每日一句:人生犹如一本书,愚蠢者草草翻过,聪明人细细阅读。为何如此。因为他们只能读它一次。
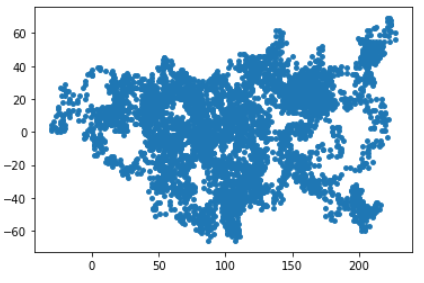
# 创建RandomWalk类 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """一个生成随机漫步数据的表""" def __init__(self,num_points=5000): """初始化随机漫步的属性""" self.num_points=num_points # 所有随机漫步都始于(0,0) self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): """计算随机漫步包含的所有点""" # 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度 while len(self.x_values) <self.num_points: # 决定前进方向以及沿着个方向前进的距离 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction * y_distance # 拒绝原地踏步 if x_step==0 and y_step==0: continue # 计算下一个点的x和y值 next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) # from random_walk import RandomWalk rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) plt.show()
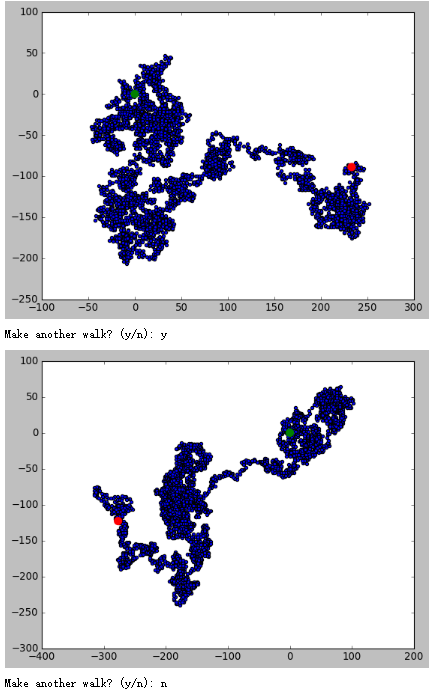
# 创建RandomWalk类 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """一个生成随机漫步数据的表""" def __init__(self,num_points=5000): """初始化随机漫步的属性""" self.num_points=num_points # 所有随机漫步都始于(0,0) self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): """计算随机漫步包含的所有点""" # 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度 while len(self.x_values) <self.num_points: # 决定前进方向以及沿着个方向前进的距离 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction * y_distance # 拒绝原地踏步 if x_step==0 and y_step==0: continue # 计算下一个点的x和y值 next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) while True: # from random_walk import RandomWalk # 创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都会指出来 rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break

# 创建RandomWalk类 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """一个生成随机漫步数据的表""" def __init__(self,num_points=5000): """初始化随机漫步的属性""" self.num_points=num_points # 所有随机漫步都始于(0,0) self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): """计算随机漫步包含的所有点""" # 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度 while len(self.x_values) <self.num_points: # 决定前进方向以及沿着个方向前进的距离 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction * y_distance # 拒绝原地踏步 if x_step==0 and y_step==0: continue # 计算下一个点的x和y值 next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) while True: # from random_walk import RandomWalk # 创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都会指出来 rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values, rw.y_values, c=point_numbers, cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolors='none', s=15) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break
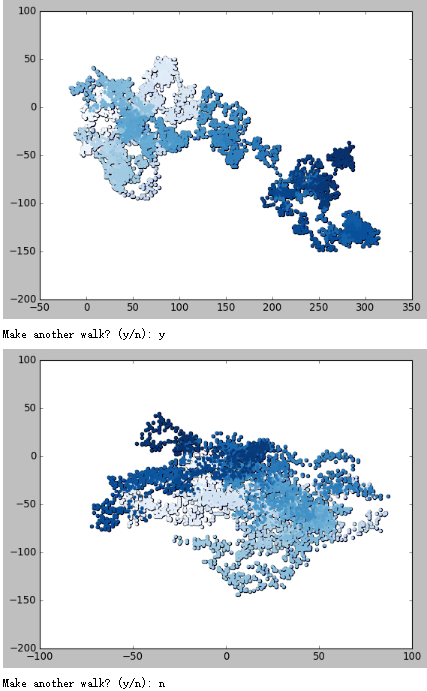
# 创建RandomWalk类 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """一个生成随机漫步数据的表""" def __init__(self,num_points=5000): """初始化随机漫步的属性""" self.num_points=num_points # 所有随机漫步都始于(0,0) self.x_values=[0] self.y_values=[0] def fill_walk(self): """计算随机漫步包含的所有点""" # 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度 while len(self.x_values) <self.num_points: # 决定前进方向以及沿着个方向前进的距离 x_direction = choice([1,-1]) x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) x_step=x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1,-1]) y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4]) y_step=y_direction * y_distance # 拒绝原地踏步 if x_step==0 and y_step==0: continue # 计算下一个点的x和y值 next_x=self.x_values[-1]+x_step next_y=self.y_values[-1]+y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y) while True: # from random_walk import RandomWalk # 创建一个RandomWalk实例,并将其包含的点都会指出来 rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) point_numbers = list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolors='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1], rw.y_values[-1], c='red', edgecolors='none', s=100) plt.show() keep_running = input("Make another walk? (y/n): ") if keep_running == 'n': break