#include<stdio.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50;
struct node{
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
int post[maxn], in[maxn];
int n;
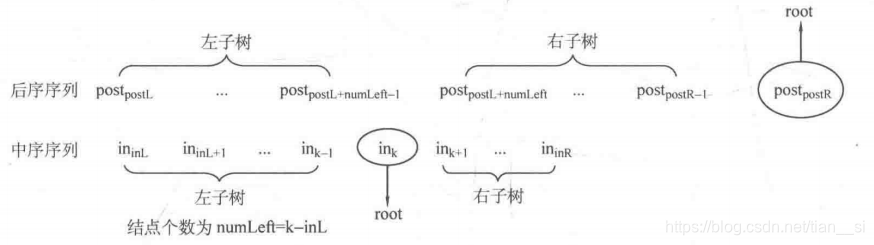
node* create(int postL, int postR, int inL, int inR)
{
if(postL > postR) return NULL;
node* root = new node;
root->data = post[postR];
int k;
for(k = inL; k <= inR; k++)
{
if(in[k] == post[postR])
break;
}
int numLeft = k - inL;
root->lchild = create(postL, postL + numLeft - 1, inL, k - 1);
root->rchild = create(postL + numLeft, postR - 1, k + 1, inR);
return root;
}
int num = 0;
void BFS(node* root)
{
queue<node*> Q;
Q.push(root);
while(!Q.empty())
{
node* now = Q.front();
Q.pop();
printf("%d", now->data);
num++;
if(num < n) printf(" ");
if(now->lchild != NULL) Q.push(now->lchild);
if(now->rchild != NULL) Q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
int main()
{
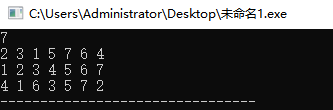
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &post[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &in[i]);
}
node* root = create(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
BFS(root);
return 0;
}