ES6模块化如何使用,开发环境如何打包?
1.模块化的基本语法
/* export 语法 */
// 默认导出
export default {
a: '我是默认导出的',
}
// 单独导出
export function fn1() {
console.log('我是函数1')
}
export function fn2() {
console.log('我是函数2')
}
/* import 语法 */
// 导入
// 默认导入
import util1 from './demo'
// 单独导入
import { fn1, fn2 } from './demo'
console.log(util1)
fn1()
fn2()
2.开发环境配置
- Babel
ES6新语法需要进行编译,即转换为ES5或者更早版本的语法,这个时候就需要Babel来进行转换
Babel是什么?Babel是一个 JavaScript 编译器,主要用于将 ECMAScript 2015+ 版本的代码转换为向后兼容的 JavaScript 语法,以便能够运行在当前和旧版本的浏览器或其他环境中。Babel中文网 - Webpack模块化工具
3.关于JS众多模块化标准

class和普通构造函数有何区别?
1.JS构造函数
function MathHandle(x, y) {
this.x = x
this.y = y
}
MathHandle.prototype.add = function () {
return this.x + this.y
}
var m = new MathHandle(1, 2)
console.log(m.add()) // 3
2.class基本语法
class MathHandle {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x
this.y = y
}
add() {
return this.x + this.y
}
}
const m = new MathHandle(1, 2)
console.log(m.add()) // 3
3.语法糖
/* 本质只是一个语法糖 */
console.log(typeof MathHandle) // 'function'
console.log(MathHandle === MathHandle.prototype.constructor) // true
console.log(m.__proto__ === MathHandle.prototype) // true
4.继承
// class 的继承
class Father {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
money() {
console.log('我有100元钱')
}
sum() {
console.log(this.name + '有' + this.age + '岁')
}
}
// extends 继承父类
class Son extends Father {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name, age) // super 调用了父类中的构造函数
}
}
var son = new Son('小鑫', 22)
//可以使用父类的方法
son.money() // 我有100元钱
son.sum() // 小鑫有22岁
5.总结
class更加贴合面向对象的写法;更加易读、理解;本质还是语法糖,还是使用 prototype 实现的
Promise的基本使用和原理
为了解决“回调地狱”(链式发送ajax请求)而出现的一种解决方案,比如下面这种情况
$.ajax({
url: 'http:/localhost:3000/data',
success: function (response) {
console.log(response);
$.ajax({
url: 'http:/localhost:3000/data2',
success: function (response) {
console.log(response);
$.ajax({
url: 'http:/localhost:3000/data3',
success: function (response) {
console.log(response);
}
})
}
})
}
})
这个时候就需要使用promise来处理ajax请求,主要分为以下四个步骤:
new Promist实例,而且要return;new Promist时要传入函数,函数有resolvereject两个参数;- 成功时执行
resolve(),失败时执行reject() .then.catch监听结果
/**
* @description 基于Promise发送Ajax请求
* @param {String} url 请求地址
*/
function queryDate(url) {
const promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('get', url)
xhr.send()
if (xhr.onload) {
// onload 只有状态码为4时才能回调一次函数
xhr.onload = function () {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
// 处理正常情况
resolve(xhr.responseText)
} else {
// 处理异常的情况
reject('服务器错误')
}
}
} else {
// 支持低版本ie
// onreadystatechange是只要返回的状态码只要变化时就回调一次函数
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && xhr.status === 200) {
// 处理正常情况
resolve(xhr.responseText)
} else {
// 处理异常情况
reject('服务器错误')
}
}
}
})
return promise
}
// 发送多个ajax请求并且保证顺序 链式调用
// 第一次ajax请求
queryData('http://localhost:3000/data')
.then(function (data) {
console.log(data)
// 第二次ajax请求
return queryData('http://localhost:3000/data2')
})
.then(function (data) {
console.log(data)
// 第三次ajax请求
return queryData('http://localhost:3000/data3')
})
.then(function (data) {
console.log(data)
})
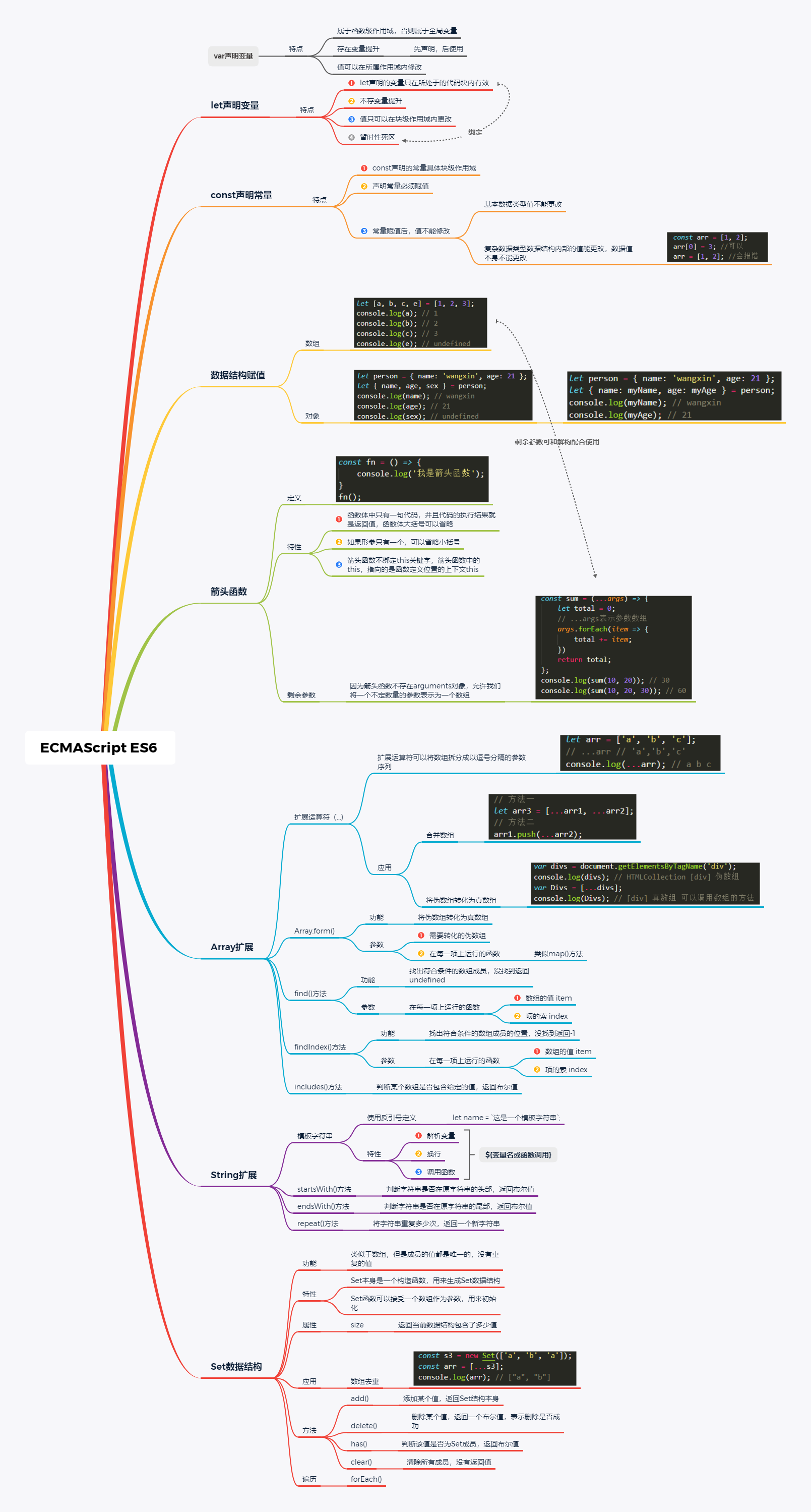
ES6其他常用的功能
- let/const
- 多行字符串/模板变量
- 结构赋值
- 块级作用域
- 函数默认参数
- 箭头函数(注意:是普通js函数的补充,修正this的指向)
附带上一张学习ES6基础时的思维导图