1.下载和安装(网上有这里就不细说啦)
2.创建工程


3.编码
一个C#程序主要包括:
- 1.命名空间声明
- 2.一个class
- 3.class属性
- 4.main方法
- 5.语句和表达式
代码系统已经帮我们写好 。
using 关键字用于在程序中包含 System 命名空间,为什么要包含它?因为下文中的Console是在System中申明的;
namespace Test 是命名空间声明;
class Program是class声明;
Main方法;
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!")是一条输出语句;
这里没有class的变量;
using System;
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
}
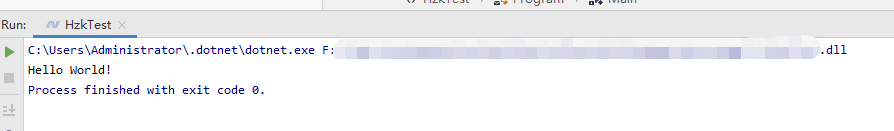
}4.运行
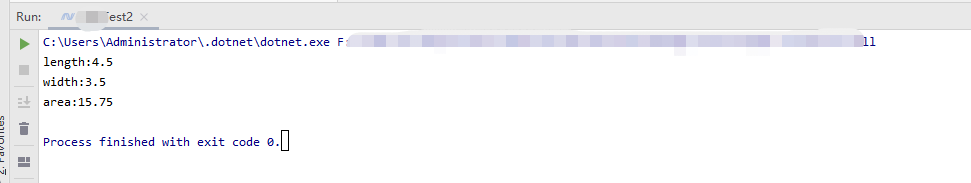
输出矩形的相关信息

using System;
namespace Test
{
public class Rectangle
{
private double length;
private double width;
public void initData()
{
length = 4.5;
width = 3.5;
}
public double getArea()
{
return length * width;
}
public void display()
{
Console.WriteLine("length:"+length);
Console.WriteLine("width:"+width);
Console.WriteLine("area:"+getArea());
}
}
class ShowRectangle
{
//psvm
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r=new Rectangle();
r.initData();
r.display();
}
}
}
数据类型
值类型
引用类型:引用类型又分为对象类型(装箱、拆箱)、动态类型(对象类型变量的类型检查是在编译时发生的,而动态类型变量的类型检查是在运行时发生的)、字符串类型
指针类型:C# 中的指针与 C 或 C++ 中的指针有相同的功能
类型转换
隐式类型转换:以安全方式进行的转换, 不会导致数据丢失,从小的整数类型转换为大的整数类型,从派生类转换为基类
显式类型转换:即强制类型转换,会造成数据丢失
基本变量类型
| 类型 | 举例 |
|---|---|
| 整数类型 | sbyte、byte、short、ushort、int、uint、long、ulong 和 char |
| 浮点型 | float 和 double |
| 十进制类型 | decimal |
| 布尔类型 | true 或 false 值,指定的值 |
| 空类型 | 可为空值的数据类型 |
常量类型
整数常量、浮点常量、字符常量或者字符串常量,还有枚举常量,常量是使用 const 关键字来定义的,被const申明的常量不能修改
const int c1 = 5;运算符
算术运算符
int sum = 0;
int temp = 2;
sum = 10 + 10;//算数加运算关系运算符
Console.WriteLine(sum==temp);//关系运算逻辑运算符
Console.WriteLine(true&&false);//逻辑运算位运算符
int a = 60; //60 = 0011 1100
int b = 13; //13 = 0000 1101
int c = 0;
c = a & b; //12 = 0000 1100 与运算
c = a | b; //61 = 0011 1101 或运算
c = a ^ b; //49 = 0011 0001 非运算
c = ~a; //-61 = 1100 0011 取反运算
c = a << 2; //240 = 1111 0000 二进制左移运算符
c = a >> 2; //15 = 0000 1111 二进制右移运算符赋值运算符
int a2 = 21;
int c2;
c = a;
c += a;
c <<= 2;//等同于 C = C << 2
c &= 2;//等同于 C = C & 2其他运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| sizeof() | 返回数据类型的大小。 | sizeof(int),将返回 4. |
| typeof() | 返回 class 的类型。 | typeof(StreamReader); |
| & | 返回变量的地址。 | &a; 将得到变量的实际地址。 |
| * | 变量的指针。 | *a; 将指向一个变量。 |
| ? : | 条件表达式 | 如果条件为真 ? 则为 X : 否则为 Y |
| is | 判断对象是否为某一类型。 | If( Ford is Car) // 检查 Ford 是否是 Car 类的一个对象。 |
| as | 强制转换,即使转换失败也不会抛出异常。 | Object obj = new StringReader("Hello"); StringReader r = obj as StringReader; |
运算符优先级(从高到低列出)
| 类别 | 运算符 | 结合性 |
|---|---|---|
| 后缀 | () [] -> . ++ - - | 从左到右 |
| 一元 | + - ! ~ ++ - - (type)* & sizeof | 从右到左 |
| 乘除 | * / % | 从左到右 |
| 加减 | + - | 从左到右 |
| 移位 | << >> | 从左到右 |
| 关系 | < <= > >= | 从左到右 |
| 相等 | == != | 从左到右 |
| 位与 AND | & | 从左到右 |
| 位异或 XOR | ^ | 从左到右 |
| 位或 OR | | | 从左到右 |
| 逻辑与 AND | && | 从左到右 |
| 逻辑或 OR | || | 从左到右 |
| 条件 | ?: | 从右到左 |
| 赋值 | = += -= *= /= %=>>= <<= &= ^= |= | 从右到左 |
| 逗号 | , | 从左到右 |
判断语句
if (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("true");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("false");
}
Console.WriteLine(c > 0 ? c : 0);循环语句
//while循环
while(true)
{
Console.WriteLine("123");
}
//for循环
for (int q=10;q<20;q++)
{
Console.WriteLine(q);
}
//foreach循环
int[] fibarray = new int[] { 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 };
foreach (int element in fibarray)
{
Console.WriteLine(element);
}
//do-while循环
int w = 10;
do
{
Console.WriteLine(w);
w += 1;
} while (w < 20);访问修饰符
- public:所有对象都可以访问;
- private:对象本身在对象内部可以访问;
- protected:只有该类对象及其子类对象可以访问
- internal:同一个程序集的对象可以访问;带有 internal 访问修饰符的任何成员可以被定义在该成员所定义的应用程序内的任何类或方法访问
- protected internal:访问限于当前程序集或派生自包含类的类型。
定义方法
public int Find(int num1,int num2)
{
return num1>num2?num1:num2;
}调用方法
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p=new Program();
p.Find(1, 0);
}参数传递
| 方式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 值参数 | 这种方式复制参数的实际值给函数的形式参数,实参和形参使用的是两个不同内存中的值。在这种情况下,当形参的值发生改变时,不会影响实参的值,从而保证了实参数据的安全。 |
| 引用参数 | 这种方式复制参数的内存位置的引用给形式参数。这意味着,当形参的值发生改变时,同时也改变实参的值。 |
| 输出参数 | 这种方式可以返回多个值。 |
特别说一下输出参数的使用
using System;
namespace Test5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p=new Program();
int a, b;
p.getValues(out a,out b);
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.WriteLine(b);
}
public void getValues(out int x,out int y)
{
x = 5;
y = 6;
}
}
}C#中的?
单问号用于对 int,double,bool 等无法直接赋值为 null 的数据类型进行 null 的赋值
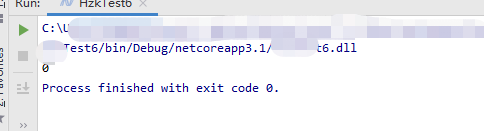
using System;
namespace Test6
{
class Program
{
int? i;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p=new Program();
Console.WriteLine(p.get());
}
public int? get()
{
if (i == null)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return i;
}
}
}
}
using System;
namespace Test6
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int? i=null;
double? num=new double?();
Console.WriteLine("num:"+num);
Program p=new Program();
Console.WriteLine("i:"+i);
}
}
}
双问号:用于定义可空类型和引用类型的默认值
double? num2 = null;
double num3;
num3 = num2 ?? 5.34; // 如果num2为空则返回5.34
Console.WriteLine(num3);数组
using System;
namespace Test7
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] n=new int[10];//申明数组
// int[] n=new int[]{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}//不需要指定数组大小的方式申明
for (int i=0;i<10;i++)//数组赋值
{
n[i] = i + 100;
}
for (int j=0;j<10;j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(n[j]);
}
}
}
}//申明并初始化二维数组
int[,] a = new int[5, 2]
{
{0, 0}, {1, 2}, {2,4},{3, 6}, {4,8}
};
for (int i=0;i<5;i++) {
for (int j=0;j<2;j++) {
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}]={2}",i,j,a[i,j]);
}
}//交错数组申明并初始化,交错数组即数组的数组,是一维数组
int[][] a = new int[][]
{
new int[] {0, 0},
new int[] {1, 2},
new int[] {2, 4},
new int[] {3, 6},
new int[] {4, 8}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0}][{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i][j]);
}
}int[] arr = new int[] {1000, 2, 3, 17, 50};
Program p=new Program();
Console.WriteLine(p.getAverage(arr, arr.Length));
public double getAverage(int[] arr,int size)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
sum += arr[i];
}
return (double)sum / size;
}//参数数组,适用于不能确定要传递给函数作为参数的参数数目
Program p=new Program();
int sum=p.add(512, 720, 250, 567, 889);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
public int add(params int[] arr)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (int i in arr)
{
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}//Array类的使用
int[] list = {34, 72, 13, 44, 25, 30, 10};
// Array.Reverse(list);//数组反转
Array.Sort(list);//从小到大排序,仅支持一维数组
foreach (int i in list)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}字符串
使用以下方法之一来创建 string 对象:
- 通过给 String 变量指定一个字符串
- 通过使用 String 类构造函数
- 通过使用字符串串联运算符( + )
- 通过检索属性或调用一个返回字符串的方法
- 通过格式化方法来转换一个值或对象为它的字符串表示形式
using System;
namespace Test8
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建字符串对象
string name = "test";//1
char[] letters = {'T', 'e', 's', 't', '2'};//2
string name2=new string(letters);
string name3 = "test1" + "test2";//3
string[] sarray = {"Hello", "From", "Tutorials", "Point"};
string name4 = String.Join("", sarray);//4
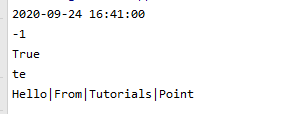
DateTime time=new DateTime(2020,09,24,16,41,00);
//string date = String.Format("{0:D} {0:t} ", time);
//string date = String.Format("{0:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}", time);
string date = time.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Console.WriteLine(date);
Console.WriteLine(String.Compare(name, name2));//字符串比较
Console.WriteLine(name.Contains("test"));//字符串是否包含
Console.WriteLine(name.Substring(0, 2));//字符串截取
Console.WriteLine(String.Join("|", sarray));//字符串拼接
}
}
} 
using System;
namespace Test9
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Books books,books2;
books.title = "1";
books.author = "user1";
books.id = 1;
books2.title = "2";
books2.author = "user2";
books2.id = 2;
Console.WriteLine(books.title);
Console.WriteLine(books2.title);
}
}
}
struct Books
{
public string title;
public string author;
public int id;
}类和结构有以下几个基本的不同点:
- 类是引用类型,结构是值类型。
- 结构不支持继承。
- 结构不能声明默认的构造函数。
- 结构体中声明的字段无法赋予初值,类可以。
- 结构体的构造函数中,必须为结构体所有字段赋值,类的构造函数无此限制。
类与结构的选择
首先明确,类的对象是存储在堆空间中,结构存储在栈中。堆空间大,但访问速度较慢,栈空间小,访问速度相对更快。故而,当我们描述一个轻量级对象的时候,结构可提高效率,成本更低。当然,这也得从需求出发,假如我们在传值的时候希望传递的是对象的引用地址而不是对象的拷贝,就应该使用类了
- 1、当堆栈的空间很有限,且有大量的逻辑对象时,创建类要比创建结构好一些;
- 2、对于点、矩形和颜色这样的轻量对象,假如要声明一个含有许多个颜色对象的数组,则CLR需要为每个对象分配内存,在这种情况下,使用结构的成本较低;
- 3、在表现抽象和多级别的对象层次时,类是最好的选择,因为结构不支持继承。
- 4、大多数情况下,目标类型只是含有一些数据,或者以数据为主。
枚举
using System;
namespace Test9
{
class Program
{
enum Day { Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat };
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = (int)Day.Sun;
int y = (int) Day.Fri;
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
}类
using System;
namespace HzkTest10
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Box box1= new Box();
Box box2 = new Box();
box1.length = 5.0;
box1.width = 6.0;
box1.height = 7.0;
box2.length = 8.0;
box2.width = 9.0;
box2.height = 10.0;
Console.WriteLine(box1.length*box1.width*box1.height);
Console.WriteLine(box2.length*box2.width*box2.height);
Console.WriteLine(box1.getV());
Console.WriteLine(box2.getV());
}
}
class Box
{
public double length;
public double width;
public double height;
public static int num;//静态成员变量,所有对象公用一个静态成员变量,可以通过直接调用类而不需要创建类的实例来获取
public Box()//默认构造函数
{
Console.WriteLine("对象已创建");
}
~Box()//析构函数,它不返回值,也不带任何参数,用于在结束程序(比如关闭文件、释放内存等)之前释放资源
{
Console.WriteLine("对象已删除");
}
public Box(double length, double width, double height)//带参数构造函数
{
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public static int getStatic()//静态成员函数,只能访问静态变量
{
return num;
}
public double getV()
{
return length * width * height;
}
}
}继承
using System;
namespace Test11
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Rectangle r=new Rectangle();//不带参数的构造函数
// r.setWidth(5);
// r.setHeight(10);
Rectangle r=new Rectangle(5,10);
Console.WriteLine(r.getArea());
r.Display();
}
}
//基类
class Shape
{
protected int width;
protected int height;
public Shape(int width, int height)
{
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("width:"+width);
Console.WriteLine("height:"+height);
}
public void setWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
public void setHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
}
//派生类
class Rectangle : Shape
{
private double area;
public Rectangle(int width, int height) : base(width, height)
{
}
public int getArea()
{
return width * height;
}
public void Display()
{
base.Display();
Console.WriteLine("Area:"+width*height);
}
}
}多继承
using System;
namespace Test11_2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Rectangle r=new Rectangle();
r.setWidth(5);
r.setHeight(10);
Console.WriteLine(r.getArea());
int area = r.getArea();
Console.WriteLine(r.getCost(area));
}
}
class Shape
{
protected int width;
protected int height;
public void setWidth(int w)
{
width = w;
}
public void setHeight(int h)
{
height = h;
}
}
public interface Shape2
{
int get();
}
public interface PaintCost
{
int getCost(int area);
}
class Rectangle : Shape, Shape2, PaintCost //子类只能继承一个父类,但可以继承多个父接口
{
public int getCost(int area)
{
return area * 70;
}
public int get()
{
return 0;
}
public int getArea()
{
return width * height;
}
}
}多态性
静态多态性
函数重载
using System;
namespace Test12
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test t=new Test();
int t1=t.Add(1, 2);
int t2 = t.Add(1, 2, 3);
double t3 = t.Add(1, 2.3, 4.625);
}
}
public class Test
{
public int Add(int a,int b)
{
return a + b;
}
public int Add(int a,int b,int c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
public double Add(int a,double b,double c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
}
}运算符重载
using System;
namespace Test12_2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Box box1=new Box();
Box box2=new Box();
Box box3=new Box();
box1.setLength(6.0);
box1.setBreadth(7.0);
box1.setHeight(5.0);
box2.setLength(12.0);
box2.setBreadth(13.0);
box2.setHeight(10.0);
box3 = box1 + box2;
Console.WriteLine(box3.getV());
}
}
class Box
{
private double length;
private double width;
private double height;
public void setLength( double len )
{
length = len;
}
public void setBreadth( double bre )
{
width = bre;
}
public void setHeight( double hei )
{
height = hei;
}
public static Box operator+(Box a,Box b)
{
Box box=new Box();
box.length = a.length + b.length;
box.width = a.width + b.width;
box.height = a.height + b.height;
return box;
}
public double getV()
{
return length * width * height;
}
}
}可重载和不可重载运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| +, -, !, ~, ++, -- | 这些一元运算符只有一个操作数,且可以被重载。 |
| +, -, *, /, % | 这些二元运算符带有两个操作数,且可以被重载。 |
| ==, !=, <, >, <=, >= | 这些比较运算符可以被重载。 |
| &&, || | 这些条件逻辑运算符不能被直接重载。 |
| +=, -=, *=, /=, %= | 这些赋值运算符不能被重载。 |
| =, ., ?:, ->, new, is, sizeof, typeof | 这些运算符不能被重载 |
动态多态性
抽象类,用于提供接口的部分类的实现
using System;
namespace Test12_3
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Shape s = new Shape();//不能创建抽象类的实例
Rectangle r=new Rectangle();
double area=r.area();
}
}
sealed class Shape2//密封类不能被继承
{
public int num;
}
abstract class Shape
{
abstract public int area();
}
class Rectangle : Shape
{
private int width;
private int length;
public override int area()
{
return length * width;
}
// abstract public int get()//不能在抽象类外部定义抽象方法
// {
// return 0;
// }
}
}当有一个定义在类中的函数需要在继承类中实现时,可以使用虚方法。以下做一个对比
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace HzkTest12_4
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var shapes = new List<Shape>
{
new Rectangle(),
new Circle()
};
foreach (var shape in shapes)
{
shape.Draw();
}
}
}
public class Shape
{
public void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("开始");
}
}
class Circle : Shape
{
public void Draw()
{
base.Draw();
Console.WriteLine("Circle");
}
}
class Rectangle : Shape
{
public void Draw()
{
base.Draw();
Console.WriteLine("Rectangle");
}
}
}![]()
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace HzkTest12_4
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var shapes = new List<Shape>
{
new Rectangle(),
new Circle()
};
foreach (var shape in shapes)
{
shape.Draw();
}
}
}
public class Shape
{
public virtual void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("开始");
}
}
class Circle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
base.Draw();
Console.WriteLine("Circle");
}
}
class Rectangle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
base.Draw();
Console.WriteLine("Rectangle");
}
}
}
接口
using System;
namespace Test13
{
class Program:MyInterface
{
public void method()
{
Console.WriteLine("test");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p=new Program();
p.method();
}
}
interface MyInterface
{
void method();
}
}using System;
namespace Test13_2
{
class Program:MyInterface3
{
public void method2()
{
Console.WriteLine("2");
}
public void method3()
{
Console.WriteLine("3");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p=new Program();
p.method2();
p.method3();
}
}
interface MyInterface2
{
void method2();
}
interface MyInterface3:MyInterface2
{
void method3();
}
}命名空间
在一个命名空间中声明的类的名称与另一个命名空间中声明的相同的类的名称不冲突
using System;
using test_space;
using test_space2;
namespace Test14
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
test_space.test t1=new test_space.test();
test_space2.test t2=new test_space2.test();
t1.func();
t2.func();
}
}
}
namespace test_space
{
class test
{
public void func()
{
Console.WriteLine("program");
}
}
}
namespace test_space2
{
class test
{
public void func()
{
Console.WriteLine("program2");
}
}
}using:指令告诉编译器随后的代码使用了指定命名空间中的名称,例如using System是使用了Console.WriteLine ("...")
嵌套命名空间
using System;
namespace Test14_2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
MyTest.Test.hello();
MyTest2.Test.hello();
}
}
namespace MyTest
{
public class Test
{
public static void hello()
{
Console.WriteLine("hello!");
}
}
}
}
namespace MyTest2
{
public class Test
{
public static void hello()
{
Console.WriteLine("hello2!");
}
}
}预处理指令:
预处理器指令指导编译器在实际编译开始之前对信息进行预处理,所有的预处理器指令都是以 # 开始。且在一行上,只有空白字符可以出现在预处理器指令之前。预处理器指令不是语句,所以它们不以分号(;)结束。一个预处理器指令必须是该行上的唯一指令。
C# 预处理器指令列表
| 预处理器指令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| #define | 它用于定义一系列成为符号的字符。 |
| #undef | 它用于取消定义符号。 |
| #if | 它用于测试符号是否为真。 |
| #else | 它用于创建复合条件指令,与 #if 一起使用。 |
| #elif | 它用于创建复合条件指令。 |
| #endif | 指定一个条件指令的结束。 |
| #line | 它可以让您修改编译器的行数以及(可选地)输出错误和警告的文件名。 |
| #error | 它允许从代码的指定位置生成一个错误。 |
| #warning | 它允许从代码的指定位置生成一级警告。 |
| #region | 它可以让您在使用 Visual Studio Code Editor 的大纲特性时,指定一个可展开或折叠的代码块。 |
| #endregion | 它标识着 #region 块的结束。 |
#define PI
#define PI2
using System;
namespace Test15
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// #if(PI)
// Console.WriteLine("123");
// #else
// Console.WriteLine("234");
// #endif
Program p=new Program();
p.test();
}
public void test()
{
#if(PI && !PI2)
Console.WriteLine("123");
#elif(!PI && PI2)
Console.WriteLine("234");
#else
Console.WriteLine("345");
#endif
}
}
}public void test2()
{
#if PI && PI2
//编译器遇到 #error 指令,就会给用户显示后面的文本,作为一条编译错误消息,然后会立即退出编译
#error "123"
#endif
Console.WriteLine("456");
} ![]()
public void test3()
{
#if PI && PI2
#endif
//编译器遇到 #warning 指令,会给用户显示 #warning 指令后面的文本,之后编译继续进行
#warning "234"
Console.WriteLine("45678");
}![]()
#define PI
#define PI2
using System;
namespace Test15
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// #if(PI)
// Console.WriteLine("123");//若PI不存在,则这条语句不编译
// #else
// Console.WriteLine("234");//若PI存在,则这条语句不编译
// #endif
Program p=new Program();
p.test5();
}
public void test()
{
#if(PI && !PI2)
Console.WriteLine("123");
#elif(!PI && PI2)
Console.WriteLine("234");
#else
Console.WriteLine("345");
#endif
}
public void test2()
{
#if PI && PI2
//编译器遇到 #error 指令,就会给用户显示后面的文本,作为一条编译错误消息,然后会立即退出编译
/*#error "123"*/
#endif
Console.WriteLine("456");
}
public void test3()
{
#if PI && PI2
#endif
//编译器遇到 #warning 指令,会给用户显示 #warning 指令后面的文本,之后编译继续进行
//#warning "234"
Console.WriteLine("45678");
}
public void test4()
{
//使用该指令使代码在屏幕上更好地布局
#region test4
// int x;
// double d;
#endregion
}
public void test5()
{
//用于改变编译器在警告和错误信息中显示的文件名和行号信息
#line 164 "123.cs"
// Core.cs, before the intermediate
// package mangles it.
// later on
#line default
}
//可以抑制或还原指定的编译警告,可以在类或方法级别执行,对抑制警告的内容和抑制的时间进行更精细的控制
#pragma warning disable 169
public class Test
{
int never;
}
#pragma warning restore 169
}
}正则表达式(略)
异常处理
using System;
namespace HzkTest16
{
class Program
{
private int r=0;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p=new Program();
p.div(25,0);
}
public void div(int num1,int num2)
{
try
{
r = num1/num2;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine(r);
}
}
}
}using System;
namespace Test16
{
class Program
{
private int r=0;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p=new Program();
p.div(25,0);
p.test();
}
public void div(int num1,int num2)
{
try
{
r = num1/num2;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine(r);
}
}
public void test()
{
MyException my=new MyException();
try
{
my.show();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
}
class MyException
{
private int num = 0;
public void show()
{
if(num==0)
{
throw (new MyException2("error"));
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("success");
}
}
}
class MyException2 : ApplicationException
{
public MyException2(string? message) : base(message)
{
}
}
}输入与输出
从根本上说,流是通过通信路径传递的字节序列,输入流用于从文件读取数据(读操作),输出流用于向文件写入数据(写操作)
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace Test17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FileStream f=new FileStream("test.dat",FileMode.OpenOrCreate,FileAccess.ReadWrite);
for (int i=1;i<=20;i++) {
f.WriteByte((byte)i);
}
f.Position = 0;//把文件当前位置重置为最开始的位置
for (int i=0;i<=20;i++) {
Console.Write(f.ReadByte()+" ");
}
f.Close();
}
}
}文本文件的读写
二进制文件的读写
Windows文件系统的操作
C#集合
C#泛型
C#多线程