一、简介
setup和teardown是每次用例开始前和结束后都去执行一次。
更高级一点的,setupClass和teardownClass,需要配合@classmethod装饰器一起使用,在做selenium自动化的时候,它的效率尤为突出,可以只启动一次浏览器执行多个用例。
pytest框架也有类似于setup和teardown的语法,并且还不只这四个。
二、用例运行级别
1.模块级(setup_module/teardown_module)开始于模块始末,全局的;
2.函数级(setup_function/teardown_function)只对函数用例生效(不在类中);
3.类级(setup_class/teardown_class)只在类中前后运行一次(在类中);
4.方法级(setup_method/teardown_method)开始于方法始末(在类中);
5.类里面的(setup/teardown)运行在调用方法的前后。
三、函数级
1.setup_function/teardown_function(每个用例开始和结束时调用一次)
(1)代码实现
import pytest def setup_function(): print("setup_function: 每个用例开始前都会执行") def teardown_function(): print("teardown_function: 每个用例结束后都会执行") def test_one(): print("正在执行----test_one") x = "this" assert 'h' in x def test_two(): print("正在执行----test_two") x = "hello" assert hasattr(x, 'check') def test_three(): print("正在执行----test_three") a = "hello" b = "hello world" assert a in b if __name__ == "__main__": pytest.main(["-s", "test_fixt.py"])
(2)运行结果
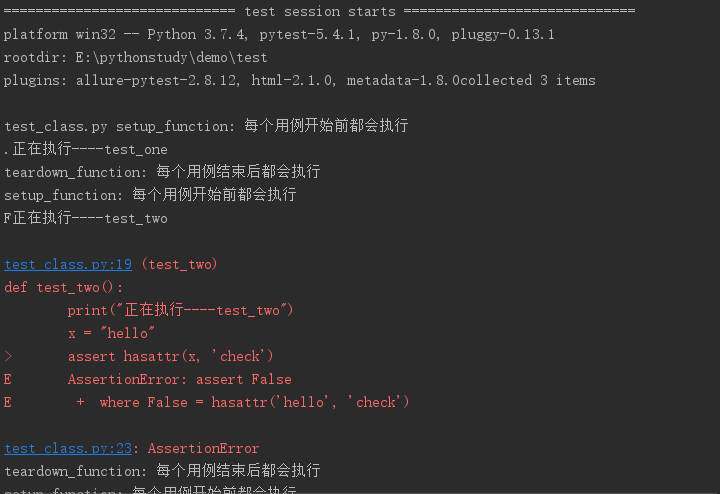
2.setup_module/teardown_module(所有用例开始和结束时调用一次)
(1)代码实现
import pytest def setup_module(): print("setup_module: 整个.py模块只执行一次") print("比如:所有用例开始前只打开一次浏览器") def teardown_module(): print("teardown_module: 整个.py模块只执行一次") print("比如:所有用例开始前只最后关闭浏览器") def setup_function(): print("setup_function: 每个用例开始前都会执行") def teardown_function(): print("teardown_function: 每个用例结束前都会执行") def test_one(): print("正在执行----test_one") x = "this" assert 'h' in x def test_two(): print("正在执行----test_two") x = "hello" assert hasattr(x,'check') def test_three(): print("正在执行----test_three") a = "hello" b = "hello world" assert a in b if __name__ == "__main__": pytest.main(["-s","test_module.py"])
(2)运行结果

3.类和方法
(1)setup/teardown和unittest里面的setup/teardown是一样的功能,setup_class和teardown_class等价于unittest里面的setupClass和teardownClass
(2)代码实现
import pytest class TestClass: def setup(self): print("setup: 每个用例开始前执行") def teardown(self): print("teardown: 每个用例结束后执行") def setup_class(self): print("setup_class: 所有用例执行之前") def teardown_class(self): print("teardown_class: 所有用例结束后执行") def setup_method(self): print("setup_method: 每个用例开始前执行") def teardown_method(self): print("teardown_method: 每个用例结束后执行") def test_one(self): print("正在执行----test_one") x = "this" assert 'h' in x def test_two(self): print("正在执行----test_two") x = "hello" assert hasattr(x,'check') def test_three(self): print("正在执行----test_three") a = "hello" b = "hello world" assert a in b if __name__ == "__main__": pytest.main(["-s","test_class.py"])
(3)运行结果
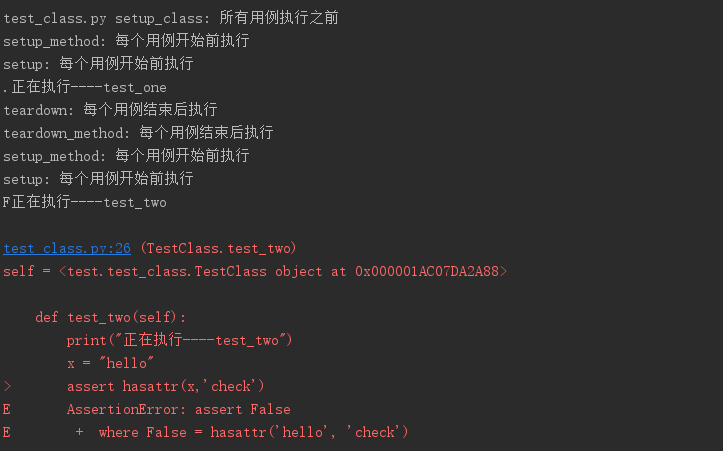
ps:这里setup_method和teardown_method的功能和setup/teardown功能是一样的,一般两者用其中一个即可。
4.函数和类混合
(1)如果一个.py的文件里面既有函数用例又有类和方法用例,运行顺序又是怎么样的呢?
(2)代码实现
import pytest def setup_module(): print("setup_module: 整个.py模块只执行一次") print("比如:所有用例结束只最后关闭浏览器") def teardown_module(): print("teardown_module:整个.py模块只执行一次") print("比如:所有用例结束后只最后关闭浏览器") def setup_function(): print("setup_function: 每个用例开始前都会执行") def teardown_function(): print("teardown_function: 每个用例结束前都会执行") def test_one(): print("正在执行----test_one") x = "this" assert 'h' in x def test_two(): print("正在执行----test_two") x = "hello" assert hasattr(x,'check') class TestCase(): def setup_class(self): print("setup_class: 所有用例执行之前") def teardown_class(self): print("teardown_class:所有用例执行之后") def test_three(self): print("正在执行----test_three") x = "this" assert 'h' in x def test_four(self): print("正在执行----test_four") x = "hello" assert hasattr(x,'check') if __name__ == "__main__": pytest.main(["-s","test_f+c.py"])
(3)运行结果

从结果看错,setup_module/teardown_module的优先级是最大的,然后函数里面用到的setup_function/teardown_function与类里面的setup_class/teardown_class互补干涉
参考文章:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/basmOut7Lq2RLO2ICkmslA