Java AIO 详解
jdk1.7 (NIO2)才是实现真正的异步 AIO、把 IO 读写操作完全交给操作系统,学习了 linux epoll 模式,下面我们来做一些演示。
AIO(Asynchronous IO)基本原理
服务端:AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
客服端:AsynchronousSocketChannel
用户处理器:CompletionHandler 接口,这个接口实现应用程序向操作系统发起 IO 请求,当完成后处理具体逻辑,否则做自己该做的事情,
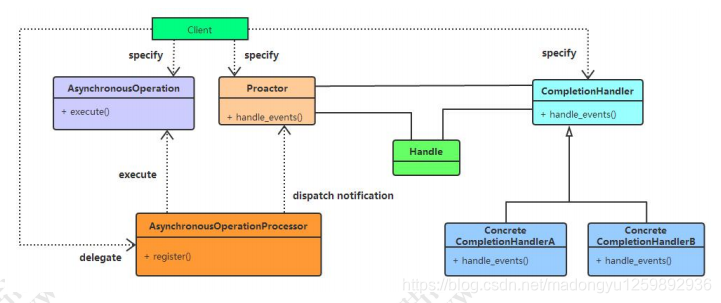
“真正”的异步IO需要操作系统更强的支持。在IO多路复用模型中,事件循环将文件句柄的状态事件通知给用户线程,由用户线程自行读取数据、处理数据。而在异步IO模型中,当用户线程收到通知时,数据已经被内核读取完毕,并放在了用户线程指定的缓冲区内,内核在IO完成后通知用户线程直接使用即可。异步IO模型使用了Proactor设计模式实现了这一机制,如下图所示:
![]()
AIO 初体验
服务端代码:
public class AIOServer {
private final int port;
public static void main(String args[]) {
int port = 8000;
new AIOServer(port);
}
public AIOServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
listen();
}
private void listen() {
try {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
AsynchronousChannelGroup threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(executorService, 1);
final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel server = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup);
server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("服务已启动,监听端口" + port);
server.accept(null, new CompletionHandler < AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object > () {
final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel result, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("IO 操作成功,开始获取数据");
try {
buffer.clear();
result.read(buffer).get();
buffer.flip();
result.write(buffer);
buffer.flip();
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
} finally {
try {
result.close();
server.accept(null, this);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
System.out.println("操作完成");
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("IO 操作是失败: " + exc);
}
});
try {
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch(InterruptedException ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
} catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
客户端代码:
/*** AIO 客户端 */
public class AIOClient {
private final AsynchronousSocketChannel client;
public AIOClient() throws Exception {
client = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
}
public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception {
client.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port), null, new CompletionHandler < Void, Void > () {@Override public void completed(Void result, Void attachment) {
try {
client.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("这是一条测试数据".getBytes())).get();
System.out.println("已发送至服务器");
} catch(Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}@Override public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
final ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
client.read(bb, null, new CompletionHandler < Integer, Object > () {@Override public void completed(Integer result, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("IO 操作完成" + result);
System.out.println("获取反馈结果" + new String(bb.array()));
}@Override public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch(InterruptedException ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
new AIOClient().connect("localhost", 8000);
}
}执行结果:
服务端

![]()
客户端
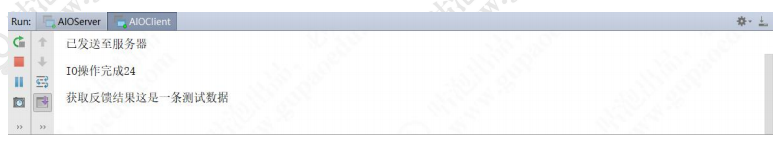
![]()
各 IO 模型对比与总结
最后再来一张表总结

![]()

![]()