前言
链表的结构有很多种,其中用的比较多的就是单向不带头不循环链表和双向带头循环链表,这两种链表都有各自应用的场合。
双向带头循环链表结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。今天就用C语言来实现一下带头双向链表的增删查改。
一、双向带头循环链表
1.双向带头循环链表结构
首先:来看一下双向带头循环链表的结构
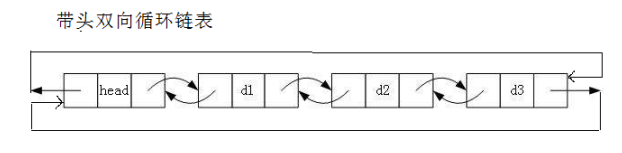
可以看到双向带头循环链表的每一个节点都与前后相连接,因此组成了一个循环,要实现该结构,需要先创造一个头结点,该头结点的尾指针指向自己,头指针也指向自己,在此基础上实现其他节点的插入和删除。
1.双向带头循环链表实现代码
以下是代码部分:
头文件
ListNode.h
#define pragama once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
//typedef方便修改结构体变量的类型
typedef int LTDataType;
//构建链表结构体,结构体变量包括头指针,尾指针及data值
typedef struct ListNode {
struct ListNode* pre;
struct ListNode* next;
LTDataType data;
}ListNode;
//创建新节点
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x);
//链表初始化->创造头结点
ListNode* InitListNode();
//打印链表
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead);
//销毁链表
void ListDistory(ListNode* phead);
//增删查改
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead);
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead);
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
void Listchange(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
主体
ListNode.c
#include"ListNode.h"
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->pre = NULL;
return newnode;
}
ListNode* InitListNode()
{
//构造头结点
ListNode* phead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
phead->next = phead;
phead->pre = phead;
return phead;
}
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
//从头结点后开始,到头结点结束
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void ListDistory(ListNode* phead)
{
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
ListErase(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}
//以下注释掉的代码段和留下的代码功能是一样的
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
/*assert(phead);
ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
ListNode* tail = phead->pre;
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->pre = tail;
newnode->next = phead;
phead->pre = newnode;*/
ListInsert(phead, x);
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
/*assert(phead);
ListNode* next = phead->next;
ListNode* newnode = buyListNode(x);
newnode->next = next;
next->pre = newnode;
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->pre = phead;*/
ListInsert(phead->next, x);
}
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{
/*assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* tail = phead->pre;
ListNode* tailpre = tail ->pre;
tailpre->next = phead;
phead->pre = tailpre;
free(tail);*/
ListErase(phead->pre);
}
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{
/*assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* next = phead->next;
ListNode* newnext = next ->next;
phead->next = newnext;
newnext->pre = phead;
free(next);*/
ListErase(phead->next);
}
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//POS之前插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* pospre = pos->pre;
ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
pospre->next = newnode;
newnode->pre = pospre;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->pre = newnode;
}
//pos不能是phead! 否则会破坏双向链表的结构;
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* pospre = pos->pre;
ListNode* posnext = pos->next;
pospre->next = posnext;
posnext->pre = pospre;
free(pos);
}
void Listchange(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
pos->data = x;
}
测试代码
test.c
#include"ListNode.h"
void test()
{
ListNode* phead = InitListNode();
ListPushBack(phead, 1);
ListPushBack(phead, 2);
ListPushBack(phead, 3);
ListPushBack(phead, 4);
ListPushBack(phead, 5);
ListPushFront(phead, 6);
ListPrint(phead);
ListNode* pos = ListFind(phead, 2);
ListInsert(pos, 8);
ListErase(pos);
ListPrint(phead);
ListNode* pos2 = ListFind(phead, 4);
Listchange(pos2, 9);
//ListDistory(phead);
ListPrint(phead);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
运行结果

二、双向带头循环链表优缺点
以下双向循环列表的优缺点都是与顺序表和单向不循环链表相比较的,因此同时总结了了下顺序表的优缺点。
1.双向带头循环链表优缺点
- 优点:支持任意位置时间复杂度为O(1)的插入和删除,不需要扩容、不存在空间浪费。
- 缺点:不支持随机访问,缓存命中率相对低。
2.顺序表优缺点
优点:
- 相对而言空间利用率更高,不需要额外空间,占用空间小(链表需要存指针)。
- 物理空间是连续的。支持随机访问,可以用下标访问(最大优势);缓存命中率较高。
缺点:
- 头部或中间插入或删除数据,需要一个一个挪动数据,时间复杂度是O(N)。
- 空间不够时需要增容,一般增容是按照倍数增加的、因此可能存在一定内存浪费。