一、简介
“D*算法”的名称源自 Dynamic A Star,最初由Anthony Stentz于“Optimal and Efficient Path Planning for Partially-Known Environments”中介绍。它是一种启发式的路径搜索算法,适合面对周围环境未知或者周围环境存在动态变化的场景。
1 算法介绍
同A算法类似,D-star通过一个维护一个优先队列(OpenList)来对场景中的路径节点进行搜索,所不同的是,D不是由起始点开始搜索,而是以目标点为起始,通过将目标点置于Openlist中来开始搜索,直到机器人当前位置节点由队列中出队为止(当然如果中间某节点状态有动态改变,需要重新寻路,所以才是一个动态寻路算法)。
2 .1 符号表示
本部分主要介绍一下论文中用到的一些符号及其含义。
论文中将地图中的路径点用State表示,每一个State包含如下信息:
Backpointer: 指向前一个state的指针,指向的state为当前状态的父辈,当前state称为指针指向state的后代,目标state无Backpointer。(路径搜索完毕后,通过机器人所在的state,通过backpointer即可一步步地移动到目标Goal state,GoalState以后用 G表示),b(X)=Y表示X的父辈为Y。
Tag:表示当前state的状态,有 New、Open、Closed三种状态,New表示该State从未被置于Openlist中,Open表示该State正位于OpenList中,Closed表示已不再位于Openlist中。
H(X):代价函数估计,表示当前State到G的开销估计。
K(X):Key Function,该值是优先队列Openlist中的排序依据,K值最小的State位于队列头 ,对于处于OpenList上的State X,K(X)表示从X被置于Openlist后,X到G的最小代价H(X),可以简单理解为。K(X)将位于Openlist的State X划分为两种不同的状态,一种状态为Raise(如果K(X)<H(X)),用来传递路径开销的增加(例如某两点之间开销的增加,会导致与之相关的节点到目标的路径开销随之增加);另一种状态为 Lower(如果K(X)<H(X)),用来传递路径开销的减少(例如某两点之间开销的减少,或者某一新的节点被加入到Openlist中,可能导致与之相关的节点到目标的路径开销随之减少)。
kmin:表示所有位于Openlist上的state的最小K值。
C(X,Y) :表示X与Y之间的路径开销。
Openlist 是依据K值由小到大进行排序的优先队列。
1.2 算法描述
搜索的关键是state的传递过程,即由G向机器人所在位置进行搜索的过程,这种传递过程是通过不断地从当前OpenList中取出K值最小的State来实现的,每当一个State由Openlist中移出时,它会将开销传递给它的邻居state,这些邻居state会被置于Openlist中,持续进行该循环,直到机器人所在State的状态为 Closed ,或者Openlist为空(表示不存在到G的路径)。
算法最主要的是两个函数, Process-State 和 Modify-Cost ,前者用于计算到目标G的最优路径,后者用于改变两个state之间的开销C(X,Y)并将受影响的state置于Openlist中。
算法的主要流程,在初始时,所有state的t(Tag)被设置为 New ,H(G)被设置为0,G被放置于OpenList,然后Process-State函数被不断执行,直到机器人所处state X由openlist中出队,然后可以通过机器人的当前state按backpointer指向目标G。当移动过程中发现新探测到的障碍时,Modify-Cost函数立刻被调用,来更正C(°)中的路径开销并将受影响的state重新置于openlist中。令Y表示robot发现障碍时所在的state,通过不断调用Process-State直到kmin≥H(Y),这时表示路径开销的更改已经传播到了Y,此时,新的路径构建完成。
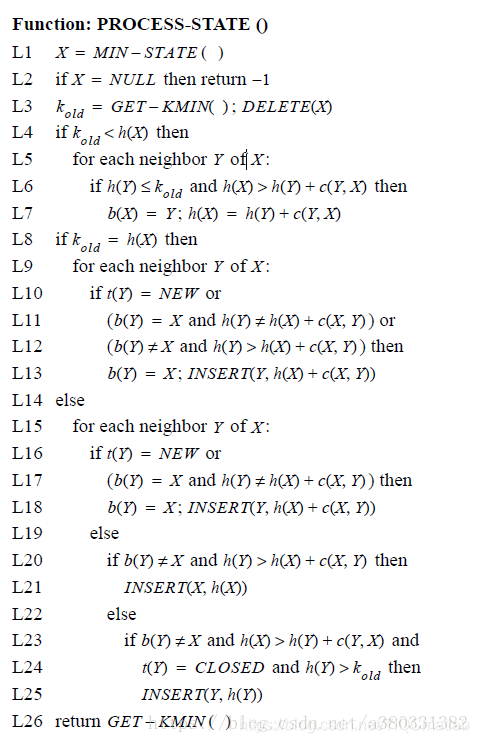
上图中L1-L3表示拥有最低K值的X由openlist中移出,如果X为Lower,那么它的路径代价为最优的。
在L8-L13,X的所有邻接state都被检测是否其路径代价可以更低,状态为New的邻接state被赋予初始路径开销值,并且开销的变动被传播给每一个backpointer指向X的邻接state Y(不管这个新的开销比原开销大或者小),也就是说只要你指向了X,那么X的路径开销变动时,你的路径代价必须随之改变。这里可能存在由于X路径开销变动过大,Y可以通过非X的其他state到达目标且路径开销更小的情况,这点在L8-13中并没有处理,而是放在后续针对Y的process-state函数中,在对Y进行处理时,会将其backpointer指向周围路径开销最小的state。如果X的邻接State状态为New时,应将其邻接state的backpointer指向X。所有路径开销有所变动的state都被置于Openlist中进行处理,从而将变动传播给邻接的state。
上述讨论的时X为Lower状态,接下来讨论X为Raise状态。
如果X为Raise,它的路径开销H可能不是最优的,在L4-L7中,通过其邻居state中已经处于最优开销(即h(Y)≤kold)的节点来优化X的路径开销,如果存在更短的路径,则将X的backpointer指向其neighbor。在L15-L18中,开销变动传播到状态为New的邻居state。如果X可以使一个backpointer并不指向X的邻居state的路径开销最小,即Y通过X到目标G的距离更短,但是此时Y的backpointer并不指向X,针对这种情况,可以将X重新置于Openlist中进而优化Y。在L23-25中,如果X可以通过一个状态为closed的并不是最理想的邻居stateY来减小路径开销,那么将Y重新置于Openlist中。

在modify-cost中,更新C(X,Y)并将X重新置于Openlist中,当X通过process-state进行传播时,会对Y进行开销计算,h(Y)=h(X)+c(X,Y)。
2 算法总结
相比A-star算法,D-star的主要特点就是由目标位置开始向起始位置进行路径搜索,当物体由起始位置向目标位置运行过程中,发现路径中存在新的障碍时,对于目标位置到新障碍之间的范围内的路径节点,新的障碍是不会影响到其到目标的路径的。新障碍只会影响的是物体所在位置到障碍之间范围的节点的路径。在这时通过将新的障碍周围的节点加入到Openlist中进行处理然后向物体所在位置进行传播,能最小程度的减少计算开销。 路径搜索的过程我个人感觉其实和Dijkstra算法比较像,A-star算法中f(n)=g(n)+h(n),h(n)在D-star中并没有体现,路径的搜索并没有A-star所具有的方向感,即朝着目标搜索的感觉,这种搜索更多的是一种由目标位置向四周发散搜索,直到把起始位置纳入搜索范围为止,更像是Dijkstra算法。
二、源代码
function varargout = A_GUI(varargin)
% A_GUI MATLAB code for A_GUI.fig
% A_GUI, by itself, creates a new A_GUI or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = A_GUI returns the handle to a new A_GUI or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% A_GUI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in A_GUI.M with the given input arguments.
%
% A_GUI('Property','Value',...) creates a new A_GUI or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before A_GUI_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to A_GUI_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help A_GUI
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 21-Oct-2018 17:10:48
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @A_GUI_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @A_GUI_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{
1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{
1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{
1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{
:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{
:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before A_GUI is made visible.
function A_GUI_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to A_GUI (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for A_GUI
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes A_GUI wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = A_GUI_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{
1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% set up color map for display 生成彩色地图
global cmap;
global map;
global n_r;
global n_c;
global state;
cmap = [1 1 1; ...% 1 -白色-无障碍
0 0 0; ...% 2 -黑色-有障碍
0 0.8 0; ...% 3 -绿色-已搜索
0 0.4 0; ...% 4 -粉色-正在搜索
0 1 1; ...% 5 -浅蓝色-起始点
1 1 0; ...% 6 -黄色-目标点
0 0 1]; % 7 -蓝色-最终路径
colormap(cmap);
%生成随机地图
map = zeros(n_r,n_c);
randmap = rand(n_r,n_c);
for i = 2:(sub2ind(size(randmap),n_r,n_c)-1)
if (randmap(i) >= 0.75)
map(i) = 2;
end
end
map(1, 1) = 5; % start_coords 起点坐标
map(n_r, n_c) = 6; % dest_coords 终点坐标
image(1.5,1.5,map);
grid on;
axis image;
set(handles.text5,'string','随机地图生成完毕');
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%搜索最佳路径
global n_r;
global n_c;
global cmap;
global map;
global state;
nrows = n_r;
ncols = n_c;
start_node = sub2ind(size(map), 1, 1);
%sub2ind()函数将矩阵中的某个元素的线性序号计算出来
%线性索引号例子:2*2矩阵[1 3;中,1是第一个,5是第二个
% 5 7] ,3是第三个,7是第四个
%(matlab是列优先,不是我们通常习惯的行优先)
dest_node = sub2ind(size(map), n_r, n_c);
% Initialize distance array 初始化距离数组
distanceFromStart = Inf(nrows,ncols);
distanceFromStart(start_node) = 0 ;
% For each grid cell this array holds the index of its parent 对于每个网格单元,该数组都保存其父单元的索引
parent = zeros(nrows,ncols);
% Main Loop
while true
% Draw current map
map(start_node) = 5;
map(dest_node) = 6;
image(1.5, 1.5, map);
grid on; %网格
axis image; %显示坐标
drawnow; %刷新屏幕
% Find the node with the minimum distance 找到距离最短的节点
[min_dist, current] = min(distanceFromStart(:));
if ((current == dest_node) || isinf(min_dist)) %TF = isinf(A) 返回一个和A尺寸一样的数组, 如果A中某个元素是inf (无穷), 则对应TF中元素是1, 否则TF中对应元素是0。
break;
end;
%搜索中心的索引坐标:current,
%搜索中心与起始点的路程:min_dist
% 这两个值后面会用。
map(current) = 3;
distanceFromStart(current) = Inf;
[i, j] = ind2sub(size(distanceFromStart), current); %索引号变为坐标
neighbor = [i-1,j;
i+1,j;
i,j+1;
i,j-1];
outRangetest = (neighbor(:,1)<1) + (neighbor(:,1)>nrows)+(neighbor(:,2)<1) + (neighbor(:,2)>ncols);
locate = find(outRangetest>0); %返回outRangetest中大于0的元素的相对应的线性索引值。
neighbor(locate,:)=[];
neighborIndex = sub2ind(size(map),neighbor(:,1),neighbor(:,2));
for i=1:length(neighborIndex)
if (map(neighborIndex(i))~=2) && (map(neighborIndex(i))~=3 && map(neighborIndex(i))~= 5)
map(neighborIndex(i)) = 4;
if (distanceFromStart(neighborIndex(i))>= min_dist + 1 )
distanceFromStart(neighborIndex(i)) = min_dist+1;
parent(neighborIndex(i)) = current;
% pause(0.02);
end
end
end
end
三、运行结果
四、备注
完整代码或者代写添加QQ 1564658423
