在Java项目的实际开发和应用中,常常需要用到将对象转为String这一基本功能。本文将对常用的转换方法进行一个总结。
常用的方法有(String)要转换的对象,Object#toString(),String.valueOf(Object)等。
(String)
- 这是标准的类型转换,将object转成String类型的值。使用这种方法时,需要注意的是类型必须能转成String类型。因此最好用instanceof做个类型检查,以判断是否可以转换。否则容易抛出CalssCastException异常。此外,需特别小心的是因定义为Object 类型的对象在转成String时语法检查并不会报错,这将可能导致潜在的错误存在。这时要格外小心。如:
12
Object obj =newInteger(100);String strVal = (String)obj;
在运行时将会出错,因为将Integer类型强制转换为String类型,无法通过。

- toString
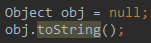
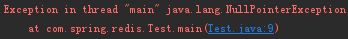
- 在这种使用方法中,因为java.lang.Object类里已有public方法.toString(),所以对任何严格意义上的java对象都可以调用此方法。但在使用时要注意,必须保证object不是null值,否则将抛出NullPointerException异常。采用这种方法时,通常派生类会覆盖Object里的toString()方法。
- String.valueOf
- 这个方法是静态的,直接通过String调用,可以说是完美,只是平时不习惯这样写而已,这样的实现避免了前面两个的不足和缺点。首先来看看他内部的实现机制:
123
publicstaticString valueOf(Object obj){return(obj==null) ?"null": obj.toString()};在内部就是做了为空的判断的,所以就不会报出空指针异常。
从上面的源码可以很清晰的看出null值不用担心的理由。但是,这也恰恰给了我们隐患。我们应当注意到,当object为null 时,String.valueOf(object)的值是字符串”null”,而不是null!!!在使用过程中切记要注意。
试想一下,如果我们用
123if(String.valueOf(object)==null){System.out.println(“传入的值是null!”);}这样的语句将可能会发生什么问题。再想一下,向控制台输出时,在视觉上如下语句在执行的结果上有什么不同:
Object obj = null;
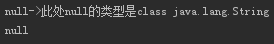
System.out.println(String.valueOf(obj) + "->此处null的类型是" + String.valueOf(obj).getClass());
System.out.println(obj);我们看到的输出将是一模一样的东西:null,但它们意义相同吗?
java里,所有的类,不管是java库里面的类,或者是你自己创建的类,全部是从object这个类继承的。object里有一个方法就是toString(),那么所有的类创建的时候,都有一个toString的方法。
这个方法是干什么的呢?
首先我们得了解,java输出用的函数print();是不接受对象直接输出的,只接受字符串或者数字之类的输出。那么你想把一个创建好的对象拿来输出怎么办?例如:
package com.spring.h3; public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("new Test2()==="+new Test2()); //输出结果为:new Test2()===com.spring.h3.Test2@18a992f } }
按照print接受的类型来说,s1是不能直接输出的,那么是否代表这个是不能编译运行的呢?当然不是。因为当print检测到输出的是一个对象而不是字符或者数字时,那么它会去调用这个对象类里面的toString 方法,输出结果为[类型@哈希值]。Object类中的toString()方法的源代码如下:
/** * Returns a string representation of the object. In general, the * <code>toString</code> method returns a string that * "textually represents" this object. The result should * be a concise but informative representation that is easy for a * person to read. * It is recommended that all subclasses override this method. * <p> * The <code>toString</code> method for class <code>Object</code> * returns a string consisting of the name of the class of which the * object is an instance, the at-sign character `<code>@</code>', and * the unsigned hexadecimal representation of the hash code of the * object. In other words, this method returns a string equal to the * value of: * <blockquote> * <pre> * getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()) * </pre></blockquote> * * @return a string representation of the object. */ public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()); }
而数组类中并没有对此方法重写(override),仅仅是重载(overload)为类的静态方法(参见java.util.Arrays)。所以,数组直接使用toString()的结果也是[类型@哈希值]。
所以数组转为字符串应写成:
Arrays.toString(a)
这种方法的toString()是带格式的,也就是说输出的是[a, b, c],如果仅仅想输出abc则需用以下两种方法:
方法1:直接在构造String时转换。
char[] data = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; String str = new String(data);
方法2:调用String类的方法转换。
String.valueOf(char[] ch)
