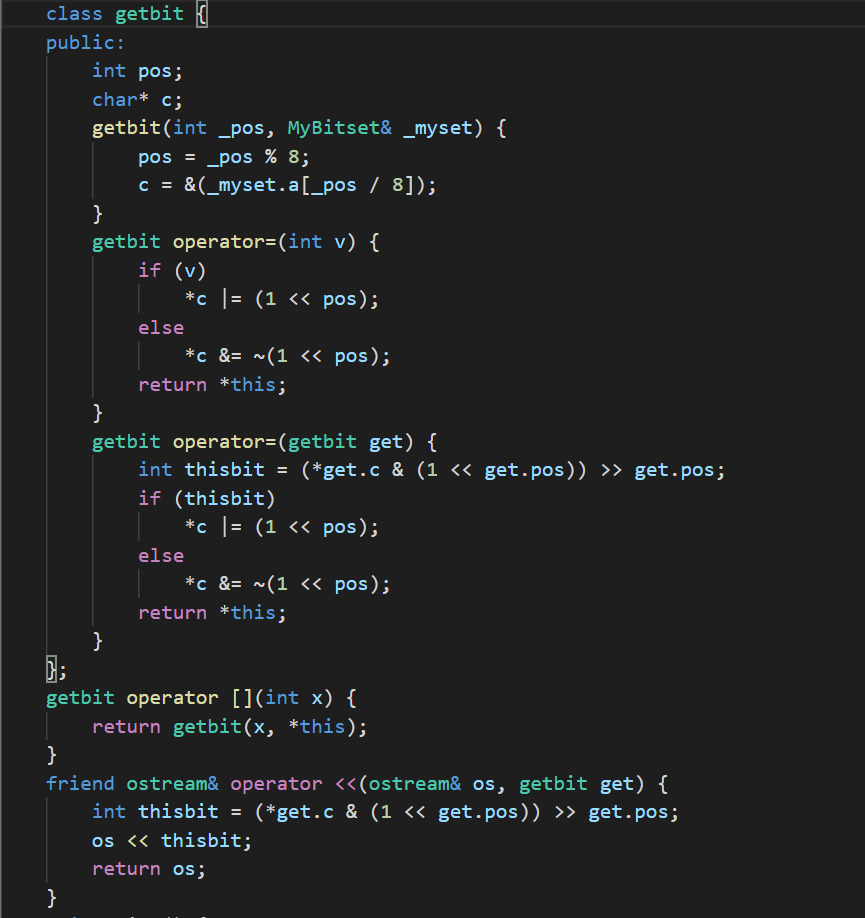
附上学弟的话:如果要在原来的类里直接重载[]的话需要返回一个那个位的引用,mybitset里只有两个char型,不太方便,所以可以再写一个类来代替每一位。思路就是用一个内部类来代替每一位达到用=修改的目的。