sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp)
- sort的区间范围为[first,last),默认的排序方式是升序
- 第三个参数存在,则按照自定义的cmp排序方式
sort 的案例1:
// sort algorithm example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::sort
#include <vector> // std::vector
bool myfunction (int i,int j) { return (i<j); } //系统中定义了 “<” 的数据类型,如 int string
struct myclass {
bool operator() (int i,int j) { return (i<j);} //未定义 “<” 的数据类型(自定义的class或struct)
} myobject;
int main () {
int myints[] = {32,71,12,45,26,80,53,33};
std::vector<int> myvector (myints, myints+8); // 32 71 12 45 26 80 53 33
// using default comparison (operator <):
std::sort (myvector.begin(), myvector.begin()+4); //(12 32 45 71)26 80 53 33
// using function as comp
std::sort (myvector.begin()+4, myvector.end(), myfunction); // 12 32 45 71(26 33 53 80)
// using object as comp
std::sort (myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), myobject); //(12 26 32 33 45 53 71 80)
// print out content:
std::cout << "myvector contains:";
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it=myvector.begin(); it!=myvector.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
sort的案例1中对未定义 “<”的详解(自定义的class 、struct)
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int grade;
char name[101];
int age;
//student(int Grade ,string Name, int Age):grade(Grade),name(Name),age(Age){}
}stu[101];
bool cmp(student a,student b)//定义比较规则
{
int temp = strcmp(a.name,b.name);
if(a.grade!=b.grade)
return a.grade<b.grade; //升序
else if(temp != 0)//升序 ,要做是否相等的判断
return temp<0; //此处一定要用 TEMP < 0 返回,否侧会出错,原因未知
else
return a.age < b.age;//升序
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>stu[i].name>>stu[i].age>>stu[i].grade;
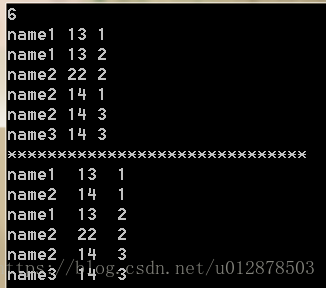
sort(stu,stu+n,cmp);
cout<<"******************************"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<stu[i].name<<" "<< stu[i].age<<" "<< stu[i].grade<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
- 定义一个Person,将所有不重复的学生按照年龄进行排序
1.自定义set,保证不重复
2.年龄做一个比较器,将set中元素按照年龄排序
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> //无此头文件,应输出为str.c_str
#include <set>
#include<string>
using namespace std ;
struct Person{
int age;
double sd;
string name; // char name[20];-> Person(int Age , const char Name[]):age(Age){strcpy(name,Name);}
Person(int Age ,double SD, string Name):age(Age),sd(SD),name(Name){} //{}不可省略
};
struct cmp{
bool operator ()(const Person a , const Person b)
{
return a.age < b.age ; // 从小到大 ;
}
};
int main()
{
set<Person,cmp> s ;
set<Person> s1 ; //可定义,但在插入时,没有比较函数,无法排序,报错
Person n1(46, 12.3, "ggg"); //数据类型应按照定义时的顺序,struct非顺序插入,否则报错
Person n2(-16,12.3, "fff"); //年龄无负数,只是为了测试代码,下同
Person n3(45,15.6, "eee");
Person n4(-25,14.6, "ddd");
Person n5(34,12.5, "ccc");
Person n6(22,18.4, "bbb");
Person n7(2,14.5, "aaa");
s.insert(n1);
s.insert(n2);
s.insert(n3);
s.insert(n4);
s.insert(n5);
s.insert(n6);
s.insert(n7);
//s1.insert(n1); //可定义,但在插入时,没有比较函数,无法排序,报错
for(set<Person,cmp>::iterator i =s.begin() ; i != s.end() ; ++i) //auto i 也可
{
cout<<i->age<<" "<<i->name<<endl ;
}
system("pause");
return 0 ;
} 比较器优秀文章:
C++排序函数中cmp()比较函数详解