写在前面:
笔记是因为考红帽所以整理的,主要是常用模块整理,后面有些类似考试的实战题目,还在完善中.. 额,不是教程,教程建议大家到下面的学习网站,适合温习用。
建议学习网站:Ansible文档:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/installation_guide/intro_installation.html
Ansible是一款简洁、高效的运维自动化工具。只需要将ansible安装在主控机器上,就可以通过SSH协议实现针对大量受管服务器的批量化、剧本化的管理。通过过Ansible实现远程控制,主控机=被控机,通过SSH实现。基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。主要包括:
- (1)、连接插件connection plugins:负责和被监控端实现通信;
- (2)、host inventory:指定操作的主机,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机;
- (3)、各种模块核心模块、command模块、自定义模块;
- (4)、借助于插件完成记录日志邮件等功能;
- (5)、playbook:剧本执行多个任务时,非必需可以让节点一次性运行多个任务。
Ansible概念
- 控制机(节点):任何安装了Ansible的计算机。您可以通过从任何控制节点调用
ansibleoransible-playbook命令来运行Ansible命令和剧本。您可以将安装了Python的任何计算机用作控制节点-便携式计算机,共享台式机和服务器都可以运行Ansible。但是,不能将Windows计算机用作控制节点。您可以有多个控制节点。
- 受管机(节点):您使用Ansible管理的网络设备(和/或服务器)。受管节点有时也称为“主机”。未在受管节点上安装Ansible。
- 主机清单:受管节点的列表。清单文件有时也称为“主机文件”。您的清单可以为每个受管节点指定诸如IP地址之类的信息。库存还可以组织受管节点,创建和嵌套组以便于扩展。
- 模块:执行代码单元Ansible。从管理特定类型的数据库上的用户到管理特定类型的网络设备上的VLAN接口,每个模块都有特定的用途。您可以通过任务调用单个模块,也可以在剧本中调用多个不同的模块。
- 任务:Ansible中的行动单位。您可以使用临时命令一次执行一个任务。
- 剧本:保存任务的有序列表,以便您可以按该顺序重复运行这些任务。剧本可以包含变量以及任务。剧本采用YAML编写,易于阅读,编写,共享和理解。
安装和配置ansible环境
学习环境:
查看yum 安装的文件位置 : rpm -ql yum包名字
我要用control去控制另外的四台node[1...5]机器,这五台机器都是linux虚拟机。默认我们设置了Ip。做好了主机名映射。

1、ansible安装
软件包:ansible、sshpass、python3-jinja2、python3-pyramiko等
# yum -y install ansible //装包# ansible --version //确认版本相关信息

需要的依赖包:

查看版本控制
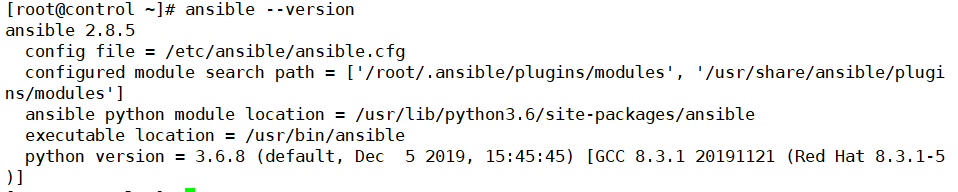
查看主机清单

[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 --list-hosts
hosts (1):
127.0.0.1
[root@control ~]# ansible all --list-hosts
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
implicit localhost does not match 'all'
hosts (0):
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m ping
127.0.0.1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m command -a 'uname -r'
127.0.0.1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
4.18.0-193.el8.x86_64
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m command -a 'echo "sy"'
127.0.0.1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
sy
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m command -a 'echo sy"'
ERROR! failed at splitting arguments, either an unbalanced jinja2 block or quotes: echo sy"
[root@control ~]#
Command 是默认模块,可以不写。OK。我们先简单尝试一下。
- 使用 ansible all --list-hosts 命令可以查看主机列表。
- 使用 ansible 127.0.0.1 -m ping 命令可以查看被控主机是否连接正常,这里使用ping模块
- 使用 ansible 127.0.0.1 -m command -a 'bash 命令' 命令可以执行bash命令,这里使用command模块,-m command 可以省略。
#查看主机清单
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 --list-hosts
hosts (1):
127.0.0.1
[root@control ~]# ansible all --list-hosts
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
implicit localhost does not match 'all'
hosts (0):
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m ping
127.0.0.1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m command -a 'uname -r'
127.0.0.1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
4.18.0-193.el8.x86_64
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m command -a 'echo "sy"'
127.0.0.1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
sy
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -m command -a 'echo sy"'
ERROR! failed at splitting arguments, either an unbalanced jinja2 block or quotes: echo sy"
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -u zhsan -a 'touch /zhanshan.txt'
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=touch rather than running
'touch'. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you can add
'warn: false' to this command task or set 'command_warnings=False' in
ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
127.0.0.1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@control ~]# useradd zhsan
[root@control ~]# echo 123456 | passwd --stdin zhsan
Changing password for user zhsan.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -u zhsan -a 'thuch /zhsan.file'
127.0.0.1 | FAILED | rc=2 >>
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'thuch': 'thuch'
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -u zhsan -a 'tonch /zhsan.file'
127.0.0.1 | FAILED | rc=2 >>
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'tonch': 'tonch'
[root@control ~]# ansible 127.0.0.1 -u zhsan -a 'touch /zhsan.file'
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=touch rather than running
'touch'. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you can add
'warn: false' to this command task or set 'command_warnings=False' in
ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
127.0.0.1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@control ~]# ansible node1 -m ping
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
[WARNING]: Could not match supplied host pattern, ignoring: node1
[root@control ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[root@control ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@control ~]# ansible node1 -m ping
node1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@control ~]# ssh node1
Last login: Thu Feb 11 01:18:11 2021 from 172.25.254.100
[root@node1 ~]# useradd lisi
[root@node1 ~]# echo 123456 | passwd --stdin lisi
Changing password for user lisi.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@node1 ~]# quit
-bash: quit: command not found
[root@node1 ~]# exit
logout
Connection to node1 closed.
[root@control ~]# ansible node1 -u lisi -k -a 'mkdir /tmp/lisidir'
SSH password:
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=directory rather than
running 'mkdir'. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you
can add 'warn: false' to this command task or set 'command_warnings=False' in
ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@control ~]# ansible node1 -u lisi -k -a 'mkdir /tmp/lisidir'
SSH password:
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=directory rather than
running 'mkdir'. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you
can add 'warn: false' to this command task or set 'command_warnings=False' in
ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
node1 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
mkdir: cannot create directory ‘/tmp/lisidir’: File existsnon-zero return code
ansible环境配置文件
- 全局配置:/etc/
- ansible/ansible.cfg(设置被管机,用户权限)
- 默认主机清单:/etc/ansible/hosts //存放受管主机列表
- 默认角色目录:/etc/ansible/roles //存放预设的各种任务角色资料
- 默认用户身份:root
- 扩展配置:
- ~/.ansible.cfg //用户配置,会覆盖全局配置
- ./ansible.cfg //工作目录配置(本文采用这种配置方式),会覆盖全局、用户配置
在用户目录下创建配置文件目录。ansible的默认解析配置文件的位置的优先级顺序是,(使用man ansible-config)
- 目录配置文件,
- 用户配置文件,
- 默认配置文件。

在alice的家目录下创建配置文件
在编写配置文件的时候,我们可以参考默认的配置文件编写:
使用 ctrl + z 将当前vim挂到后台,然后打开默认配置文件的 vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg ,copy到需要的之后,ctrl + z 挂到后台,然后使用 fg 1 打开挂到后台的之前的vim。

主配置文件 vim ansible.cfg
[defaults]
# 主机清单文件,就是要控制的主机列表
inventory=inventory
# 连接受管机器的远程的用户名
remote_user=alice
# 角色目录
roles_path=roles
# 设置用户的su 提权
[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False

主机清单:
被控机列表,可以是 域名,IP,分组([组名]),聚合([组名:children]),也可以主动的设置用户名密码
[test01] # 创建组,名字是test01
node1 # test01组中的成员
node2 # test01组中的成员
[test02] # 再创建组,名字是test02
node[3:4] # test02组中的成员
[web:children] # 创建嵌套组,组名是web,后面:children是关键字,表示该组可以包含其他组
test01 # web组中包含的其他组
test02
node1 ansible_ssh_user-lisi ansible_ssh_password=123456 ansible_ssh_port=2222 #主动设置用户名密码
[alice@control ansible]$ cat ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory=invertory
remote_user=alice
roles_path=roles
[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False
[alice@control ansible]$ vim invertory
[alice@control ansible]$ cat invertory
[test01]
node1
[test02]
node2
[web]
node[3:4]
[test05]
node5
[webtest:children]
web
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test01 --list-hosts
hosts (1):
node1
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test02 --list-hosts
hosts (1):
node2
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible web --list-hosts
hosts (2):
node3
node4
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible webtest --list-hosts
hosts (2):
node3
node4
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test05 --list-hosts
hosts (1):
node5
[alice@control ansible]$
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible localhost -m ping //检测对本机的可控性(应返回pong)
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible all -m ping //检测对所有清单主机的可控性
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible websvrs -m ping //检测对websvrs组内各主机的可控性
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1,node5 -m ping //检测node1和node2的可控性
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node* -m ping //检测node开头的主机的可控性
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible websvrs[0] -m ping //检测websvrs组中第1个主机的可控性
测试一下:

受管机接受控制的方式:
- a. 受管机提供root用户+密码
- b. 受管机提供已授sudo特权的普通用户(比如alice)
使用用户名密码的方式实现 ansible 远程控制
[root@control ~]# ansible node1 -u lisi -k -b -a 'mkdir /tmp/lisidir1'
SSH password:
node1 | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "Invalid/incorrect password: Permission denied, please try again.",
"unreachable": true
}
[root@control ~]# ansible node1 -u lisi -k -b -a 'mkdir /tmp/lisidir1'
SSH password:
node1 | FAILED | rc=-1 >>
Missing sudo password
[root@control ~]# ansible localhost -m ping
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@control ~]# ansible node1 -m ping
node1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@control ~]# ansible all --list-hosts
hosts (1):
node1
[root@control ~]#
sudo 提权:sudo提权设置
受管机接受控制的方式:
- a. 受管机提供root用户+密码
- b. 受管机提供已授sudo特权的普通用户(比如alice)
# visudo
alice ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL[zhsan@control /]$ ls
bin cemo etc lib media opt root sbin sys usr zhanshan.txt
boot dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var zhsan.file
[zhsan@control /]$ mkdir /demo
mkdir: cannot create directory ‘/demo’: Permission denied
[zhsan@control /]$ sudo mkdir /demo
[zhsan@control /]$ ls
bin demo home media proc sbin tmp zhanshan.txt
boot dev lib mnt root srv usr zhsan.file
cemo etc lib64 opt run sys var
[zhsan@control /]$ ls -l demo*
total 0
[zhsan@control /]$ ls -l /demo*
total 0
[zhsan@control /]$ ls -lhd /demo*
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Feb 11 08:33 /demo
[zhsan@control /]$ date
Thu Feb 11 08:34:06 CST 2021
[zhsan@control /]$
SSH免密登录
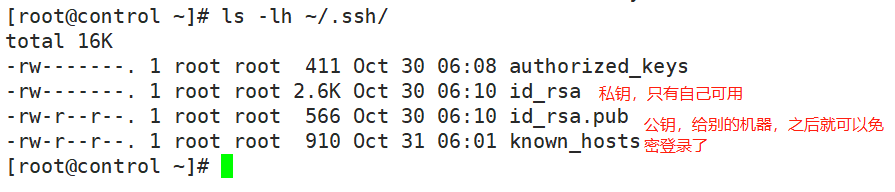

使用ssh-keygen生成密钥,使用特定的用户执行
[root@control ~]# su - alice
Last login: Sat Oct 31 06:02:41 CST 2020 on pts/0
[alice@control ~]$ ssh node1
Last login: Fri Oct 30 14:54:47 2020
[alice@node1 ~]$ exit
logout
Connection to node1 closed.
[alice@control ~]$ ssh node2
Last login: Fri Oct 30 14:55:04 2020
[alice@node2 ~]$ exit
logout
Connection to node2 closed.
[alice@control ~]$
创建和运行Ansible
ansible管理方式(adhoc、playbook)
adhoc方式(临时命令):
直接使用ansible命令,调用xx模块来完成远程运维任务(类似于手动执行Linux命令)
adhoc方式基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机地址列表 -m 模块名 [-a '任务参数']playbook方式:
提前写好任务剧本,需要由ansible-playbook工具加载批量执行(类似于使用Shell脚本)
通过ansible-doc获取模块帮助
等号必须,减号可选。EXAMPLES: 各模块文档都有剧本应用示范
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-doc -l //列出所有可用模块
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-doc -l | grep yum //列出名称包含yum的模块
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-doc yum_repository //查看yum_repository模块的说明文档
.. ..
EXAMPLES: //各模块文档都有剧本应用示范
- name: Add repository
yum_repository:
name: epel
description: EPEL YUM repo
baseurl: https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/$releasever/$basearch/
.. ..ansible常用模块
使用万能command/shell模块/script模块,推送命令行
command模块:
缺省模块,向受管主机发送简单命令行,不支持管道/重定向/通配符等高级特性
shell模块:
向受管主机发送复杂命令行,支持管道/重定向/通配符等特性
script模块:
将本地的脚本拷贝到远程主机执行
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -a 'ip add list eth0' //查看node1的IP地址
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible -m command node1 -a 'ip add list eth0' //查看node1的IP地址
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible -m shell node1 -a 'echo hello > /root/a.file' //在node1上创建一个文件
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -a 'cat /root/a.file' //查看node1上的文件内容
[alice@control ansible]$ cat aa.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "Welcome to $(hostname)"
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m script -a './aa.sh' //将./aa.sh文件拷贝到受控机运行
node1 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to node1 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to node1 closed."
],
"stdout": "Welcome to node1\r\n",
"stdout_lines": [
"Welcome to node1"
]
}
使用yum_repository模块,配置软件源
基本用法:等号之间不能有空格。
# ansible 清单主机 -m yum_repository [-a '任务参数']- file="文件名" //指定新生成的yum源配置文件名(不含 .repo 后缀的部分)
- name="源ID" //如果省略file,则文件名使用name的名称
- description="源的描述"
- baseurl="源的URL访问地址"
- gpgcheck="yes|no" //是否开启签名检查
- gpgkey="软件签名密钥文件地址"
编写脚本 /home/alice/ansible/adhoc.sh,用来为所有受管机配置 2 个 yum 仓库。
[alice@control ansible]$ vim yumdoc.sh
#!/bin/bash
ansible node1,node2 -m yum_repository -a 'name=BASH description="sofware base" baseur.lab0.example.com/rhel8/BaseOS gpgcheck=yes gpgkey=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8edhat-release enabled=yes'
ansible node1,node2 -m yum_repository -a 'name=STREAM description="sofware stream" //study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/Appstream gpgcheck=yes gpgkey=http://study.lab0.examplM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release enabled=yes'
[alice@control ansible]$ ls
ansible.cfg invertory yumdoc.sh
[alice@control ansible]$ chmod +x yumdoc.sh
[alice@control ansible]$ ./yumdoc.sh
我们开了两台机器node1,node2,所以其他的机器都报错。

软件管理模块(yum/dnf)
- ++ name:软件名、软件名-版本号、逗号分隔的列表、@组名、*通配符
- ++ state:present、absent,
- ++ list:软件名、installed、available



装包:
将 php 和 tftp 软件包安装到 test01、test02 主机组中的主机上
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test01,test02 -m yum -a 'pkg=php,tftp state=installed'
node1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Installed: php",
"Installed: tftp",
"Installed: apr-util-openssl-1.6.1-6.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: php-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: httpd-2.4.37-21.module+el8.2.0+5008+cca404a3.x86_64",
"Installed: php-cli-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: mod_http2-1.11.3-3.module+el8.2.0+4377+dc421495.x86_64",
"Installed: php-common-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: httpd-filesystem-2.4.37-21.module+el8.2.0+5008+cca404a3.noarch",
"Installed: mailcap-2.1.48-3.el8.noarch",
"Installed: apr-1.6.3-9.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: php-fpm-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: apr-util-1.6.1-6.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: redhat-logos-httpd-81.1-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: apr-util-bdb-1.6.1-6.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: tftp-5.2-24.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: httpd-tools-2.4.37-21.module+el8.2.0+5008+cca404a3.x86_64",
"Installed: nginx-filesystem-1:1.14.1-9.module+el8.0.0+4108+af250afe.noarch"
]
}
node2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Installed: php",
"Installed: tftp",
"Installed: apr-util-openssl-1.6.1-6.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: httpd-2.4.37-21.module+el8.2.0+5008+cca404a3.x86_64",
"Installed: php-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: mod_http2-1.11.3-3.module+el8.2.0+4377+dc421495.x86_64",
"Installed: php-cli-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: php-common-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: httpd-filesystem-2.4.37-21.module+el8.2.0+5008+cca404a3.noarch",
"Installed: php-fpm-7.2.24-1.module+el8.2.0+4601+7c76a223.x86_64",
"Installed: mailcap-2.1.48-3.el8.noarch",
"Installed: apr-1.6.3-9.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: apr-util-1.6.1-6.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: redhat-logos-httpd-81.1-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: apr-util-bdb-1.6.1-6.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: tftp-5.2-24.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: httpd-tools-2.4.37-21.module+el8.2.0+5008+cca404a3.x86_64",
"Installed: nginx-filesystem-1:1.14.1-9.module+el8.0.0+4108+af250afe.noarch"
]
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test01,test02 -m yum -a 'pkg=php,tftp state=installed'
node1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Nothing to do",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Installed: php",
"Installed: tftp"
]
}
node2 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Nothing to do",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Installed: php",
"Installed: tftp"
]
}
装一个包组:
将 RPM Development Tools 软件包组安装到 test01 主机组中的主机上
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -a 'yum grouplist'
[WARNING]: Consider using the yum module rather than running 'yum'. If you nee
use command because yum is insufficient you can add 'warn: false' to this comman
task or set 'command_warnings=False' in ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Unable to read consumer identity
This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use suption-manager to register.
Last metadata expiration check: 0:47:34 ago on Sat 13 Feb 2021 02:10:18 PM CST.
Available Environment Groups:
Server with GUI
Server
Workstation
Custom Operating System
Virtualization Host
Installed Environment Groups:
Minimal Install
Available Groups:
Legacy UNIX Compatibility
Container Management
Development Tools
.NET Core Development
Graphical Administration Tools
Headless Management
Network Servers
RPM Development Tools
Scientific Support
Security Tools
Smart Card Support
System Tools
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m yum -a 'pkg=@RPM Development Tools'
ERROR! this task 'yum' has extra params, which is only allowed in the following modules: group_by, include_tasks, include_role, raw, command, shell, import_role, import_tasks, script, win_command, include, meta, include_vars, add_host, win_shell, set_fact
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m yum -a 'pkg="@RPM Development Tools" state=installed '
node1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Group rpm-development-tools installed.",
"Installed: rpm-build-4.14.2-37.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Net-SSLeay-1.88-1.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: patch-2.7.6-11.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: libatomic_ops-7.6.2-3.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: rpmdevtools-8.10-7.el8.noarch",
"Installed: elfutils-0.178-7.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: bzip2-1.0.6-26.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: libbabeltrace-1.5.4-2.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-srpm-macros-1-25.el8.noarch",
"Installed: python-srpm-macros-3-38.el8.noarch",
"Installed: emacs-filesystem-1:26.1-5.el8.noarch",
"Installed: unzip-6.0-43.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-IO-Socket-SSL-2.066-4.el8.noarch",
"Installed: dwz-0.12-9.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-libnet-3.11-3.el8.noarch",
"Installed: gdb-headless-8.2-11.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Carp-1.42-396.el8.noarch",
"Installed: efi-srpm-macros-3-2.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Data-Dumper-2.167-399.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: libtool-ltdl-2.4.6-25.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Encode-4:2.97-3.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Errno-1.28-416.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Exporter-5.72-396.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-File-Path-2.15-2.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-File-Temp-0.230.600-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Getopt-Long-1:2.50-4.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-HTTP-Tiny-0.074-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-IO-1.38-416.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: zstd-1.4.2-2.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-MIME-Base64-3.15-396.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-PathTools-3.74-1.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Pod-Escapes-1:1.07-395.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Pod-Perldoc-3.28-396.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Pod-Simple-1:3.35-395.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Pod-Usage-4:1.69-395.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Scalar-List-Utils-3:1.49-2.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Socket-4:2.027-3.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Storable-1:3.11-3.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: zip-3.0-23.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: qt5-srpm-macros-5.12.5-3.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Term-ANSIColor-4.06-396.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Term-Cap-1.17-395.el8.noarch",
"Installed: guile-5:2.0.14-7.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-Text-ParseWords-3.30-395.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Text-Tabs+Wrap-2013.0523-395.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Time-Local-1:1.280-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Unicode-Normalize-1.25-396.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-constant-1.33-396.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-interpreter-4:5.26.3-416.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-IO-Socket-IP-0.39-5.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-libs-4:5.26.3-416.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-macros-4:5.26.3-416.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-parent-1:0.237-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-podlators-4.11-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-threads-1:2.21-2.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: perl-threads-shared-1.58-2.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: ghc-srpm-macros-1.4.2-7.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-URI-1.73-3.el8.noarch",
"Installed: gc-7.6.4-3.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: go-srpm-macros-2-16.el8.noarch",
"Installed: redhat-rpm-config-122-1.el8.noarch",
"Installed: libipt-1.6.1-8.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: ocaml-srpm-macros-5-4.el8.noarch",
"Installed: tar-2:1.30-4.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: python3-rpm-macros-3-38.el8.noarch",
"Installed: rust-srpm-macros-5-2.el8.noarch",
"Installed: binutils-2.30-73.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: openblas-srpm-macros-2-2.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Digest-1.17-395.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Mozilla-CA-20160104-7.el8.noarch",
"Installed: perl-Digest-MD5-2.55-396.el8.x86_64"
]
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m yum -a 'pkg="@RPM Development Tools" state=installed '
node1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Nothing to do",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Group rpm-development-tools installed."
]
}
[alice@control ansible]$
包升级更新:
将 test01、02 主机组中的主机上所有软件包升级到最新版本
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test01,test02 -m yum -a 'pkg=* state=latest'
node1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Nothing to do",
"rc": 0,
"results": []
}
node2 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Nothing to do",
"rc": 0,
"results": []
}
[alice@control ansible]$ 文件管理模块(file/copy/template)
file模块:
创建目录/文件/链接文件(不包括内容)|| ===》path、state、src、owner、group、mode
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m file -a '任务参数'- ++ path="新文件路径" //指定要创建的新文件路径(必选参数)
- ++ state="directory|touch|link" //新文件的类型为目录|空文件|链接文件
- ++ src="被链接的原始文件路径" //如果是创建符号链接文件,需要指定此参数
- ++ force="yes|no" //目标文件已存在时是否替换,或者被链接文件不存在时是否仍然创建链接
- ++ owner=属主 //指定新文件的属主
- ++ group=属组 //指定新文件的属组
- ++ mode=权限标记 //指定新文件的权限
- ++ setype=SELinux类型 //指定新文件的SELinux标签类型

[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m file -a 'name=/a.txt state=file'
node1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/a.txt",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:etc_runtime_t:s0",
"size": 0,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m file -a 'src=/ path=/linkroot state=link'
node1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/linkroot",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:root_t:s0",
"size": 1,
"src": "/",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
[alice@control ansible]$
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m file -a 'src=/ path=/linkroot state=absent
[WARNING]: The src option requires state to be 'link' or 'hard'. This will become a
error in Ansible 2.10
node1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/linkroot",
"state": "absent"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m file -a 'path=mulu state=directory mode=0750'
node1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0750",
"owner": "root",
"path": "mulu",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m file -a 'path=mulu state=directory owner=alice'
node1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0750",
"owner": "alice",
"path": "mulu",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 1000
}
- 创建目录/webdev,常规权限为 rwxrwxr-x,具有 SetGID 特殊权限


- 使用符号链接/var/www/html/webdev 链接到/webdev 目录

copy模块:
复制目录/文件、创建指定内容(content 建议少量文本)的文件:|| ===》src、dest、force、owner、group、mode
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m copy -a '任务参数'- ++ dest="目标文件路径" //指定拷贝到远程后的新文件路径(必选参数)
- ++ content="文本内容" //指定要拷贝的文本内容
- ++ src="原始文件路径" //指定要拷贝的本地文件路径
- ++ force="yes|no" //目标文件已存在时是否替换
- ++ owner=属主 //指定新文件的属主
- ++ group=属组 //指定新文件的属组
- ++ mode=权限标记 //指定新文件的权限
- ++ setype=SELinux类型 //指定新文件的SELinux标签类型




template模块:
根据模板文件(适合多行文字)在被控机上生成指定的新文件,使用template模块,从模板上传文件
- src=模板文件路径 //指定被复制的本地文件(必选参数)
- dest=目标文件路径 //指定上传到目标主机的新文件(必选参数)
- force="yes|no" //目标文件已存在时是否替换
- owner=属主 //指定新文件的属主
- group=属组 //指定新文件的属组
- mode=权限标记 //指定新文件的权限
- setype=SELinux类型 //指定新文件的SELinux标签类型
# ansible 清单主机 -m template -a '任务参数'[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m template -a 'src=welcome.html dest=/tmp/welcome.html mode=644 force=yes'
.. .. //上传文件到主机node1,强制覆盖
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -a 'ls -lh /tmp/welcome.html'
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 23 Apr 17 07:22 /tmp/welcome.html
.. .. //检查结果
- 创建文件/webdev/index.html,内容是 It's works!

用户管理模块(user/group)
user模块:
添加/修改/删除用户账号,设置密码
参数:name、state、uid、groups、append、remove、password
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m user -a '任务参数'- name="登录名" //指定用户名(必选参数)
- password="加密的密码串" //一般使用 { {'123456'|password_hash('sha512')}} 形式
- uid="用户ID号" //指定用户的UID
- group="基本组名" //指定用户的基本组名
- groups="附属组名" //将用户添加到xx附属组,结合append=yes
- append="yes|no"//是否向xx组追加此用户,如果选no用户只属于这个组
- state="present|absent" //创建|删除用户(缺省值为present)
- force="yes|no" //是否强制删除用户,即使此用户已经登录
- remove="yes|no" //删除用户时是否同时删除家目录

|| password={ {"明文密码" | password_hash("sha512")}}

[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m user -a 'name=dongfang uid=1234 groups=users append=yes'
.. .. //添加新用户,加入到users组
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m user -a "name=bubai password={
{' 123456'|password_hash('sha512') }}"
.. .. //添加新用户并设置密码
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m user -a 'name=dongfang state=absent remove=yes'
.. .. //删除用户group模块
添加/修改/删除组账号|| name、state、gid
- ++ setype="SELinux标签类型" //指定标签类型(必选参数),比如网页内容 httpd_sys_content_t
- ++ target="目录路径" //指定要设置的目录路径
- ++ state="present|absent" //添加|取消上下文标记(缺省值为present)


服务控制模块(service)
代替systemctl 指令来控制服务的启动/停止/重启、开机自启动状态的设置
参数: name、state、enabled
- name=服务名 //指定系统服务名(必选参数)
- state="started|stoped|restarted|reloaded" //启动|停止|重启|重载服务
- enable="yes|no" //是否开机自启
# ansible 清单主机 -m service -a '任务参数'[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m service -a "name=crond state=restarted enabled=yes"
.. .. //重启crond服务,并设置开机自启
练习 —— 从control把node2远程部署一个支持PHP网页的Web服务器
- 1)为主机node2安装httpd、php这两个包
- 2)为主机node2准备网页 /var/www/html/index.php,内容如下:LIRUILONG。。。
- 3)为主机node2启动httpd服务、关闭firewalld服务
- 4)从server1上浏览器访问 http://node2.net0.example.com
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=installed'
node2 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Nothing to do",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Installed: httpd"
]
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m copy -a 'content="LIRUILONG I LOVE .." dest=/var/www/html/index.php'
node2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "fc99d7c0185aef310990bb4c4e153c353921f25c",
"dest": "/var/www/html/index.php",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "8ac9bcd94020e2284a3522af4a13d1a3",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0",
"size": 19,
"src": "/home/alice/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1613309455.7519739-91578945277811/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=yes'
node2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "started",
"status": {
"ActiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveState": "inactive",
"After": "remote-fs.target -.mount network.target nss-lookup.target systemd-journald.socket tmp.mount systemd-tmpfiles-setup.service system.slice basic.target httpd-init.service sysinit.target",
"AllowIsolate": "no",
...
}
}
[alice@control ansible]$ curl http://node2/
curl: (7) Failed to connect to node2 port 80: No route to host
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m service -a 'name=firewalld state=stopped enabled=no'
node2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"enabled": false,
"name": "firewalld",
"state": "stopped",
"status": {
"ActiveEnterTimestamp": "Sun 2021-02-14 20:59:54 CST",
"ActiveEnterTimestampMonotonic": "99056499",
"ActiveExitTimestampMonotonic": "0",
"ActiveState": "active",
"After": "basic.target sysinit.target polkit.service system.slice dbus.socket dbus.service",
"AllowIsolate": "no",
}
}
[alice@control ansible]$ curl http://node2/
LIRUILONG I LOVE ..[alice@control ansible]$
安全控制模块(firewalld/sefcontext)
1. firewalld模块
- Linux防火墙服务 firewalld,默认是开启的
- 防火墙规则的作用范围:运行时(临时)、永久(重启后仍有效)
- 默认安全区使用的 public (仅允许ping本机、SSH远程连本机,拒绝其他几乎任何访问)
2.其他常用安全区:
- trusted 信任区(允许任何访问,办公区域,允许SSH、Samba少数几个服务)
- block 阻塞区(阻止任何访问)
- drop 丢弃区(丢弃任何来访数据包)
|| firewall-cmd --get-default-zone ==》查看当前使用的默认安全区
|| firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=区域名 ==》设置默认使用哪一个安全区
预设保护服务:
http、https、dns……
防火墙管理工具:
firewall-cmd、firewall-config
防火墙规则的作用范围:
++ 运行配置 —— 当前有效,重启firewalld服务后失效
++ 永久配置 —— 当前无效,重启firewalld服务后有效 ,通过添加 --permanent 选项设置
++ 在默认使用public安全区的情况下,如何管理防火墙规则
- 如何开放xx服务(执行firewall-cmd --get-services 了解防火墙预设的服务有哪些)
- 命令行 firewall-cmd --add-service=服务名
- 如何开放xx端口(端口号/协议)
- 命令行 firewall-cmd --add-port=端口号/协议
- 如何封锁一个网段
- 命令行 firewall-cmd --add-source=来源IP地址或网段地址 --zone=drop
++ 常用参数:permanent(永久开启)、port(端口)、service(服务)、source、state、immediate(立即生效)

2. sefcontext模块
sefcontext ==》设置文件的SELinux安全上下文/属性
- 查看文档的安全属性:ls -Z /var/www
- 设置指定目录允许作为网页目录 semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /网页目录的路径
基本用法:
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m sefcontext -a "target='/webdev(/.*)?' setype=httpd_sys_content_t state=present"
.. .. //将node1的/webdev目录设置为网页目录ansible node2 -m yum -a 'name=policycoreutils-python-utils state=present'
yum provides semanage
ansible node2 -m sefcontext -a 'path="/webdev(/.*)?" setype=httpd sys content t'
ansible node2 -a 'restorecon -R /webdev'练习:
- 1)为node2创建新目录 /webdev
- 2)确认node2上 /webdev目录的安全属性
- 3) 通过sefcontext去修改node2主机上 /webdev 目录的安全属性(结合restorecon命令)
- 4)确认node2上 /webdev目录的安全属性
- 5)为node2部署网页 /webdev/index.html,内容为"SELinux Test"
- 6)访问 http://node2/webdev/ 时能看到上述网页内容
方法一:直接关闭SELinux属性
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m file -a 'name=/webdev state=directory'
node2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/webdev",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m file -a 'name=/webdev state=directory'
node2 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/webdev",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -a 'ls -lZd /webdev /var/www/html'
node2 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 23 Feb 14 21:30 /var/www/html
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 6 Feb 15 10:15 /webdev
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -a 'setenforce 0'
node2 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[alice@control ansible]$ curl http://node2/webdev/
SElinux Love[alice@controansible node2 -a 'cat /var/www/html/webdev/index.html'
node2 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
SElinux Love
[alice@control ansible]$ curl http://node2/webdev/
SElinux Love[alice@control ansible]$
方法二,通过sefcontext修改SElinux权限设置。
ansible node2 -m yum -a 'name=policycoreutils-python-utils state=present'
yum provides semanage
ansible node2 -m sefcontext -a 'path="/webdev(/.*)?" setype=httpd sys content t'
ansible node2 -a 'restorecon -R /webdev'
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m yum -a 'name=policycoreutils-python-utils state=present'
node2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Installed: policycoreutils-python-utils",
"Installed: python3-setools-4.2.2-2.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: policycoreutils-python-utils-2.9-9.el8.noarch",
"Installed: python3-libsemanage-2.9-2.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: python3-policycoreutils-2.9-9.el8.noarch",
"Installed: checkpolicy-2.9-1.el8.x86_64",
"Installed: python3-audit-3.0-0.17.20191104git1c2f876.el8.x86_64"
]
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m sefcontext -a 'path="/webdev(/.*)?" setype=httpd_sys_content_t'
node2 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"ftype": "a",
"serange": "s0",
"setype": "httpd_sys_content_t",
"seuser": "system_u",
"state": "present",
"target": "/webdev(/.*)?"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -a 'restorecon -R /webdev'
node2 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[alice@control ansible]$ curl http://node2/webdev/
SElinux Love[alice@control ansible]$

磁盘管理模块(parted/lvg/lvol/filesystem)
parted模块:
规划硬盘的分区,device、number、state、part_start、part_end
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m parted -a '任务参数'- device="磁盘设备" //指定操作的磁盘设备(必选参数)
- label="gpt|msdos" //新磁盘分区表类型
- number="分区编号" //指定分区编号
- part_start="起始位置" //指定新建分区的起始位置
- part_end="起始位置" //指定 新建分区的结束位置
- state="present|absent|info" //创建|删除|查看信息
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb state=info'
node2 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"disk": {
"dev": "/dev/vdb",
"logical_block": 512,
"model": "Virtio Block Device",
"physical_block": 512,
"size": 1048576.0,
"table": "gpt",
"unit": "kib"
},
"partitions": [
{
"begin": 1024.0,
"end": 684032.0,
"flags": [],
"fstype": "",
"name": "primary",
"num": 1,
"size": 683008.0,
"unit": "kib"
}
],
"script": "unit 'KiB' print"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m ping
node4 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb state=info'
node4 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"disk": {
"dev": "/dev/vdb",
"logical_block": 512,
"model": "Virtio Block Device",
"physical_block": 512,
"size": 2097152.0,
"table": "unknown",
"unit": "kib"
},
"partitions": [],
"script": "unit 'KiB' print"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb state=
present number=1 part_start=0% part_end=300MiB'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"disk": {
"dev": "/dev/vdb",
"logical_block": 512,
"model": "Virtio Block Device",
"physical_block": 512,
"size": 2097152.0,
"table": "msdos",
"unit": "kib"
},
"partitions": [
{
"begin": 1024.0,
"end": 307200.0,
"flags": [],
"fstype": "",
"name": "",
"num": 1,
"size": 306176.0,
"unit": "kib"
}
],
"script": "unit KiB mklabel msdos mkpart primary 0% 300MiB"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb state=info'
node4 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"disk": {
"dev": "/dev/vdb",
"logical_block": 512,
"model": "Virtio Block Device",
"physical_block": 512,
"size": 2097152.0,
"table": "msdos",
"unit": "kib"
},
"partitions": [
{
"begin": 1024.0,
"end": 307200.0,
"flags": [],
"fstype": "",
"name": "",
"num": 1,
"size": 306176.0,
"unit": "kib"
}
],
"script": "unit 'KiB' print"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'lsblk'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 50G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─vda2 252:2 0 49G 0 part
├─rhel-root 253:0 0 46.9G 0 lvm /
└─rhel-swap 253:1 0 2.2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
vdb 252:16 0 2G 0 disk
└─vdb1 252:17 0 299M 0 part
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb state=absent'
node4 | FAILED! => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "state is absent but all of the following are missing: number"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb number=1 state=absent'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"disk": {
"dev": "/dev/vdb",
"logical_block": 512,
"model": "Virtio Block Device",
"physical_block": 512,
"size": 2097152.0,
"table": "msdos",
"unit": "kib"
},
"partitions": [],
"script": "rm 1"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'lsblk'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 50G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─vda2 252:2 0 49G 0 part
├─rhel-root 253:0 0 46.9G 0 lvm /
└─rhel-swap 253:1 0 2.2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
vdb 252:16 0 2G 0 disk
[alice@control ansible]$
lvg模块:
管理卷组,vg、pvs、pesize、state
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m lvg -a '任务参数'- vg="卷组名" //指定操作的卷组名(必选参数)
- state="present|absent" //创建|删除卷组
- force="yes|no" //是否强制删除卷组(即使有逻辑卷)
- pvs="物理卷列表" //新建卷组时,指定由哪些物理设备组成
- pesize="PE大小" //指定Physical Extent的大小
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'lsblk'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 50G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─vda2 252:2 0 49G 0 part
├─rhel-root 253:0 0 46.9G 0 lvm /
└─rhel-swap 253:1 0 2.2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
vdb 252:16 0 2G 0 disk
├─vdb1 252:17 0 299M 0 part
└─vdb2 252:18 0 700M 0 part
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m lvg -a 'vg=redhat pvs=/dev/vdb2'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'lsblk'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 50G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─vda2 252:2 0 49G 0 part
├─rhel-root 253:0 0 46.9G 0 lvm /
└─rhel-swap 253:1 0 2.2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
vdb 252:16 0 2G 0 disk
├─vdb1 252:17 0 299M 0 part
└─vdb2 252:18 0 700M 0 part
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'vgscan'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Found volume group "redhat" using metadata type lvm2
Found volume group "rhel" using metadata type lvm2
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m lvg -a 'vg=redhat pvs=/dev/vdb2 start=absent'
node4 | FAILED! => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Unsupported parameters for (lvg) module: start Supported parameters include: force, pesize, pv_options, pvs, state, vg, vg_options"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m lvg -a 'vg=redhat pvs=/dev/vdb2 state=absent'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'vgscan'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Found volume group "rhel" using metadata type lvm2
lvol模块:
管理逻辑卷,lv、size、vg、state、force
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m lvol -a '任务参数'- ++ lv="逻辑卷名" //指定操作的逻辑卷名(必选参数)
- ++ size="逻辑卷大小" //指定逻辑卷大小
- ++ vg="卷组名" //指定逻辑卷所在卷组
- ++ state="present|absent" //创建|删除逻辑卷
- ++ force="yes|no" //是否强制删除或调整逻辑卷大小
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m lvg -a 'vg=redhat pvs=/dev/vdb2 state=present pesize=300MiB'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'vgscan'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Found volume group "redhat" using metadata type lvm2
Found volume group "rhel" using metadata type lvm2
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m lvol -a 'lv=rhcsa size=200M vg=redhat start=present'
node4 | FAILED! => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": "Unsupported parameters for (lvol) module: start Supported parameters include: active, force, lv, opts, pvs, resizefs, shrink, size, snapshot, state, thinpool, vg"
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m lvol -a 'lv=rhcsa size=200M vg=redhat state=present'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"msg": ""
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'lvscan'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
ACTIVE '/dev/redhat/rhcsa' [300.00 MiB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/rhel/swap' [2.16 GiB] inherit
ACTIVE '/dev/rhel/root' [<46.84 GiB] inherit
[alice@control ansible]$
filesystem:格式化,dev、fstype、force
# ansible 清单主机 -m filesystem -a '任务参数'- dev="逻辑卷名" //指定要格式化的设备路径(必选参数)
- fstype="文件系统类型" //指定格式化类型(xfs、ext4等)
- force="yes|no" //是否强制格式化(即使已经有文件系统)
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'blkid /dev/redhat/rhcsa'
node4 | FAILED | rc=2 >>
non-zero return code
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m filesystem -a 'dev=/dev/redhat/rhcsa fstype=ext3'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'blkid /dev/redhat/rhcsa'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
/dev/redhat/rhcsa: UUID="a25eff1d-31c8-4568-b01b-4f9fd2da23b5" SEC_TYPE="ext2" TYPE="ext3"
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -m filesystem -a 'dev=/dev/redhat/rhcsa fstype=xfs force=yes'
node4 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node4 -a 'blkid /dev/redhat/rhcsa'
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
/dev/redhat/rhcsa: UUID="54cf0807-92cd-4aeb-ba40-47b4e9e30dba" TYPE="xfs"
[alice@control ansible]$
练习:
- 1)为node4的/dev/vdb建立2个分区,分别300M、700M。
- 2)使用node4的/dev/vdb2创建一个名为redhat的卷组。
- 3)在node4上的redhat卷组中创建一个200M、名为rhcsa的逻辑卷。
- 4)将node4上的逻辑卷/dev/redhat/rhcsa格式为xfs文件系统。
ansible node4 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb state=present number=1 part_start=0% part_end=300MiB'
ansible node4 -m parted -a 'device=/dev/vdb state=present number=2 part_start=300MiB part_ end=1000MiB'
ansible node4 -m lvg -a 'vg=redhat pvs=/dev/vdb2'
ansible node4 -m lvol -a 'lv=rhcsa size=200M vg=redhat state=present force=yes'
ansible node4 -m filesystem -a 'dev=/dev/redhat/rhcsa fstype=xfs force=yes'文件修订模块(replace/lineinfile)
replace模块:
使用replace模块,修改文件中的关键词,替换文件内的xx关键词,path、regexp、replace。
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m replace -a '任务参数'- ++ dest="文件路径" //指定要修改的文件路径(必选参数)
- ++ regexp="旧字符串" //指定要替换的字符串(必选参数),使用正则表达式
- ++ replace="新字符串" //指定要替换的新字符串
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -m replace -a 'path=/etc/selinux/config regexp="=enforcing" replace=disabled'
node2 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false,
"msg": ""
}
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node2 -a 'cat /etc/selinux/config'
node2 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted

lineinfile模块:
确认文件中存在/不存在/替换 xxxx 行,path、regexp、line、state。
get_url:
从指定的网址下载一个文件,url、dest、force。
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m get_url -a '任务参数'- ++ dest="目标文件路径" //指定下载后存放的新文件路径(必选参数)
- ++ url="文件的URL网址" //指定要下载的文件的URL地址(必选参数)
- ++ force="yes|no" //目标文件已存在时是否替换
- ++ owner=属主 //指定新文件的属主
- ++ group=属组 //指定新文件的属组
- ++ mode=权限标记 //指定新文件的权限
- ++ setype=SELinux类型 //指定新文件的SELinux标签类型

playbook剧本的作用及语法构成
什么是剧本:
- 即playbook,因作用类似于拍电影的剧本而得名,也有翻译为“编排”的
- 指的是包含一系列ansible自动化运维任务操作的特殊文件,一般以 .yml 作为扩展名
- 剧本代码使用YAML(YAML Ain't a Markup Language)数据标记规则
编剧 ==》 提供 playbook 剧本 ==》 ansible-playbook 执行剧本
剧本的语法构成:
++ 每一个playbook剧本中可以包括多个play剧情(场景1-小巷子英雄救美、场景2-大教堂美女成婚、……)
++ 每一个剧情由以下组件构成:name、hosts、tasks、vars、roles等等
- 名称(name),此项剧情的描述(非必须,但是建议写上,方便跟踪执行过程)
- 清单主机(hosts),在哪些主机上(剧情上演场地,小巷子、大教堂等)执行
- 任务列表(tasks),需要执行的具体的模块操作(美女出场、劫匪出场、英雄出场)
- 变量列表/文件(vars,vars_files),定义变量或导入变量文件(穿啥衣服、背啥包等等)
- 角色(roles),加载预设的任务角色(剧本+变量+模板……等资源套餐)

2)执行playbook剧本
- 通过ansible-playbook加载剧本,任务按顺序依次执行
- 添加 --syntax-check 选项时,可以对剧本做语法检查
- 添加 -C 选项时,只测试剧本,不真正执行
- 返回结果时,changed表示有更改(橙色),ok表示已经执行过(绿色),failed表示失败(红色)
比如:
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook file.yml
PLAY [configure yum repository] ************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
fatal: [node3]: UNREACHABLE! => {"changed": false, "msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: connect to host node3 port 22: No route to host", "unreachable": true}
fatal: [node4]: UNREACHABLE! => {"changed": false, "msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: connect to host node4 port 22: No route to host", "unreachable": true}
ok: [node2]
ok: [node1]
ok: [node5]
TASK [base] ********************************************************************
ok: [node2]
ok: [node1]
ok: [node5]
TASK [stream] ******************************************************************
ok: [node1]
ok: [node2]
ok: [node5]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
node1 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
node2 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
node3 : ok=0 changed=0 unreachable=1 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
node4 : ok=0 changed=0 unreachable=1 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
node5 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[alice@control ansible]$
- hosts: all
tasks:
- yum_repository:
name: abc
description: abcabc
file: test
baseurl: http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/BaseOS gpgcheck=yes gpgkey=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release'
- yum_repository: 'name=abc01 description="abc abc" file=test01 baseurl=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/AppStream gpgcheck=yes gpgkey=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release'
比如:
YAML基本语法:
- # 表示注释,起始行标记 --- ,结束行标记 ... ,非必需
- 以2个或更多空格缩进来确定层次关系,相同层次的代码缩进必须对齐
- 代码文件以 .yml 或 .yaml 作为扩展名
- 代码中不能使用Tab标记,建议调整编辑器设置(自动缩进、Tab替换为空格)
比如:
[alice@control ansible]$ vim ~/.vimrc //修改vim个性化配置(" 是注释行标记)
#方法一
"autocmd FileType yaml setlocal autoindent shiftwidth=2 tabstop=2 expandtab
# 方法二
au FileType yaml set ai sw=2 ts=2 et
# 方法三
set ai
set ts=2++ 键值对使用 : 分隔,列表/数组使用 - ,后面必须有空格标记
++ 键值对可以写成一行、缩进的多行
比如,以下两种写法等效:

- hosts: node1,node2
tasks:
- yum: name=httpd state=present
- copy: content="RHCE Test" dest=/var/www/html/index.html force=yes
- service: name=httpd state=restarted enabled=yes
- service: name=firewalld state=restarted enabled=yes
- firewalld: service=http state=enabled permanent=yes immediate=yes
~
~
~
~ [alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook -C demo.yml
PLAY [node1,node2] *************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [node2]
ok: [node1]
TASK [yum] *********************************************************************
changed: [node2]
changed: [node1]
TASK [copy] ********************************************************************
changed: [node1]
changed: [node2]
TASK [service] *****************************************************************
changed: [node2]
changed: [node1]
TASK [firewalld] ***************************************************************
changed: [node2]
changed: [node1]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
node1 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
node2 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[alice@control ansible]$


gnore_errors:
4)ignore_errors忽略错误
++ 在剧本中即使遇到错误,仍然执行后续操作

register接受shell模块输出变量

使用loop循环
- ++ 通过loop语句可以构造一个值列表(队列)
- ++ 针对loop队列中的值,可以共享同一个任务操作,从而节省代码量、提高效率
- ++ 任务要调用队列中的值时,使用固定变量 { {item}},需要时
比如:
[alice@control ansible]$ cat lamp.yml
---
- name: Deploy LAMP Platform
hosts: host1
tasks:
- name: install LAMP packages
yum: name={
{item}} state=present //调用循环变量(固定名称item)
loop: //配置列表循环项
- httpd
- mariadb
- mariadb-server
- php
- php-mysqlnd
- name: enable LAMP services
service: name={
{item}} state=started enabled=yes
loop:
- httpd
- mariadb使用when条件(if)
when条件用来判断系统指标,当满足条件时才会执行某个任务
- ++ 常见条件操作符如下:==、!=、>、>=、<、<=、in、not in、is defined、is not defined
- ++ 使用and或or可以组合多个条件
- ++ when表达式中调用变量时,不需要使用 { { }}
[alice@control ansible]$ cat when.yml
---
- name: when test
hosts: node1,node3
tasks:
- file: path="/tmp/yes.txt" state=touch //在目录/tmp/下创建文件yes.txt
when: ('web' in group_names) //当主机属于web组时执行
- debug: msg="vg myvg not found" //显示一段文本
when: ('myvg' not in ansible_lvm.vgs) //当卷组myvg不存在时
...failed_when中断控制
- ++ failed_when条件的用法与when类似
- ++ 但是当满足failed_when的条件时,playbook就认为失败,不再执行后续任务
block语句块的使用(Java的try{}catch(){}finally{})
block语句可以将多个任务操作捆绑到一起,当成一个整体
- ++ 当满足when条件后要执行多个操作时,就可以使用block把这些操作捆在一块
- ++ 当然,when条件也不是必需的,可以只是捆绑多个任务
- ++ rescue抢救机制(非必需),当block任务失败时,可以执行rescue任务
- ++ always完结机制(非必需),无论block任务是否成功,最后都去执行always任务
block:
- 任务1: .. ..
- 任务2: .. ..
when:条件测试
rescue:
- 任务3: .. ..
- 任务4: .. ..
always:
- 任务5: .. ..—— 执行结果是:
- 当条件测试不成立时,任务1-5都不执行
- 当条件测试成立时,执行任务1、任务2;如果任务1、2中有失败的,则执行任务3、4
- 当条件测试成立时,任务5始终都会执行
[alice@control ansible]$ cat block.yml
---
- name: block test
hosts: node1
tasks:
- block:
- debug: msg="vg myvg not found" //提示卷组没找到
- debug: msg="create vg myvg .. .." //做其他操作(比如创建这个卷组...)
when: ('myvg' not in ansible_lvm.vgs) //当卷组myvg不存在时
rescue:
- debug: msg="creating failed .. .." //block失败时提示创建卷组失败
always:
- shell: vgscan //列出卷组信息
register: list //保存到名为list的变量
- debug: msg={
{list.stdout_lines}} //提示卷组扫描结果
...handlers任务处理(布雷)、notify通知触发(引爆)
handlers可以设置一个或一块任务,仅当收到某个任务通知时才会执行
- ++ 每个剧情中handlers任务只会执行一次,即使收到多个任务的触发通知
- ++ handlers组的每一个任务都要设置名称(name)
- ++ handlers的层次与tasks平级
- ++ 其他任务在必要时,使用notify语句通知handlers任务名
- ++ 仅当发起notify的任务的执行状态为changed时,handlers任务才会被执行
比如:
[alice@control ansible]$ cat handlers.yml
---
- name: handlers test
hosts: node5
tasks:
- lvol: lv=vo001 size=100M vg=search //创建逻辑卷vo001
notify: mkfs //如果changed则通知格式化(否则无需格式化)
handlers:
- name: mkfs //定义格式化操作处理
filesystem: dev=/dev/search/vo001 fstype=xfs force=yes
...ansible-vault
ansible的vault保险库:
- ++ 为了方便保护一些敏感文件(如账号的密码)而设置的文件加密机制
- ++ 加密/解密主要工具 ansible-vault
- ++ 通过ansible-playbook调用保险库文件时,添加 --ask-vault-pass 选项会提示从键盘输入密码
- ++ 需要验证密码的地方,都可以添加 --vault-password-file= 来指定密码文件以免除交互
- ++ 在重设密码时,可以添加 --new-vault-password-file 来指定存放新密码的文件

ansible-vault基本操作(以下为手动验密):
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault create new.txt //直接创建新加密文件
.. .. //根据提示设置密码
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault view new.txt //查看已加密的文件
.. .. //根据提示输入正确的密码验证
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault decrypt new.txt //将文件解密(恢复成明文数据)
.. .. //根据提示输入正确的密码验证
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault encrypt new.txt //将现有文件加密(变成密文)
.. .. //根据提示设置密码
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault rekey new.txt //修改已加密文件的密码
.. .. //根据提示验证旧密码
.. .. //再设置新密码
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault view new.txt --vault-password-file=key.txt //通过密码文件输入密码主机信息搜集(gather_facts: yes)
Ansible每次执行playbook剧本时,默认第一个任务就是Gathering Facts搜集主机信息。
所有收集到的系统信息都被保存在ansible_facts指标变量中,可以通过setup模块查看,或者在playbook剧本中调用。
当添加参数 gather_facts:no 时,不会采集


playbook变量的作用及定义、调用方法
什么是变量:
- ++ 通过固定的名称来调用可能变化的值,方便ansible重复调用以提高管理效率
- ++ 采用 key=value,或者 key: value 的方式定义
- ++ 调用时一般采用 { {key}} 方式
变量的领域:
- 清单变量:在inventory清单主机中定义,作用于某个主机或某个主机组 主机名后面
node1 ansible_ssh_user-lisi ansible_ssh_password=123456 ansible_ssh_port=2222 #主动设置用户名密码- 剧本变量:在playbook剧本中定义,只在当前剧本中有效,patam那个

- 系统变量:通过剧本的gather_facts=yes自动搜集(默认调用setup模块),对任务主机有效,系统指标
- 魔法变量:由ansible预设,用来获取清单组、清单主机名等管理信息

setup模块
使用setup模块,过滤出清单主机的系统指标
基本用法:
# ansible 清单主机 -m setup [-a 'filter=系统指标名']
filter参数用来过滤出特定名称的系统指标,未知指标名部分可以使用 * 通配符
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m setup //查看node1的所有系统指标
node1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"172.25.254.101"
],
"ansible_all_ipv6_addresses": [
"fe80::6a52:a669:ccc3:13cc"
],
"ansible_apparmor": {
"status": "disabled"
},
.. ..
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m setup -a "filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses"
.. .. //查看指定名称的系统指标
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m setup -a "filter=*_ipv4_addresses"
.. .. //指定系统指标时,名称中允许使用通配符 *
debug模块
使用debug模块,通过msg参数显示变量的内容、自定义文本
- ++ 需要在playbook剧本中测试(adhoc方式未搜集信息,会提示变量未定义)
- ++ 使用msg显示变量时,变量名需要加 { { }} 括起来
- ++ 使用var显示变量时,变量名无需 { { }} 标记;var与msg不能同时使用

常用系统指标:
- ansible_eth0 //网卡eth0的配置信息
- ansible_fqdn //完整的主机名
- ansible_hostname //主机名
- ansible_all_ipv4_addresses//系统IPv4地址列表
- ansible_bios_version //主机BIOS版本
- ansible_date_time //系统日期时间信息
- ansible_devices //硬件设备信息
- ansible_distribution //操作系统版本
- ansible_env //用户环境变量列表
- ansible_kernel //内核版本信息
- ansible_lvm //逻辑卷存储相关信息
- ansible_memtotal_mb //总的内存大小
- ansible_memfree_mb //空闲内存大小
- ansible_mounts //已挂载的文件系统信息
- ansible_interfaces //网络接口列表
- ansible_distribution //当前系统的发行版名称
ansible魔法变量
- ++ 指的是ansible为管理目的而预设的特殊变量
- ++ 通过adhoc方式或者playbook方式,都可以调用/或者msg查看
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -m debug -a 'msg={
{hostvars}}' |grep playbook_*
"ansible_playbook_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python",
"playbook_dir": "/ansible"
"ansible_playbook_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python",
"playbook_dir": "/ansible"
"ansible_playbook_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python",
"playbook_dir": "/ansible"
"ansible_playbook_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python",
"playbook_dir": "/ansible"
"ansible_playbook_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python",
"playbook_dir": "/ansible"
常用魔法变量:
- hostvars //包含所有可控清单主机的魔法变量
- hostvars.node1 //主机node1的魔法变量
- hostvars.node1.group_names //主机node1在清单中所在的组名
- group_names //当前主机所在的清单组名
- hostvars.node1.inventory_hostname//主机node1在清单中的主机名
- inventory_hostname //当前主机的清单主机名
- groups//主控机清单中的所有主机组及成员主机信息
- groups.all //主控机清单中的所有主机
- groups.web //主控机清单中web组的所有主机
playbook中使用变量:
使用vars列表项定义
[alice@control ansible]$ cat var.yml //定义v1、v2两个变量
---
- name: vars test
hosts: node1
vars: //直接定义变量
- yonghu: zhsan
- mima: ab1234
tasks:
- debug:
msg: msg="username:{
{yonghu}}, password:{
{mima}}"
...
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook var.yml //测试剧本
.. ..
TASK [debug] ***************************************************************************************
ok: [node1] => {
"msg": "username:zhsan, password:ab1234"
}
.. ..使用vars_files列表项定义,从外部变量文件加载变量
[alice@control ansible]$ cat vars_files.yml
---
- name: vars_files test
hosts: node1
vars_files: //调用变量文件
- v3v4.txt
tasks:
- debug: msg="username:{
{yonghu}}, password:{
{mima}}"
...
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook vars_files.yml
.. ..
TASK [debug] ***************************************************************************************
ok: [node1] => {
"msg": "username:lisi, password:cd5678"
}
.. ..使用vars_prompt从键盘输入变量值
[alice@control ansible]$ cat vars_prompt.yml
---
- name: vars_prompt test
hosts: node1
vars_prompt: //人机交互为变量赋值
- name: ilogin
prompt: "login"
private: no //回显
- name: ipass
prompt: "password"
private: yes //不回显(缺省)
tasks:
- name: create an user
user: name="{
{ilogin}}" password="{
{ ipass | password_hash('sha512') }}"
...
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook vars_prompt.yml //执行剧本
login: wangwu //输入用户名
password: //输入密码(不显示)
.. ..
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible node1 -a 'id wangwu' //检查结果
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
uid=1002(wangwu) gid=1004(wangwu) groups=1004(wangwu)通过register模块保存命令结果(类似于Shell的重定向)
[alice@control ansible]$ cat register.yml
---
- name: register test
hosts: node1
ignore_errors: yes //即使遇到错误,仍然执行后续操作
tasks:
- shell: ls -lh /etc/hosts /etc/null
register: result //将屏幕输出保存到result变量
- debug: msg="{
{result.stdout}}" //提取标准输出
- debug: msg="{
{result.stderr}}" //提权标准错误
- debug: msg="{
{result}}" //提取变量result的所有内容
...
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook register.yml //执行剧本
.. ..
TASK [debug] ***************************************************************************************
ok: [node1] => {
"msg": "-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 617 Mar 27 19:10 /etc/hosts"
}
TASK [debug] ***************************************************************************************
ok: [node1] => {
"msg": "ls: cannot access '/etc/null': No such file or directory"
}
.. ..ansible角色
什么是角色:
- ++ role指的是,为了方便复杂任务(包含大批量任务操作、模板、变量等资源)的重复使用,降低playbook剧本编写难度,而预先定义好的一套目录结构。
- ++ 针对每一个角色,ansible会到固定的目录去调取特定的数据
- ++ 角色内不指定“hosts: 清单主机列表”,而是交给调用此角色的剧本来指定
比如,名为 nginx 的角色目录构成:
- nginx/ //角色根目录
- nginx/tasks/main.yml //任务入口,最主要的文件
- nginx/defualts/main.yml //定义变量的缺省值,优先级较低
- nginx/files/ //存放静态文件
- nginx/handlers/main.yml //定义handlers处理任务
- nginx/meta/main.yml //定义作者、版本等描述信息
- nginx/README.md //整个角色的描述信息
- nginx/templates/ //存放模板文件
- nginx/vars/main.yml //定义角色变量,优先级高
rhel-system-roles软件包:
- 安装后会提供一组由红帽预先设置好的角色,方便用来管理RHEL系统
- 比如 timesync、kdump、network、postfix、……等等
- 默认位置 /usr/share/ansible/roles/*,可以按需复制到用户的roles目录下使用
设置角色变量:
- 通过修改角色目录下的 vars/main.yml 文件,可以定义角色变量
[alice@control ansible]$ cp -r /usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.timesync roles/
[alice@control ansible]$ vim roles/rhel-system-roles.timesync/vars/main.yml
.. ..
timesync_ntp_servers:
- hostname: 172.25.254.250
iburst: yes通过playbook剧本调用xx系统角色:
- 使用roles语句,指定角色名称即可调用角色任务、变量等批量数据
[alice@control ansible]$ cat timesync.yml
---
- name: timesync
hosts: all
roles:
- rhel-system-roles.timesync //调用xx角色
...ansible-galaxy工具:
- galaxy的本意为“银河系”,ansible-galaxy工具可以用来统一管理大量角色
- 联网情况下,可以通过ansible-galaxy工具访问ansible官网的公共仓库 https://galaxy.ansible.com/api/
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-galaxy list
.. .. //列出已经安装的角色
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-galaxy init roles/myrole
.. .. //创建名为myrole的自定义角色(目录结构)
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-galaxy remove myrole
.. .. //删除名为myrole的角色
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-galaxy search nginx
.. .. //从ansible官网搜索可用的角色(需联网)
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-galaxy info haproxy --offline
.. .. //查询已安装的haproxy角色的描述信息
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-galaxy install -r 角色列表文件
.. .. //根据角色列表文件的定义,下载并安装新的角色
[alice@control ansible]$ vim roles/down.yml //配置角色导入信息
- name: haproxy //指定角色1的新名称
src: http://study.lab0.example.com/roles/haproxy.tar //指定角色tar包的下载地址
- name: myphp //指定角色2的新名称
src: acandid.httpd //通过名称直接从ansible官网下载(需联网)模板中的for循环应用
- ++ 通过魔法变量 groups.all 取得所有清单主机名
- ++ 通过魔法变量 hostvars["node1"] 取得node1的魔法变量和系统变量信息(如果使用目标主机的系统变量,需要在剧本中提前搜集)
[alice@control ansible]$ vim newhosts.j2
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
{% for id in groups.all %}
{
{hostvars[id].ansible_eth0.ipv4.address}} {
{hostvars[id].ansible_fqdn}}
{
{hostvars[id].ansible_hostname}}
{% endfor %}[alice@control ansible]$ vim newhosts.yml
- hosts: all //搜集所有主机的信息
- hosts: test01 //为 xx 组部署
tasks:
- template: src=newhosts.j2 dest=/etc/newhosts force=yes //通过模板部署文件

模板文件中的if分支应用
[alice@control ansible]$ vim newissue.yml
- name: deploy /etc/issue
hosts: all
tasks:
- copy:
content: | //准备文本内容
{% if "test01" in group_names %} //如果所在组包括 dev
test01
{% elif "test02" in group_names %} //如果所在组包括 test
test02
{% elif "web" in group_names %} //如果所在组包括 prod
Webserver
{% endif %}
dest: /etc/issue //复制到指定目标文件
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook newissue.yml实战题目:
1.安装和配置ansible环境
1) 安装所需软件包
2) 在/home/alice/ansible/inventory文件中设置主机清单,要求: node1属于test01主机组 node2属于test02主机组 node3和node4属于web主机组 node5属于test05主机组 web组属于webtest主机组
3) 在/home/alice/ansible目录中创建ansible.cfg,满足以下需求:主机清单文件为 /home/alice/ansible/inventory playbook中角色位置为 /home/alice/ansible/roles
[root@control ~]# yum -y install ansible //安装ansible软件包
[root@control ~]# su - alice //切换为指定用户
[alice@control ~]$ mkdir -p ~/ansible/roles ; cd ~/ansible/ //进入工作目录
[alice@control ansible]$ vim ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory = inventory //主机清单文件
remote_user = alice //连接受管机的远程用户名
roles_path = roles //角色目录
[privilege_escalation] //设置用户sudo提权
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False
[alice@control ansible]$ vim inventory
[test01]
node1
[test02]
node2
[web]
node3
node4
[test05]
node5
[webtest:children] web //配置主机清单 2.创建和运行Ansible临时命令
编写脚本 /home/alice/ansible/adhoc.sh,用来为所有受管机配置2个yum仓库。
仓库1:
名称为BASE,描述为software base
URL为http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/BaseOS
GPG签名启用,GPG秘钥URL为http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release 仓库为启用状态
仓库2:
名称为STREAM,描述为software stream
URL为http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/AppStream
GPG签名启用,GPG秘钥URL为http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release 仓库为启用状态
[alice@control ansible]$ vim adhoc.sh
#!/bin/bash
ansible all -m yum_repository -a 'name=BASE description="software base" baseurl=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/BaseOS gpgcheck=yes gpgkey=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release enabled=yes'
ansible all -m yum_repository -a 'name=STREAM description="software stream" baseurl=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/AppStream gpgcheck=yes gpgkey=http://study.lab0.example.com/rhel8/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release enabled=yes'
[alice@control ansible]$ chmod +x adhoc.sh
[alice@control ansible]$ ./adhoc.sh 3.编写剧本远程安装软件
创建名为/home/alice/ansible/tools.yml的playbook,能够实现以下目的:
1) 将php和tftp软件包安装到test01、test02和web主机组中的主机上
2) 将RPM Development Tools软件包组安装到test01主机组中的主机上
3)将test01主机组中的主机上所有软件包升级到最新版
[alice@control ansible]$ vim tools.yml
- name: 1. install php and mariadb on test01, test02, web
hosts: test01, test02, web
tasks:
- yum: pkg=php state=present //安装php软件包
- yum: pkg=tftp state=present //安装mariadb软件包
- name: 2. install @RPM Development Tools on test01
hosts: test01
tasks:
- yum: name="@RPM Development Tools" state=present //安装xx包组
- name: 3. update all packages
hosts: test01
tasks:
- yum: name="*" state="latest" //升级所有包
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook tools.yml - hosts: test01,test02,web
tasks:
- yum: name="php,tftp" state=present
- hosts: test01
tasks:
- yum: name="@RPM Development Tools" state=present
- yum: name="*" state=latest


4.安装并使用系统角色
安装RHEL角色软件包,并创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/timesync.yml,满足以下要求:
1) 在所有受管理节点运行
2) 使用timesync角色
3) 配置该角色,使用时间服务器172.25.254.250,并启用iburst参数
[root@control ~]# yum -y install rhel-system-roles //安装rhel系统角色
[root@control ~]# su - alice
[alice@control ~]$ cd ansible/
[alice@control ansible]$ cp -r /usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.timesync roles/
//复制角色目录
[alice@control ansible]$ vim timesync.yml
- name: timesync
hosts: all
vars:
- timesync_ntp_servers: //设置NTD服务器变量
- hostname: 172.25.254.250
iburst: yes
roles:
- rhel-system-roles.timesync //调用角色
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook timesync.yml 5.通过galaxy安装角色
创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/roles/down.yml,用来从以下 URL 下载角色,并安装到
/home/alice/ansible/roles目录下: http://study.lab0.example.com/roles/haproxy.tar 此角色名为haproxy http://study.lab0.example.com/roles/myphp.tar 此角色名为myphp
[alice@control ansible]$ vim /home/alice/ansible/roles/down.yml
- name: haproxy
src: http://study.lab0.example.com/roles/haproxy.tar
- name: myphp //配置角色导入信息
src: http://study.lab0.example.com/roles/myphp.tar
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-galaxy install -r roles/down.yml //导入角色
6.创建及使用自定义角色
根据下列要求,在/home/alice/ansible/roles中创建名为httpd的角色:
1) 安装httpd软件,并能够开机自动运行
2) 开启防火墙,并允许httpd通过
3) 使用模板index.html.j2,用来创建/var/www/html/index.html网页,内容如下(其中,HOSTNAME是受管理节点的完全域名,IPADDRESS是IP地址):
Welcome to HOSTNAME on IPADDRESS
然后创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/myrole.yml,为webtest主机组启用httpd角色。
[alice@control roles]$ cd ~/ansible/roles
[alice@control roles]$ ansible-galaxy init httpd //在roles/目录下初始化角色
[alice@control roles]$ vim httpd/templates/index.html.j2 //编写角色模板(网页)
Welcome to {
{ ansible_facts.fqdn }} on {
{ ansible_facts.eth0.ipv4.address }}
[alice@control roles]$ vim httpd/tasks/main.yml //配置角色主任务
- name: 1. install httpd //装包
yum: pkg=httpd state=present
- name: 2. deploy index.html //配置网页资源
template: src=index.html.j2 dest=/var/www/html/index.html
- name: 3. httpd //起服务
service: name=httpd state=restarted enabled=yes
- name: 4. firewalld //起服务
service: name=firewalld state=restarted enabled=yes
- name: 5. configure firewall rules //配置防火墙规则
firewalld: service=http state=enabled permanent=yes immediate=yes
[alice@control roles]$ cd ~/ansible/
[alice@control ansible]$ vim myrole.yml //编写启动脚本
- name: use role
hosts: webtest
roles:
- httpd
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook myrole.yml 7.使用之前通过galaxy下载的角色
创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/web.yml,满足下列需求:
1) 该剧本中包含一个play,可以在test05主机组运行haproxy角色(此角色已经配置好网站的负载均衡服务)
2) 多次访问http://node5.net0.example.com可以输出不同主机的欢迎页面
3) 该剧本中包含另一个play,可以在webtest主机组运行myphp角色(此角色已经配置好网站的php页面)
4) 多次访问http://node5.net0.example.com/index.php也输出不同主机的欢迎页面
[alice@control ansible]$ vim web.yml
- name: use role B //先部署web节点
hosts: webtest
roles:
- myphp
- name: use role A
hosts: test05 //再配置负载均衡器
roles:
- haproxy
tasks:
- firewalld: service=http state=enabled permanent=yes immediate=yes [alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook web.yml08. 编写剧本远程管理逻辑卷
创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/lvm.yml,用来为所有受管机完成以下部署:
1) 在卷组search中创建名为mylv的逻辑卷,大小为1000MiB
2) 使用ext4文件系统格式化该逻辑卷
3) 如果无法创建要求的大小,应显示错误信息insufficient free space,并改为500MiB
4) 如果卷组search不存在,应显示错误信息 VG not found 5)不需要挂载逻辑卷
[alice@control ansible]$ vim lvm.yml
- name: manager volume
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: 1. failed when VG not found
debug: msg="VG not found"
when: "'search' not in ansible_facts.lvm.vgs" //目标VG不存在时报错
failed_when: "'search' not in ansible_facts.lvm.vgs" //停止后续任务
- name: 2. lvcreate
block: //配置指令块
- lvol: lv=mylv size=1000M vg=search
notify: mkfs //lv建成功后通知mkfs
rescue: //若块操作失败,则执行补救
- debug: msg="insufficient free space"
- lvol: lv=mylv size=500M vg=search
notify: mkfs //lv建成功后通知mkfs
handlers: //收到通知后执行
- name: mkfs
filesystem: dev=/dev/search/mylv fstype=ext4 force=yes
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook lvm.yml //定义通知接口名mkfs 09. 根据模板部署主机文件
1) 从http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/newhosts.j2 下载模板文件
2) 完成该模板,用来生成新主机清单(主机的显示顺序没有要求),结构如下
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 172.25.254.101 node1.lab0.example.com node1
172.25.254.102 node2.lab0.example.com node2
172.25.254.103 node3.lab0.example.com node3
172.25.254.104 node4.lab0.example.com node4
172.25.254.105 node5.lab0.example.com node5
3) 创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/newhosts.yml,它将使用上述模板在test01主机组的主机上生成文件/etc/newhosts
[alice@control ansible]$ sudo yum -y install wget
[alice@control ansible]$ wget http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/newhosts.j2
[alice@control ansible]$ vim newhosts.j2 //制作J2动态模板文件
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
{% for id in groups.all %}
{
{hostvars[id].ansible_facts.eth0.ipv4.address}} {
{hostvars[id].ansible_facts.fqdn}}
{
{hostvars[id].ansible_facts.hostname}}
{% endfor %}
[alice@control ansible]$ vim newhosts.yml
- name: gather groups facts
hosts: all //搜集所有主机的信息
- name: deploy /etc/newhosts
hosts: test01 //只为xx组部署
tasks:
- template: src=newhosts.j2 dest=/etc/newhosts //通过模板部署文件
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook newhosts.yml 10. 编写剧本修改远程文件内容
创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/newissue.yml,满足下列要求:
1) 在所有清单主机上运行,替换/etc/issue的内容
2) 对于test01主机组中的主机,/etc/issue文件内容为test01
3) 对于test02主机组中的主机,/etc/issue文件内容为test02
4) 对于web主机组中的主机,/etc/issue文件内容为Webserver
[alice@control ansible]$ vim newissue.yml
- name: deploy /etc/issue
hosts: all
tasks:
- copy: content: | //准备文本内容
{% if "test01" in group_names %} //如果所在组包括dev
test01
{% elif "test02" in group_names %} //如果所在组包括test
test02
{% elif "web" in group_names %}
Webserver
{% endif %} //如果所在组包括prod
dest: /etc/issue
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook newissue.yml //复制到指定目标文件
11.编写剧本部署远程Web目录
创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/webdev.yml,满足下列要求:
1) 在test01主机组运行
2) 创建目录/webdev,属于webdev组,常规权限为rwxrwxr-x,具有SetGID特殊权限 3)使用符号链接/var/www/html/webdev链接到/webdev目录 4)创建文件/webdev/index.html,内容是It's works!
5)查看test01主机组的web页面 http://node1/webdev/ 将显示It's works!
[alice@control ansible]$ vim webdev.yml
- name: Prepare Web Directory
hosts: test01
tasks:
- group: name=webdev state=present
- file: name=/webdev group=webdev mode=2775 state=directory //建目录
- file: src=/webdev name=/var/www/html/webdev state=link force=yes //建链接
- copy: content="It's works!" dest=/webdev/index.html force=yes //部署网页
- yum: name=policycoreutils-python-utils.noarch state=present //安装semanage工具
- sefcontext: target='/webdev(/.*)?' setype=httpd_sys_content_t //设置目录安全上下文
- command: restorecon -iR /webdev //应用上下文策略
- firewalld: service=http state=enabled permanent=yes immediate=yes
- service: name=httpd state=restarted enabled=yes
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook webdev.yml 
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test01 -a 'cat /etc/selinux/config'
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
SELINUX=enforcing
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook webde.yml
PLAY [test01] ******************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [group] *******************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [file] ********************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [file] ********************************************************************
[WARNING]: Cannot set fs attributes on a non-existent symlink target. follow
should be set to False to avoid this.
changed: [node1]
TASK [copy] ********************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [lineinfile] **************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [service] *****************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [command] *****************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [firewalld] ***************************************************************
ok: [node1]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
node1 : ok=9 changed=7 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible test01 -a 'cat /etc/selinux/config'
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
SELINUX=disabled
[alice@control ansible]$
12.编写剧本为受管机生成硬件报告
创建名为/home/alice/ansible/hardware.yml的playbook,满足下列要求:
1) 使所有受管理节点从以下URL下载文件:
http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/hardware.empty
2) 并用来生成以下硬件报告信息,存储在各自的/root/hardware.txt文件中
- 清单主机名称
- 以MB表示的总内存大小
- BIOS版本
- 硬盘vda的大小
- 硬盘vdb的大小
其中,文件的每一行含有一个key=value对,如果项目不存在,则显示NONE。
[alice@control ansible]$ vim hardware.yml
- name: hardware report
hosts: all
ignore_errors: yes //忽略个别错误
vars: //提取硬件检测结果
- sfile: /root/hardware.txt //硬件报告文件路径
- host: "{
{inventory_hostname}}" //提取清单主机名
- mem: "{
{ansible_facts.memtotal_mb}}" //提取总内存大小(MB)
- bios: "{
{ansible_facts.bios_version}}" //提取BIOS版本
- vdasize: "{
{ansible_facts.devices.vda.size}}" //提取磁盘vda大小
- vdbsize: "{
{ansible_facts.devices.vdb.size if ansible_facts.devices.vdb.size is defined else 'NONE' }}" //提取磁盘vdb大小,或NONE
tasks: //修改报告(根据模板内容查找替换)
- get_url: url=http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/hardware.empty dest={
{sfile}} force=yes
- replace: name={
{sfile}} regexp=inventoryhostname replace={
{host}}
- replace: name={
{sfile}} regexp=memory_in_MB replace={
{mem}}
- replace: name={
{sfile}} regexp=BIOS_version replace={
{bios}}
- replace: name={
{sfile}} regexp=disk_vda_size replace={
{vdasize}}
- replace: name={
{sfile}} regexp=disk_vdb_size replace={
{vdbsize}} [alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook hardware.yml 13.编写脚步创建保险库文件
1)创建ansible保险库 /home/alice/ansible/passdb.yml,其中有2个变量:
pw_dev,值为ab1234pw_man,值为cd5678
2) 加密和解密该库的密码是pwd@1234 ,密码存在/home/alice/ansible/secret.txt中
[alice@control ansible]$ echo 'pwd@1234' > secret.txt //创建保险库钥匙文件
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault create passdb.yml --vault-password-file=secret.txt //创建保险库文件
pw_dev: ab1234
pw_man: cd567814.编写剧本为受管机批量创建用户,要求使用保险库中的密码
从以下URL下载用户列表,保存到/home/alice/ansible目录下: http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/name_list.yml
创建剧本 /home/alice/ansible/users.yml的playbook,满足下列要求:
1) 使用之前题目中的passdb.yml保险库文件
2) 职位描述为dev的用户应在test01、test02主机组的受管机上创建,从pw_dev变量分配密码,是补充组devops的成员
3) 职位描述为man的用户应在web主机组的受管机上创建,从pw_man变量分配密码,是补充组opsmgr的成员
4) 该playbook可以使用之前题目创建的secret.txt密码文件运行
解题参考:
[alice@control ansible]$ wget http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/name_list.yml
//获取用户列表文件
[alice@control ansible]$ cat name_list.yml //确认列表内容
users:
- name: tom
job: dev //用户岗位a
- name: jerry
job: man //用户岗位b
[alice@control ansible]$ vim users.yml
- name: batch users
hosts: test01, test02, web
vars_files:
- passdb.yml //加载密码变量
- name_list.yml //加载用户名变量
tasks:
- group: name=devops //确保补充组1在指定主机已存在
when: ('test01' in group_names or 'test02' in group_names)
- group: name=opsmgr //确保补充组2在指定主机已存在
when: ('web' in group_names)
- user: name={
{item.name}} password={
{pw_dev|password_hash('sha512')}} groups=devops append=yes
when: (item.job == 'dev') and ('test01' in group_names or 'test02' in group_names)
loop: "{
{users}}" //按条件添加a岗用户
- user: name={
{item.name}} password={
{pw_man|password_hash('sha512')}} groups=opsmgr append=yes
when: (item.job == 'man') and ('web' in group_names)
loop: "{
{users}}" //按条件添加b岗用户
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-playbook users.yml --vaultid=/home/alice/ansible/secret.txt //测试效果
15.重设保险库密码
1) 从以下URL下载保险库文件到/home/alice/ansible目录: http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/topsec.yml
2) 当前的库密码是banana,新密码是big_banana,请更新该库密码
[alice@control ansible]$ wget http://study.lab0.example.com/materials/topsec.yml
//下载指定保险库文件
[alice@control ansible]$ ansible-vault rekey topsec.yml //为保险库设置新的密码
Vault password: 输入当前的库密码
New Vault password: 输入新的库密码
confirm New Vault password: 再次输入新的库密码确认
Rekey successful