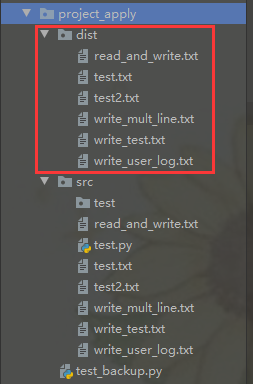
写在前面:只备份.txt文件,以下图片显示src包下的内容,其中test文件与test.py文件都不会被备份

备份文件代码:
import os
class FileBackup(object):
"""
文本文件备份
"""
def __init__(self, src, dist):
"""
构造方法
:param src: 目录 需要备份的文件目录
:param dist: 目录 备份后的文件目录
"""
self.src = src
self.dist = dist
def read_files(self):
"""读取src下的所有文件"""
ls = os.listdir(self.src)
print(ls)
for l in ls:
# 循环处理每一个文件夹
self.backup_files2(l)
def backup_files(self, file_name):
"""
处理备份
:param file_name: 文件/文件夹名称的名称
"""
# 1. 先判断dist是否存在,若不存在,创建这个目录
if not os.path.exists(self.dist):
os.makedirs(self.dist)
print("指定的目录不存在,已创建完成")
# 2. 判断文件是否为我们要备份的文件
# 拼接文件的完整路径
full_src_path = os.path.join(self.src, file_name)
full_dist_path = os.path.join(self.dist, file_name)
# 首先要判断是否为文件夹,再根据文件的后缀名进行判断
if os.path.isfile(full_src_path) and os.path.splitext(full_src_path)[-1].lower() == '.txt':
# 3. 读取文件内容,r表示只读,w表示只写
with open(full_dist_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f_dist:
print(">>开始备份【{0}】".format(file_name))
with open(full_src_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_src:
while True:
rest = f_src.read(100)
if not rest:
break
# 4. 把读取到的内容写到新的文件中
f_dist.write(rest)
f_dist.flush()
print("【{0}】备份完成".format(file_name))
else:
print("文件不符合备份类型,跳过>>")
def backup_files2(self, file_name):
"""
处理备份-优化
:param file_name: 文件/文件夹名称的名称
"""
# 1. 先判断dist是否存在,若不存在,创建这个目录
if not os.path.exists(self.dist):
os.makedirs(self.dist)
print("指定的目录不存在,已创建完成")
# 2. 判断文件是否为我们要备份的文件
# 拼接文件的完整路径
full_src_path = os.path.join(self.src, file_name)
full_dist_path = os.path.join(self.dist, file_name)
# 首先要判断是否为文件,再根据文件的后缀名进行判断
if os.path.isfile(full_src_path) and os.path.splitext(full_src_path)[-1].lower() == '.txt':
# 3. 读取文件内容
with open(full_dist_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f_dist,\
open(full_src_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_src:
print(">>开始备份【{0}】".format(file_name))
while True:
rest = f_src.read(100)
if not rest:
break
# 4. 把读取到的内容写到新的文件中
f_dist.write(rest)
f_dist.flush() # 将剩余的读取
print("【{0}】备份完成".format(file_name))
else:
print("文件不符合备份类型,跳过>>")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# # 要备份的文件目录地址
# src_path = "F:\\Code\\Python\\Step01\\Chapter02\\project_apply\\src"
# # 备份后的目录地址
# dist_path = "F:\\Code\Python\\Step01\\Chapter02\\project_apply\\dist"
# 要备份的文件目录地址
base_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
# base_path = "F:\\Code\Python\\Step01\\Chapter02\\project_apply"
src_path = os.path.join(base_path, 'src')
# src_path = "F:\\Code\\Python\\Step01\\Chapter02\\project_apply\\src"
# 备份后的目录地址
dist_path = os.path.join(base_path, 'dist')
# dist_path = "F:\\Code\Python\\Step01\\Chapter02\\project_apply\\dist"
back = FileBackup(src_path, dist_path)
back.read_files()
运行截图:
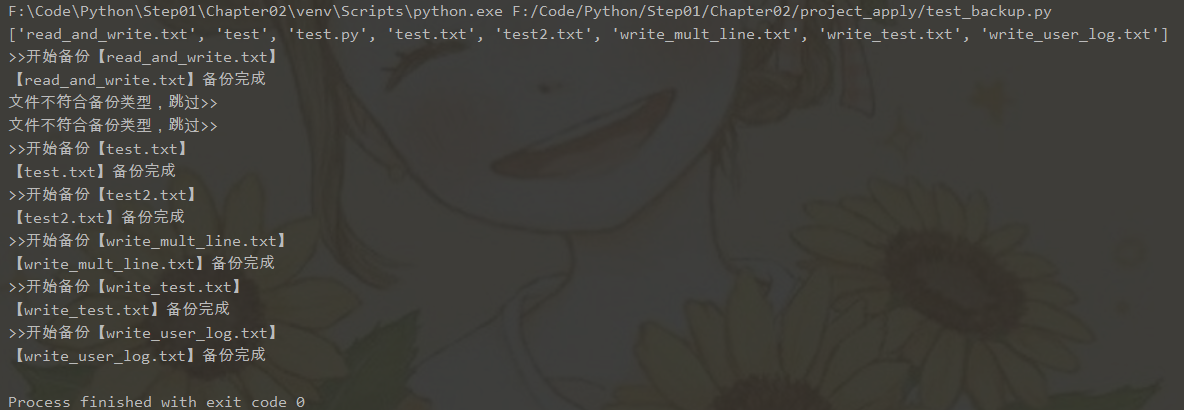
备份完成,且都只备份了 .txt 文件,以下是项目截图: