一、bind、call、apply函数的实现
改变函数的执行上下文中的this指向,但不执行该函数(位于Function构造函数的原型对象上的方法)
Function.prototype.myBind = function (target) {
if (typeof this !== 'function') {
throw Error('myBind is not a function')
}
var that = this
var args1 = [...arguments].slice(1)
var func = function () {
var args2 = [..arguments].slice(1)
return that.apply(target || window, args1.concat(args2)) }
return func
}
Function.prototype.myCall = function (context=window) {
if (typeof this !== 'function') {
throw Error('myBind is not a function')
}
context.fn = this
var args = [...arguments].slice(1)
var result = context.fn(..args)
delete context.fn
return result
}
Function.prototype.myApply = function (context=window) {
if (typeof this !== 'function') {
throw Error('myApply is not a function')
}
context.fn = this
var result
if (argument[1]) {
result = context.fn(...arguments[1])
} else {
result = context.fn()
}
delete context.fn
return result
}
二、引用数据类型的深拷贝方法的实现
function cloneDeep (target) {
function checkType(target) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(target).slice(8, -1)
}
var result, checkedType = checkType(target)
if (checkedType === 'Array') {
result = []
} else if (checkedType === 'Object') {
result = {
}
} else {
return target
}
//递归遍历对象或数组中的属性值或元素为原始值为止
for (var key in target) {
if ( checkType(target[key]) === 'Array' || checkType(target[key]) === 'Object') {
result[key] = cloneDeep(target[key])
} else {
result[key] = target[key]
}
}
return result
}
思路:
- 输入需要深拷贝的目标target,输出深拷贝后的结果
- 通过Object.prototype.toString准确判断传入的目标target的数据类型,当target的数据类型为对象或者数组时,会对target进行递归遍历直至当遍历的数组或者对象中的数据全部为基本数据类型为止
三、数组flat函数的实现
Array.prototype.flat = function () {
var temp = []
function recurision (arr) {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let item = arr[i]
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
recurision(item)
} else {
temp.push(item)
}
}
}
recurision(this)
return temp
}
四、实现n的阶乘
分析:首先找规律,举例如3的阶乘等于321,也就是等于nn-1n-2的阶乘,也就是等于321的阶乘,计算到1的阶乘之后,整个计算过程才结束。分析到很容易想到通过递归来实现这个数的阶乘,因为第一,这个计算过程有规律可循,第二它有最终停止计算的出口,也就是当计算到1的时候就停止运算,以下通过递归来实现
function factorial (num) {
if (num < 0) {
throw new Error('负数没有阶乘')
}
if (num === 1 || num === 0) {
return 1
}
return num * factorial(num-1)
}
factorial(3) //6
五、实现斐波拉契数列
分析:按照上述阶乘的分析过程分析,这里不赘述
function fibonacci (n) {
//此方法应使用尾递归法进行优化,这里不作优化,简单实现
if ( n <= 1 ) {
return 1};
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);}
六、实现一个计算字符串字节长度的函数
分析:首先我们要知道英文的字节长度是1,而中文的字节长度是2,但是如何判断当前字符位是汉字还是英文呢,通过charCodeAt来判断当前字符位的unicode编码是否大于255,如何大于255则是汉字,那就给字符串的字节长度加2,如果小于255则是英文,就给字符串的字节长度加1,以下按照这个思路实现
function countBytesLength(str){
var length = 0
//首先遍历传入的字符串
for(var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (str[i].charCodeAt(i) > 255) {
length += 2
} else {
length++
}
}
return length
}
var str = 'DBCDouble陈'
countBytesLength(str) //11
七、实现isNaN函数
分析:要判断传入的值是否是"is not a number"(isNaN全拼),首先进行一个数字的隐式类型转换,通过Number包装类来实现Number(x),再判断Numberz(x)的返回值是否是NaN,如果是的话再与NaN进行比对,但是由于NaN虽然是number类型的,但是是不能进行比较的,所以我们先将Number(x)返回的结果变成字符串形式,再去判断,实现如下
function isNaN(num) {
var ret = Number(num)
ret += ''
if (ret === 'NaN') {
return true
}
return false
}
isNaN('123abc') // true
八、实现数组的push函数
分析:首先push函数是位于Array构造函数的原型对象上的方法,所以要在Array.prototype上去定义,然后再分析push函数的作用是往数组的末尾添加元素,可以添加任意个数的元素,并且最终返回数组的长度,实现代码如下
Array.prototype.push = function () {
for (var i = 0; i< arguments.length; i++) {
this[this.length] = arguments[i]
}
return this.length
}
九、实现能够识别所有数据类型的typeof
分析:首先typeof是位于window对象上的全局方法,所以我们定义完成之后要将其挂载到window上,其次要实现识别所有数据类型包括:基本数据类型和复杂数据类型(引用数据类型),我们需要通过Object.prototype.toString方法去做才唯一能够最准确判断当前值为什么数据类型,实现代码如下
window.typeof = function (value) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(val).slice(8, -1)
}
十、实现数组的去重方法
分析:首先因为是给所有数组实例实现一个去重方法,所以同样是在原型链上进行编程
Array.prototype.unique = function () {
//这里是利用对象键hash值的唯一性来去重
var obj = {
}
var result = []
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (!obj[this[i]]) {
obj[this[i]] = true
result.push(this[i])
}
}
return result
}
var arr = [1,2,2,3,3]
arr.unique() //[1,2,3]
Array.prototype.unique = function () {
//利用ES6的Array.prototype.includes
var result = []
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (!result.includes(this[i])) {
result.push(this[i])
}
}
return result
}
Array.prototype.unique = function () {
//利用ES6的Set
var result = new Set(this) //生成一个类数组
return Array.from(result) //通过Array.from将类数组转换成真正的数组
}
Array.prototype.unique = function () {
//利用Array.prototype.filter返回符合条件的元素
//利用Array.prototype.indexOf返回数组中第一次出现当前元素的索引值
//该方法写法最为优雅,一行代码搞定,函数式编程
return this.filter((item, index) => this.indexOf(item) === index)
}
十一、实现函数的防抖、节流
function debounce (fn, wait=300) {
var timer
return function () {
if (timer) {
clearTimeOut(timer)
}
timer = setTimeout({
fn.apply(this, arguments)
}, wait)
}
}
function throttle (fn, wait=300) {
var prev = +new Date()
return function () {
var now = +new Date()
if (prev - now > 300) {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
prev = now
}
}
}
十二、封装ajax
//封装ajax方法
function ajax (options) {
options = options || {
};
options.method = options.method || 'GET';
options.url = options.url || '';
options.async = options.async || true;
options.data = options.data || null;
options.success = options.success || function () {
};
var xhr = null;
if (XMLHttpRequest) {
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else {
xhr = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP');
}
xhr.open(options.method, options.url, options.async)
if (method === 'GET') {
xhr.send(null);
} else if (method === 'POST') {
xhr.send(options.data);
}
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (( (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304 ) && xhr.readyState === 4) {
options.success(xhr.responseText)
}
}}
十三、实现new操作符
//接受一个函数
//最后返回一个对象
function new (fn) {
return function () {
var obj = {
'__proto__': fn.prototype
}
fn.apply(obj, arguments)
return obj
}
}
十四、常用六种继承方式
1、原型链继承:子类型的原型对象为父类型的实例对象
function Person (name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setName = function () {
console.log(this.name)
}
function Student (height) {
this.height = height
}
Student.prototype = new Person()
var stu = new Student('175')
console.log(stu)
2、借用构造函数实现继承:在子类的构造函数中通过call调用父类的构造函数实现继承
function Person (name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setName = function () {
console.log(this.name)
}
function Student (height, age, name) {
Person.call(this, age, name)
this.height = height
}
var stu = new Student(175, 'cs', 24)
console.log(stu)
3、原型链+借用构造函数的组合继承方式:通过在子类构造函数中通过call调用父类构造函数,继承父类的属性并保留传参的优点,再通过将父类的实例作为子类的原型对象,实现继承
function Person (name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
function Son (sex, name, age) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
this.sex = sex
}
Son.prototype = new Person()
var son = new Son('男', 'DBCDouble', 25)
console.log(son)
4、寄生组合式继承(圣杯继承)
function Person (name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.setAge = function () {
}
function Son (sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
function F () {
}
F.prototype = Person.prototype
Son.prototype = new F()
Son.prototype.constructor = Son
var s1 = new Son()
console.log(s1)
十五、instanceof和typeof实现
window.instanceof = instance
window.typeof = typeof
//instanceof的原理,实际就是沿着L的__proto__属性查找是否存在R.prototype,
//直到L.__proto__指向null
function instanceof (L, R) {
var O = R.prototype
L = L.__proto__
while (true) {
if (L === null) {
return false
}
if (L === O) {
return true
}
L = L.__proto__
}
}
function typeof () {
//使用Object.prototype.toString实现
}
十六、JS面向对象笔试题 《实现Cash》
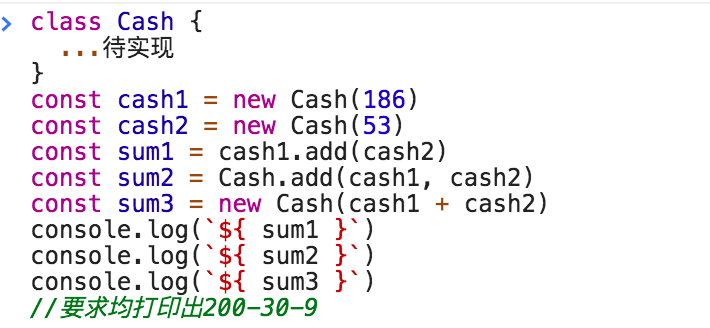
class Cash {
constructor (value) {
this.value = value
}
static add (...cashes) {
return new Cash(cashes.reduce((result, item) => result += item, 0))
}
add (...cashes) {
return Cash.add(this, ...cashes)
}
valueOf () {
return this.value
}
toString () {
const tempArr = String(this.value).split('')
const len = tempArr.length
return tempArr.map((item, index) => item * Math.pow(10, len - index - 1)).join('-')
}
}
作者:DBCdouble
链接:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903821651476493
来源:掘金
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。