LeetCode 1248. Count Number of Nice Subarrays
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k. A subarray is called nice if there are k odd numbers on it.
Return the number of nice sub-arrays.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2,1,1], k = 3
Output: 2
Explanation: The only sub-arrays with 3 odd numbers are [1,1,2,1] and [1,2,1,1].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,4,6], k = 1
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no odd numbers in the array.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,2,2,1,2,2,1,2,2,2], k = 2
Output: 16
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 50000
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^5
1 <= k <= nums.length
题解
votrubac Java/C++ with picture, deque
Intuition
This is similar to 992. Subarrays with K Different Integers.
When we find k odd numbers, we have one nice subarray, plus an additional subarray for each even number preceding the first odd number. This is also true for each even number that follows.
For example, in the picture below we found k == 2 odd numbers at idex 4. We have 3 nice subarrays therefore: [2, 4], [1, 4], [0, 4]. For even number at idex 5, we also have 3 nice subarrays: [2, 5], [1, 5], [0, 5]. Plus 3 subarrays for index 6.
When we encounter k + 1 odd number at index 7, we need to get rid of the first odd number (at index 2) to have exactly k odd numbers. So, we count nice subarrays as if the array starts at index 3.
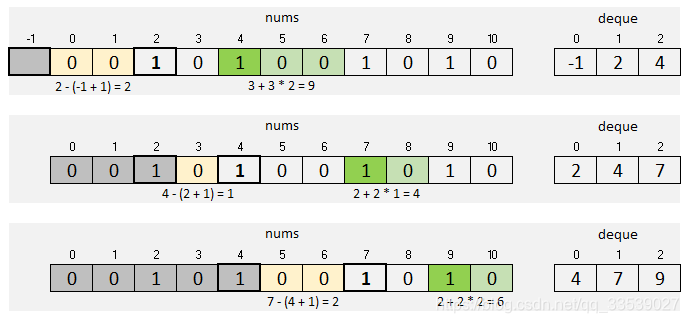
Approach 1: Deque
We do not have to use deque, but it makes tracking the window easier (comparing to moving pointers). Note that in Java, the deque interface does not provide a random access, so we’ll just use LinkedList instead.
Java
public int numberOfSubarrays(int[] nums, int k) {
LinkedList<Integer> deq = new LinkedList();
deq.add(-1);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (nums[i] % 2 == 1) deq.add(i);
if (deq.size() > k + 1) deq.pop();
if (deq.size() == k + 1) res += 1 + deq.get(1) - (deq.get(0) + 1);
}
return res;
}
C++
int numberOfSubarrays(vector<int>& nums, int k, int res = 0) {
deque<int> deq = { -1 }; //deq[-1]=-1
for (auto i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (nums[i] % 2) deq.push_back(i);
if (deq.size() > k + 1) deq.pop_front();
if (deq.size() == k + 1) res += 1 + deq[1] - (deq[0] + 1);//初始了-1,所以size=k+1
}
return res;
}
Complexity Analysis
Time: O(n).
Memory: O(k) for the deque.