一、MYSQL的基本命令大全
1. 数据库
1.增
(1)
create database if not exists`数据库名称`;
(2)默认字符集utf8和数据库排序规则utf8_general_ci
create database if not exists`数据库名称`
charset utf8 collate uft8_general_ci;
-- charset[字符集] collate[排序规则]
2.删
(1)
drop database if exists `数据库名称`;
3.改
(1)默认字符集utf8和数据库排序规则核对utf8_general_ci
alter database `数据库名称`
charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
4.查
(1)
show databases;
2. 表
1.增
(1)
create table if not exists `student01`(
id int(11) not null unique auto_increment comment'学号',
-- [列字段名] [数据类型] [属性][索引][注释]
primary key (`id`)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8
-- [引擎][默认字符集]
(2)复制表 student01 (like)
create table if not exists `student02` like `studnet01`;
2.删
(1)
drop table if exists `school`;
3.改
(1)改名
alter table `school` to `school01`;
-- alter table [原名称] to [新名称];
(2)改引擎和字符集(必须和名字单独改)
alter table `school` charset=utf8 engine=innodb;
-- alter table [需要修改的表]
-- charset=[utf8] engine=[innodb];
4.查
(1)
show tables;
3.列的字段(改变表的一部分)
1.增
alter table `school`
add column age int(10) unsigned not null comment'年龄' ,
add column phoneNumber int(20) unsigned not null comment'手机号'
;
-- add [column] [列字段名称] [数据类型] [属性][索引][注释],
-- 这里[索引]暂时不添加
-- unsigned 是 无符号,负数自动变为0;
-- null 非空
2.删 (drop)
alter table `school`
drop column `age`,
drop column `phoneNumber`
;
3.改 (change)
注意:
(1).修改列字段必须和属性字符集等一起修改,不能只改一部分,
(2).而表只能改一部分
alter table `student`
change `id` `newId` int(11) unsigned not null unique auto_increment charset=utf8 comment'学生的新id',
change `name` `newName` varchar(100) not null charset=utf8 comment'学生的新名字'
;
-- change [需要修改的列字段名] [新字段名]
-- [数据类型] [属性] [索引] [注释]
-- 这里索引暂时不加
-- 注意修改列字段必须和属性字符集等一起修改,不能只改一部分
4.查
(1)
desc `student`;
4. 行数据
1.增 (插入)
insert into (`name`,`age`) values
('王二麻子',13),
('张三',13),
('李四',14)
;
-- 插入多行数据的方法.
-- 如果 id不是自增,则必须添加id 不然报错error
2.删
delete from `student` where (`id` = 1);
--
-- 因为 Id是主键自增,所以第二个又会变成第一个,下面类推
3.改 (update)
update `student` set
`name`='王二麻子',
age = 10
where ( `id` = 1);
-- 不指定where会修改所有表!!
4.查
-- 1. 全部字段全部信息
select * from `student`;
-- 2。1.部分字段全部信息
select
`id` as 序列号,
`name` as 姓名
form `student`;
-- 2.2 部分字段,部分信息
select `id`,`name`,`age` from `student`
where (`id` >= 1 and `id` <= 100);
-- 3. 组合字段
select
`mathScore` as 数学分数,`englishScore` as 英语分数,
concat("总分: ",`mathScore`+`englishScore`) as 总分
from student where (`id`>=1 and `id`<= 10);
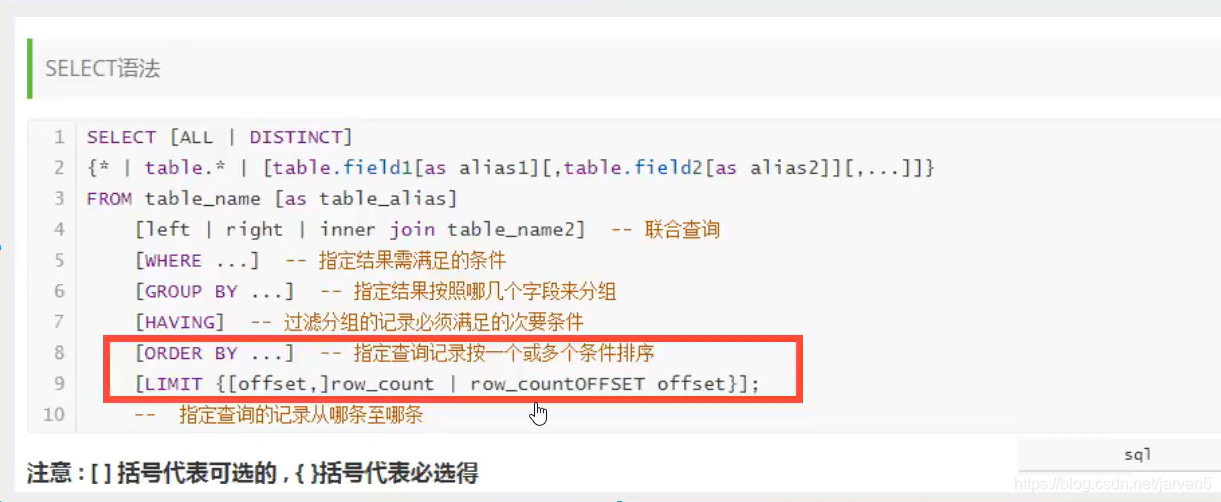
(重点)select 语法
select
[all|distanct] -- 1.字段
from
[table1|table1,table2] -- 2.表
inner join [table_2] ---3.联合查询
on [联合查询条件] --
where... -- 3.where 满足条件
group by [...] -- 4.分组
having [...] -- 分组的次要条件
order by [表.字段 desc|ASC] -- 5.排序
limit [开始查询的行数],[查询的行数];
-- 6.分页.
二、拓展学习方法
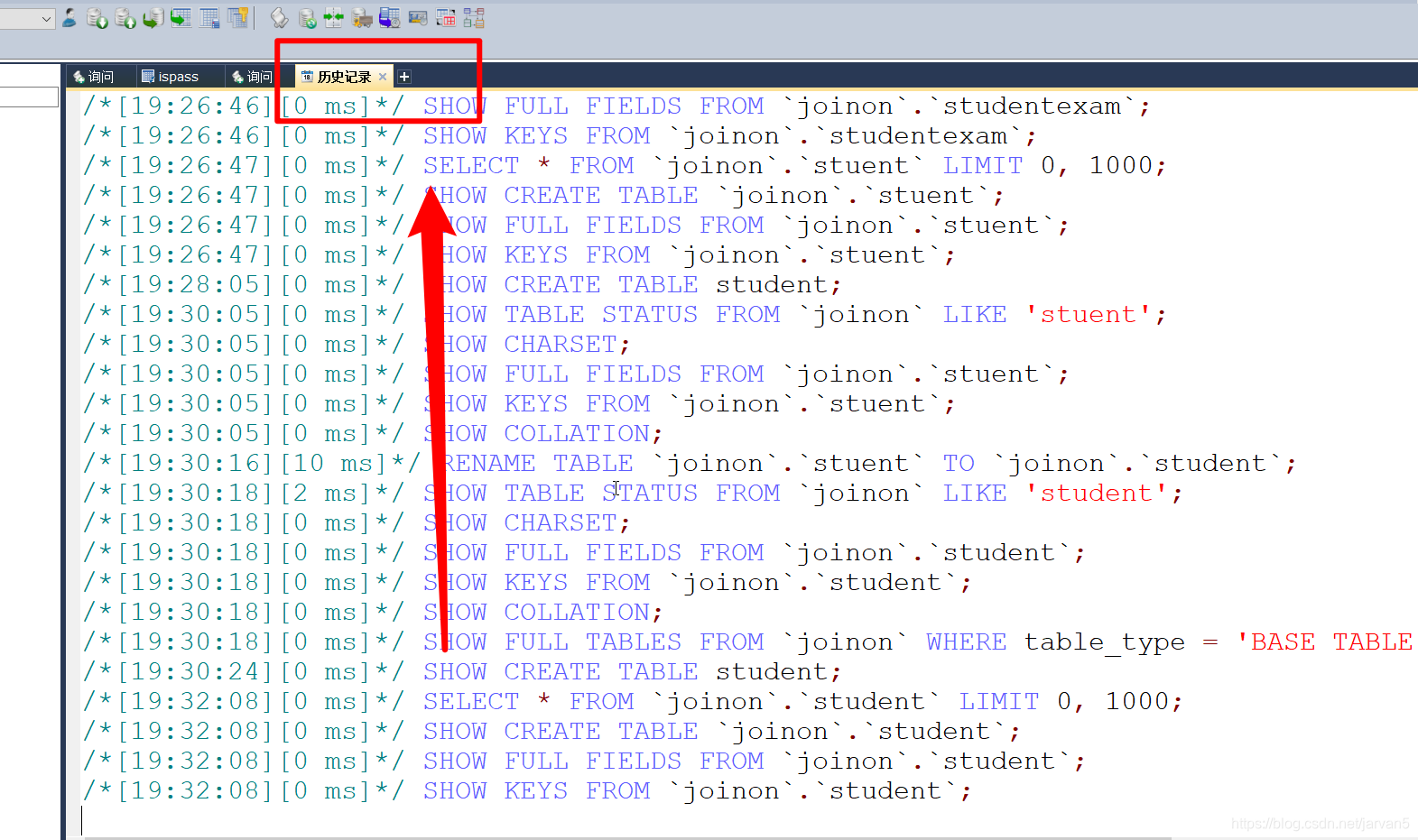
1. 使用SQLyog 的历史记录查看你每一步操作的SQL语句
2. 查看创建这个表或数据库需要的语句
1.查看创建数据库test01需要的语句
show create database `test01`;
2.查看创建表 student 需要的语句
show create table `student`;
3. 插入当前时间.
(重点)4. select 语法
select
[all|distanct] -- 1.字段
from
[table1|table1,table2] -- 2.表
inner join [table_2] ---3.联合查询
on [联合查询条件] --
where... -- 3.where 满足条件
group by [...] -- 4.分组
having [...] -- 分组的次要条件
order by [表.字段 desc|ASC] -- 5.排序
limit [开始查询的行数],[查询的行数];
-- 6.分页.