本文简单总结下java NIO相关内容及使用demo。
使用NIO完成网路通信的3个核心:
- 通道 Channel,负责连接,类似火车轨道;
- 缓冲区 Buffer,负责数据存取,类似火车车厢;
- 选择器 Selector,是SelectableChannel的多路复用器,用于监控SelectableChannel的IO状况。
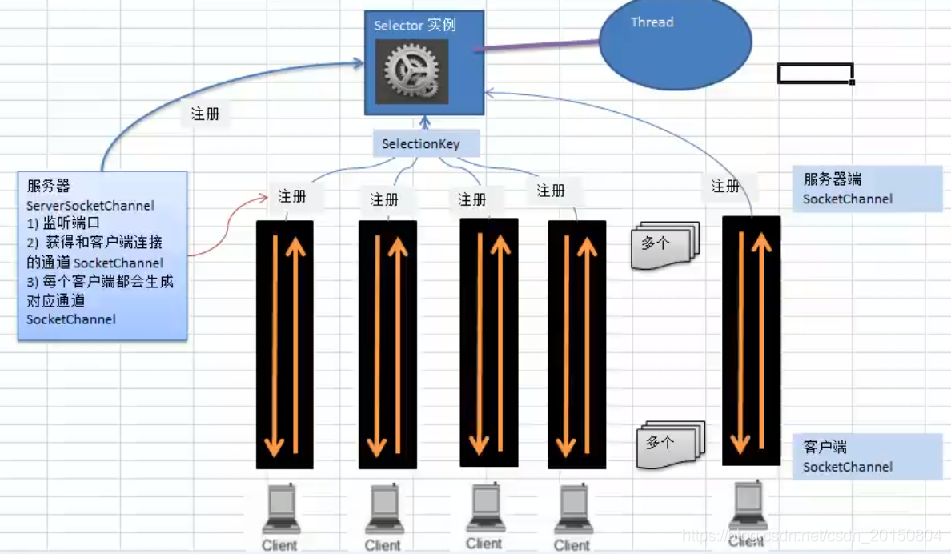
下面是demo,两个方法分别模拟客户端和服务端,客户端向服务端发送信息。
public class TestNonBlockingNIO {
@Test
public void client() {
try {
//1.获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8989));
//2.切换为非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//4.随便发送数据(当前日期)到服务器端
buf.put(new Date().toString().getBytes());
//反转缓冲区为读取模式
buf.flip();
//把buf中的数据弄到channel中传输
sChannel.write(buf);
//清空缓冲区
buf.clear();
//5.关闭通道
sChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void server() {
try {
//1.获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.切换为非阻塞模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8989));
//4.获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5.将通道注册到选择器上
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//6.轮询选择器上已经 准备就绪 的事件
while (selector.select() > 0) {
//7.获取当前选择器上注册的选择键,也就是已就绪的监听事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
//8.获取准备就绪的事件
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
//9.判断具体是什么事件准备就绪
if (sk.isAcceptable()) {
//10.若是 接收就绪,则获取客户端连接
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept();
//11.设置为非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//12.将通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (sk.isReadable()) {
//13.获取当前选择器上 读就绪的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel();
//14.读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = 0;
while ((len = sChannel.read(buf)) > 0) {
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
buf.clear();
}
}
//15.取消选择键
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
说明:
客户端:
1.首先通过SocketChannel与目标ip和端口建立管道连接;并注意设置为非阻塞模式;
2.接着创建一个缓冲区,并往里添加数据,类似往火车车厢装货;然后把buf设置为读取数据模式,也就是由装货模式改为卸货模式,因为通过管道运送到目的地后,需要卸货;
3.最后清空缓冲区位置标记,关闭管道。
服务端:
1.服务端使用ServerSocketChannel监听端口;
2.因为是非阻塞模式,使用Selector选择器,并将管道注册到其中;
3.接下来需要不停轮询选择器,拿到准备就绪的事件,然后遍历,并根据不同的事件状态,相应做不同的处理。
注意:拿到事件后,针对具体的事件状态,可以使用异步线程处理,提升处理性能;
