以下学习恋上数据结构与算法的记录,本篇主要内容是布隆过滤器
●思考:
如果要经常判断1 个元素是否存在,你会怎么做?
很容易想到使用哈希表(HashSet、HashMap),将元素作为key 去查找
✓时间复杂度:O(1),但是空间利用率不高,需要占用比较多的内存资源
如果需要编写一个网络爬虫去爬10亿个网站数据,为了避免爬到重复的网站,如何判断某个网站是否爬过?
很显然,HashSet、HashMap 并不是非常好的选择
是否存在时间复杂度低、占用内存较少的方案?
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)
1970年由布隆提出,它是一个空间效率高的概率型数据结构,可以用来告诉你:一个元素一定不存在或者可能存在
优缺点
优点:空间效率和查询时间都远远超过一般的算法
缺点:有一定的误判率、删除困难
它实质上是一个很长的二进制向量和一系列随机映射函数(Hash函数)
常见应用
网页黑名单系统、垃圾邮件过滤系统、爬虫的网址判重系统、解决缓存穿透问题
●布隆过滤器的原理
假设布隆过滤器由20位二进制、3个哈希函数组成,每个元素经过哈希函数处理都能生成一个索引位置
添加元素:将每一个哈希函数生成的索引位置都设为1
查询元素是否存在
✓如果有一个哈希函数生成的索引位置不为1,就代表不存在(100%准确)
✓如果每一个哈希函数生成的索引位置都为1,就代表存在(存在一定的误判率)
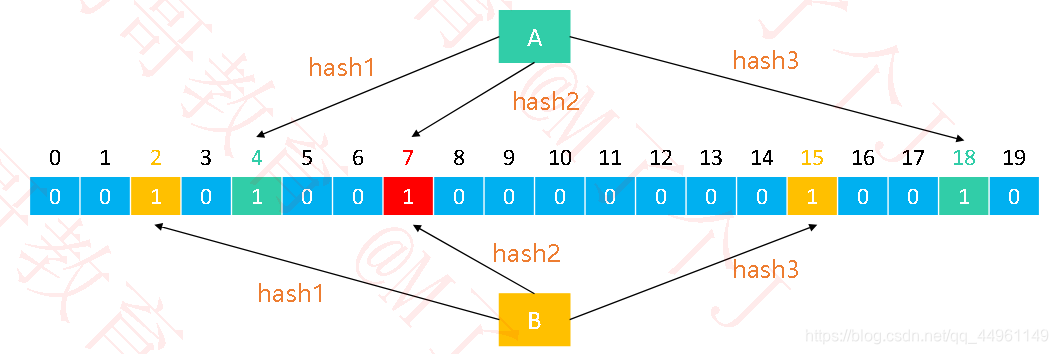 添加、查询的时间复杂度都是:O(k),k是哈希函数的个数。空间复杂度是:O(m),m是二进制位的个数
添加、查询的时间复杂度都是:O(k),k是哈希函数的个数。空间复杂度是:O(m),m是二进制位的个数
布隆过滤器的误判率
 布隆过滤器的接口设计
布隆过滤器的接口设计

谷歌实现:Guava: Google Core Libraries For Java
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.guava/guava
●布隆过滤器的Java实现
public class BloomFilter<T> {
/**
* 二进制向量的长度(一共有多少个二进制位)
*/
private int bitSize;
/**
* 二进制向量
*/
private long[] bits;
/**
* 哈希函数的个数
*/
private int hashSize;
/**
* @param n 数据规模
* @param p 误判率, 取值范围(0, 1)
*/
public BloomFilter(int n, double p) {
if (n <= 0 || p <= 0 || p >= 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("wrong n or p");
}
double ln2 = Math.log(2);
// 求出二进制向量的长度
bitSize = (int) (-(n * Math.log(p)) / (ln2 * ln2));
// 求出哈希函数的个数
hashSize = (int) (bitSize * ln2 / n);
// bits数组的长度
bits = new long[(bitSize + Long.SIZE - 1) / Long.SIZE];
// 每一页显示100条数据, pageSize
// 一共有999999条数据, n
// 请问有多少页 pageCount = (n + pageSize - 1) / pageSize
}
/**
* 添加元素1
*
* @return true 代表了bit 发生了改变
*/
public boolean put(T value) {
nullCheck(value);
// 利用value生成2个整数
int hash1 = value.hashCode();
int hash2 = hash1 >>> 16;
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= hashSize; i++) {
int combinedHash = hash1 + (i * hash2);
if (combinedHash < 0) {
combinedHash = ~combinedHash;
}
// 生成一个二进位的索引
int index = combinedHash % bitSize;
// 设置index位置的二进位为1
if (set(index)) result = true;
// 101010101010010101
// | 000000000000000100 1 << index
// 101010111010010101
}
return result;
}
/**
* 判断一个元素是否存在
*/
public boolean contains(T value) {
nullCheck(value);
// 利用value生成2个整数
int hash1 = value.hashCode();
int hash2 = hash1 >>> 16;
for (int i = 1; i <= hashSize; i++) {
int combinedHash = hash1 + (i * hash2);
if (combinedHash < 0) {
combinedHash = ~combinedHash;
}
// 生成一个二进位的索引
int index = combinedHash % bitSize;
// 查询index位置的二进位是否为0
if (!get(index))
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 设置index位置的二进位为1
*/
private boolean set(int index) {
long value = bits[index / Long.SIZE];
int bitValue = 1 << (index % Long.SIZE);
bits[index / Long.SIZE] = value | bitValue;
return (value & bitValue) == 0;
}
/**
* 查看index位置的二进位的值
*
* @return true代表1, false代表0
*/
private boolean get(int index) {
long value = bits[index / Long.SIZE];
return (value & (1 << (index % Long.SIZE))) != 0;
}
/**
* 判断是否为空,不允许为空
*
* @param value
*/
private void nullCheck(T value) {
if (value == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Value must not be null.");
}
}
}