【AOP系列】后端登录这样写才香
文章目录
在日常开发过程中,基本很多接口都会通过token的方式来检测当前用户的登录状态。
只有登录过的用户才能正常访问接口。
一方面可以防止接口的恶意调用,
另一方面可以省去前端每次请求接口时 可以省略userId字段。
后端直接从userId即可。
那么一个好的登录到底应该怎么写呢?
依赖
<!--java-jwt TokenUtil类依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.auth0</groupId>
<artifactId>java-jwt</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot-aop LoginAspect类依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
工具类
TokenUtil.java
import com.auth0.jwt.JWT;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWTCreator;
import com.auth0.jwt.JWTVerifier;
import com.auth0.jwt.algorithms.Algorithm;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.JWTDecodeException;
import com.auth0.jwt.exceptions.TokenExpiredException;
import com.auth0.jwt.interfaces.DecodedJWT;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @ IDE :IntelliJ IDEA.
* @ Author :大火yzs
* @ Date :2019/9/27 16:44
* @ Desc :简单的token工具类
*
依赖:com.auth0.java.jwt
<dependency>
<groupId>com.auth0</groupId>
<artifactId>java-jwt</artifactId>
<version>3.4.0</version>
</dependency>
*/
public class TokenUtil {
private static final String SECRET = "SECRET"; //加密时用到的key
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TokenUtil.class);
/**
* 时间常量 单位秒
*/
public static final int ONE_DAY_EXPIRE = 86400; //1天
public static final int ONE_WEEK_EXPIRE = 604800; //7天
public static final int ONE_MONTH_EXPIRE = 2592000; //30天
public static final int THREE_MONTH_EXPIRE = 7776000; //90天
/**
* 根据一个字符串生成token 有效期默认7天
* @param data 要生成token的附带信息
* @return String 返回token
*/
public static String createToken(Object data) {
return createToken(data,ONE_WEEK_EXPIRE);
}
/**
* 根据一个字符串生成token
* @param data 要生成token的附带信息
* @param expire 有效期时间 单位秒
* @return String 返回token
*/
public static String createToken(Object data, int expire) {
Date expireDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + expire*1000);
JWTCreator.Builder builder = JWT.create()
.withExpiresAt(expireDate)
.withClaim("data",data.toString())
.withClaim("alg", "HS256")
.withClaim("typ", "JWT")
.withClaim("isExpired","false");
return builder.sign(Algorithm.HMAC256(SECRET));
//使用上面的加密算法进行签名,返回String,就是token
}
/**
* 根据token解码出原字符串
* @param token 要解码的token
* @return String 返回原字符串信息
*/
public static String verifyToken(String token) {
try{
JWTVerifier verifier = JWT.require(Algorithm.HMAC256(SECRET)).build();
DecodedJWT jwt = verifier.verify(token);
return jwt.getClaims().get("data").asString();
}catch (TokenExpiredException e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("token失效,请重新授权");
}catch (JWTDecodeException e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("token错误,请重新授权");
}
}
/**
* 根据token解码出原信息,并转换成Long类型
* @param token 要解码的token
* @return Long 返回Long类型的原信息
*/
public static Long getId(String token) {
return Long.valueOf(verifyToken(token));
}
/**
* 校验token是否失效
* @param token 要校验的token
* @return boolean 返回是否失效 true失效,false有效
*/
public static boolean isTokenExpired(String token) {
try{
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.HMAC256(SECRET);
JWTVerifier verifier = JWT.require(algorithm).build();
DecodedJWT jwt = verifier.verify(token);
return false;
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error(Console.where() + e.getMessage());
return true;
}
}
}
登陆时主要通过TokenUtil来根据userId生成token
调用接口时需要校验token,并且从token中获取userId
为了方便接口的管理,我们通过两个注解来管理接口的登录检测
登录注解开发
@CheckLogin
可以用在类上,也可以用在方法上,
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @ IDE :IntelliJ IDEA.
* @ Author :大火yzs
* @ Date :2019/11/6 9:20
* @ Desc : APP接口登录校验注解
* @see IgnoreLogin
* @see LoginAspect
* 可用在方法上或者类上
* 如果用方法上,则该方法必须登录才能访问。
* 如果使用类上,则该类中的所有方法都必须登录才能访问。
* 如果有Ignore注解。则此注解不生效。
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CheckLogin {
}
/**
* 案例:
* @RestController
* class UserController{
* @CheckLogin
* @GetMapping("/get/user/sex")
* public String getUserSex(Long id){
* return userService.findById(id).getSex();
* }
* @GetMapping("/get/user/age")
* public String getUserAge(Long id){
* return userService.findById(id).getAge();;
* }
* }
* 请求/get/user/sex 需要登录权限
* 请求/get/user/age 不需要登录权限
* @CheckLogin
* @RestController
* class UserController{
* }
* 该类所有接口都需要登录权限
* @CheckLogin
* @RestController
* class UserController{
* @GetMapping("/get/user/sex")
* public String getUserSex(Long id){
* return userService.findById(id).getSex();
* }
* @IgnoreLogin
* @GetMapping("/get/user/age")
* public String getUserAge(Long id){
* return userService.findById(id).getAge();;
* }
* }
* 请求/get/user/sex 需要登录权限
* 请求/get/user/age 不需要登录权限
*
* */
@IgnoreLogin
主要用在方法上
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @ IDE :IntelliJ IDEA.
* @ Author :大火yzs
* @ Date :2019/12/18 15:56
* @ Desc :忽略登录注解
* @see CheckLogin
* @see LoginAspect
* 当@APPLogin注解在类上的时候,可以使用该注解取消需要校验的接口
* 只能用在方法上,优先级高于AppLogin注解。
* 一般在类上使用了AppLogin注解时 才使用该注解来取消不用校验登录的方法。
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface IgnoreLogin {
}
注解的实现
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @ IDE :IntelliJ IDEA.
* @ Author :大火yzs
* @ Date :2019/11/6 9:30
* @ Desc : 拦截App请求接口校验是否登录
* @see CheckLogin
* @see IgnoreLogin
*/
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoginAspect {
/**
* 获取请求中的token头,如果没有提示非法token
*/
@Around("execution(* com.【包名】.controller.*.*(..))")//拦截controller包下所有方法
public Object methodAspect(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Method method = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod();
CheckLogin onClass = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getAnnotation(CheckLogin.class); //获取类上是否有AppLogin注解
CheckLogin onMethod = method.getAnnotation(CheckLogin.class); //获取方法上是否有AppLogin注解
IgnoreLogin Ignore = method.getAnnotation(IgnoreLogin.class); //获取方法上是否有IgnoreLogin注解
Boolean checkLogin = Ignore == null && (onClass != null || onMethod != null); // 条件 没有Ignore注解。 类上或者方法上有注解
if (checkLogin){
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
String token = request.getHeader("token");
if (token==null||token.isEmpty()){
return Result.getCodeResult(401,"缺少token");
}
Long userId = TokenUtil.getId(token);
request.setAttribute("userId",userId);//将用户id存在request中
// log.debug("CheckToken|userId:{}|token:{}",userId,token);
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
public static Long getCurrUserId(){
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
return (Long) request.getAttribute("userId");
}
}
注解的使用
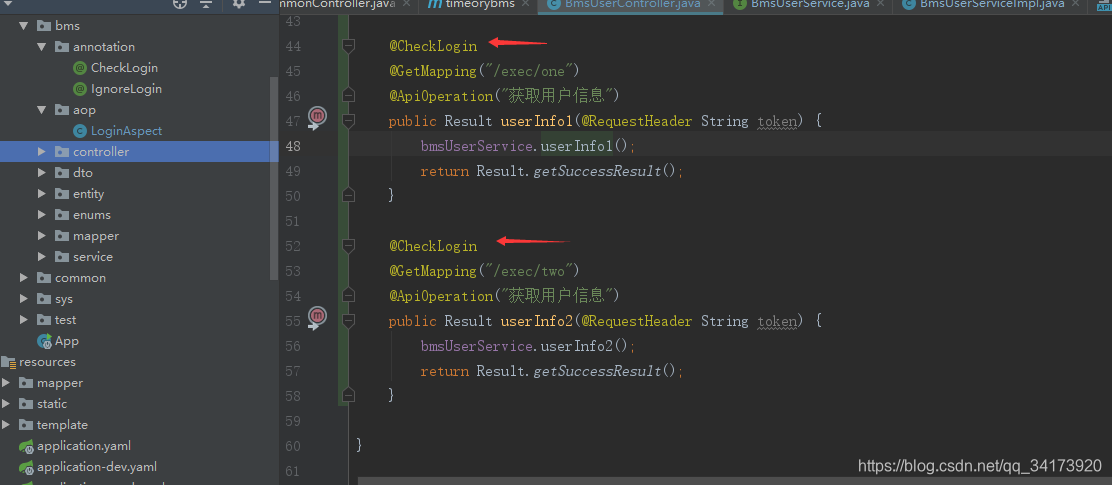
token的校验
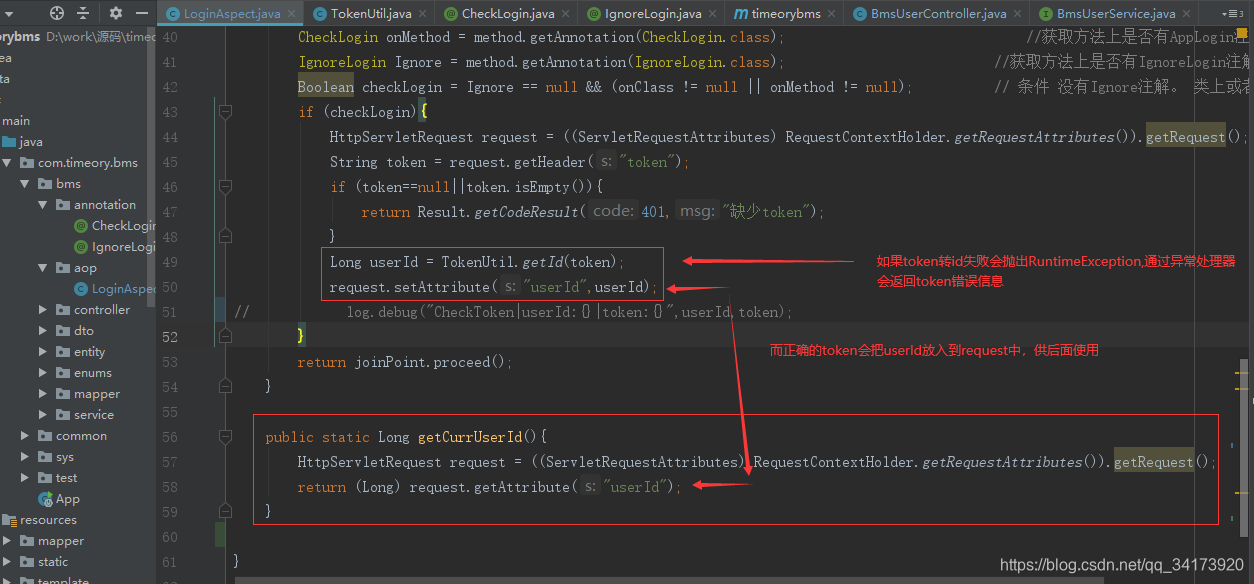
Service层获取UserId
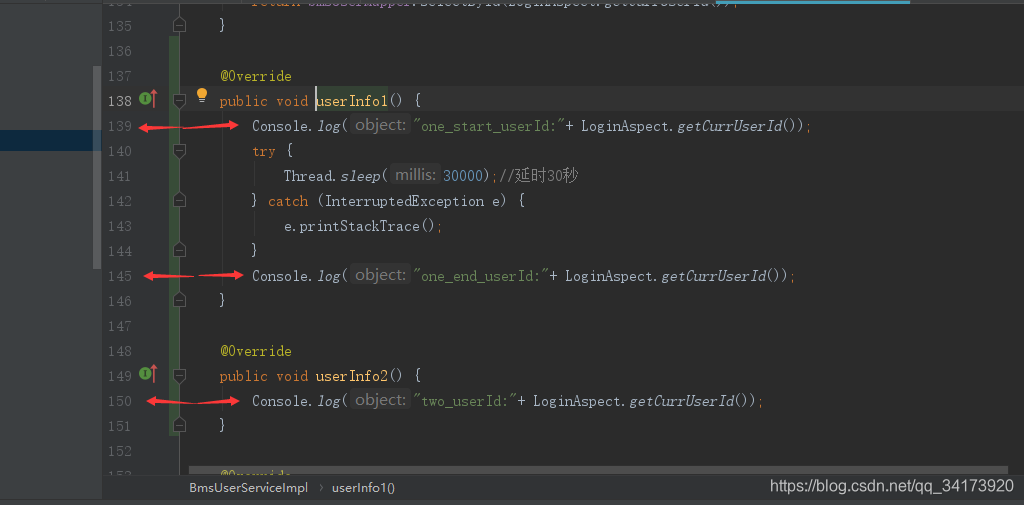
这里准备了两个接口,分别登录两个账号后,用两个不同的token请求这两个接口
这里使用 IntelliJ IDEA 插件 HTTP Client请求接口

最后结果,不仅使用token对接口进行了检测,而且通过HttpRequest对象存储了用户id,保证每个请求都能方便的拿到用户id,
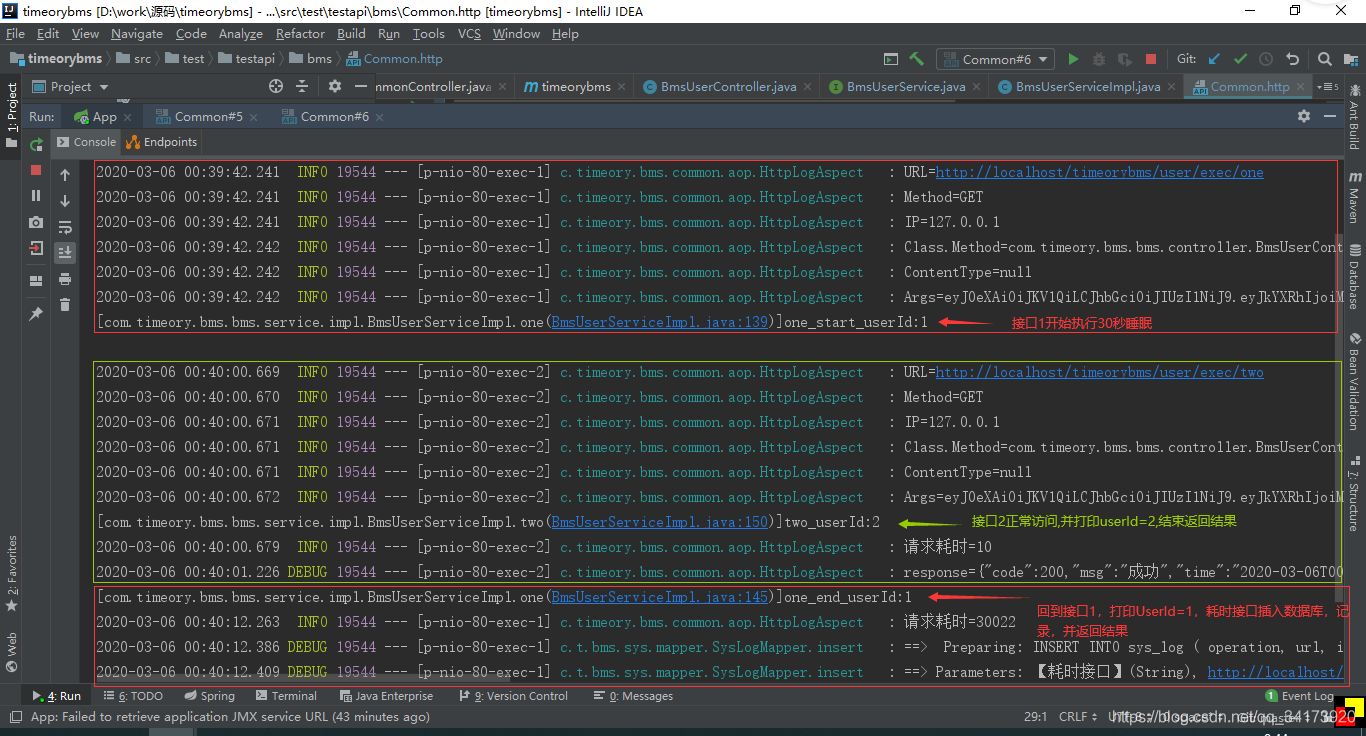
全局拿用户信息
OK成功舒适的拿到用户id后,我们可以在任何时间,任何Service中直接获取用户信息。
在UserService中写一个getCurrUser方法来获取当前对象;
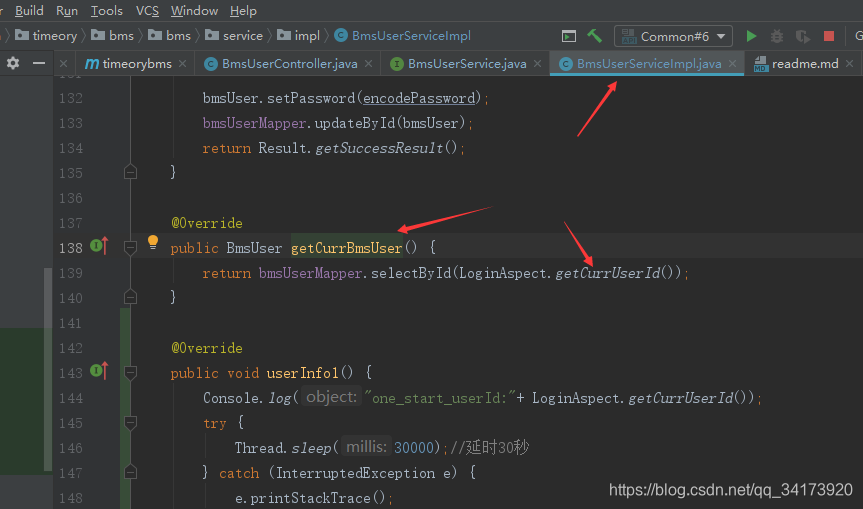
好了,全局获取User信息。而不用考录前端是否传值,只要前端请求接口时有token,那么这个请求的任何时间都能可以通过有注入**UserService并调用get.CurrUser()**即可拿到用户对象
实例代码:https://github.com/dahuoyzs/aopdemo
{
"author": "大火yzs",
"title": "【AOP系列】后端登录这样写才香",
"tag": "AOP,登录",
"createTime": "2020-03-06 1:37"
}
