T-C-T函数论文下载
论文名称:Highly Nonlinear Boolean Functions With Optimal Algebraic Immunity and Good Behavio Against Fast Algebraic Attacks
1.Combinatorial Fact
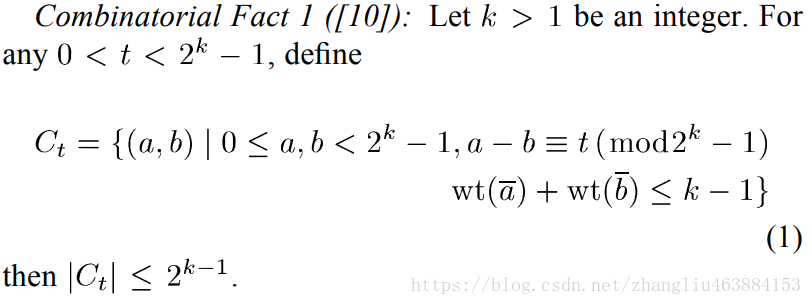
2.Construction1
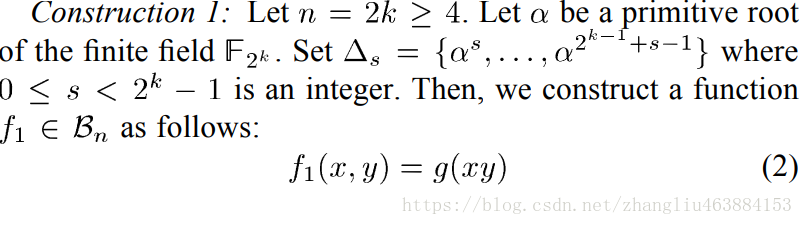
3. Construction1 optimal algebraic immunity n/2
4.Construction1 algebraic degree n-2
5.Construction1 nonlinearity
//此为magma代码
//计算Tang_Carlet_Tang函数construction1非线性度
function non(k)
for ss:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do
G<x>:=GF(2,k);
Z:=IntegerRing();
g:=[];
for tt:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do //初始化g的真值表全为0
bin1:=Eltseq(x^tt, GF(2)); toInt1 := [Z | bin1 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
k1:=&+[toInt1[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..k]]; g[k1]:=0;
end for;
n:=2*k;
F<w>:=GF(2,n);
f:=[];
for tt:=0 to 2^n-2 by 1 do //初始化f的真值表全为0
bin3:=Eltseq(w^tt, GF(2)); toInt3 := [Z | bin3 [j] : j in {1.. n by 1}];
k3:=&+[toInt3[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..n]]; f[k3]:=0;
end for;
for tt:=0+ss to 2^(k-1)+ss-1 by 1 do //根据g的支撑架生成g的真值表
bin2:=Eltseq(x^tt, GF(2)); toInt2 := [Z | bin2 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
k2:=&+[toInt2[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..k]]; g[k2]:=1;
end for;
//g:=[0] cat g;//记住教训
for tt:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do //由f(x,y)=g(xy)生成f的真值表
for dd:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do
bin4:=Eltseq(x^tt, GF(2)); toInt4 := [Z | bin4 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
bin5:=Eltseq(x^dd, GF(2)); toInt5 := [Z | bin5 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
bin6:=Eltseq(x^(tt+dd), GF(2)); toInt6 := [Z | bin6 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
toIntw:=toInt4 cat toInt5;
k4:=&+[toIntw[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..n]];
k5:=&+[toInt6[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..k]];
value:=g[k5];
f[k4]:=value;
end for;
end for;
f:=[0] cat f;
a:= [1-2*f[i]:i in [1..2^n]];
for tt:=1 to n by 1 do // butterfly algorithm
t:=2^n div 2^tt;
for j:=0 to 2^tt-1 by 2 do
for l:=1 to t by 1 do
a[t*j+l]:=a[t*j+l]+a[t*(j+1)+l];
a[t*(j+1)+l]:=a[t*j+l]-2*a[t*(j+1)+l];
end for;
end for;
end for;
b:=[Abs (a[i]):i in [1..2^n]];
nl:=2^(n-1)-Max(b) div 2;
nl;
end for;
end function;程序计算结果(选取最大值)
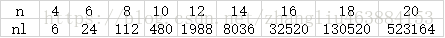
6. construction1 Immunity against fast algebraic attacks(取s=0)
n=4: (1,1)
n=6: (1,3),(2,3)
n=8: (1,5),(2,3),(3,3)
n=10: (1,7),(2,7),(3,6)
n=12: (1,9),(2,7),(3,7),(4,6)
7. Construction2
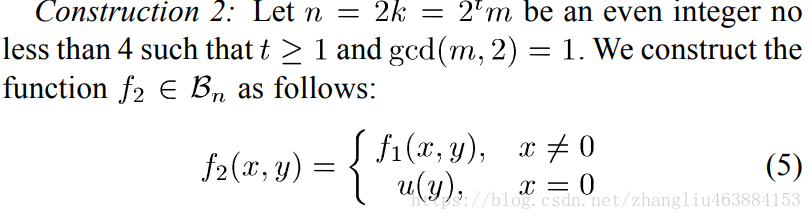
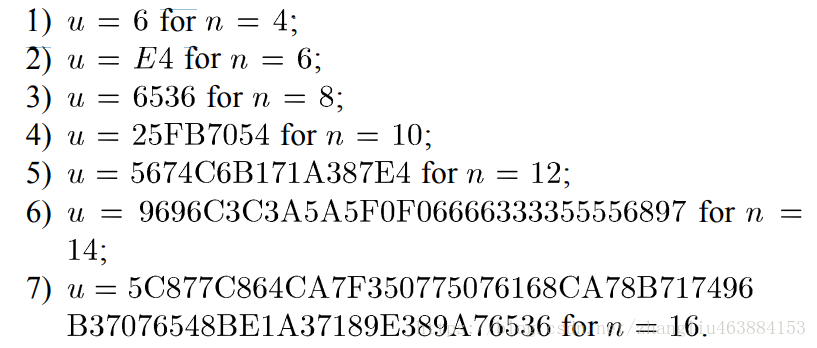
8. Construction1 optimal algebraic immunity n/2
9.Construction1 algebraic degree n-1
10.Construction2 nonlinearity
//此为magma代码
//计算Tang_Carlet_Tang函数construction2非线性度
k:=8;
for ss:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do
//ss:=0;
G<x>:=GF(2,k);
Z:=IntegerRing();
g:=[];
for tt:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do //初始化g的真值表全为0
bin1:=Eltseq(x^tt, GF(2)); toInt1 := [Z | bin1 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
k1:=&+[toInt1[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..k]]; g[k1]:=0;
end for;
n:=2*k;
F<w>:=GF(2,n);
f:=[];
for tt:=0 to 2^n-2 by 1 do //初始化f的真值表全为0
bin3:=Eltseq(w^tt, GF(2)); toInt3 := [Z | bin3 [j] : j in {1.. n by 1}];
k3:=&+[toInt3[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..n]]; f[k3]:=0;
end for;
for tt:=0+ss to 2^(k-1)+ss-1 by 1 do //根据g的支撑架生成g的真值表
bin2:=Eltseq(x^tt, GF(2)); toInt2 := [Z | bin2 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
k2:=&+[toInt2[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..k]]; g[k2]:=1;
end for;
//g:=[0] cat g;
for tt:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do //由f(x,y)=g(xy)生成f的真值表
for dd:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do
bin4:=Eltseq(x^tt, GF(2)); toInt4 := [Z | bin4 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
bin5:=Eltseq(x^dd, GF(2)); toInt5 := [Z | bin5 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
bin6:=Eltseq(x^(tt+dd), GF(2)); toInt6 := [Z | bin6 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
toIntw:=toInt4 cat toInt5;
k4:=&+[toIntw[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..n]];
k5:=&+[toInt6[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..k]];
value:=g[k5];
f[k4]:=value;
end for;
end for;
//设定u(x)真值表
u2:=[0,1,1,0];
u3:=[1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0];
u4:=[0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,0];
u5:=[0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0];
u6:=[0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,\
0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0];
u7:=[1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,\
0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,\
1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,\
1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1];
u8:=[0,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,\
1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,\
1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,\
1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,\
0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,\
0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,\
0,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,\
0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,0];
for dd:=0 to 2^k-2 by 1 do //当x=0,根据不同k值,选取不同u(x)的真值表
bin7:=Eltseq(x^dd, GF(2)); toInt7 := [Z | bin7 [j] : j in {1.. k by 1}];
k7:=&+[toInt7[i]*(2^(i-1)): i in [1..k]]; f[k7]:=u8[k7+1];//此处有u
end for;
f:=[u8[1]] cat f;//此处有u
a:= [1-2*f[i]:i in [1..2^n]];
for tt:=1 to n by 1 do // butterfly algorithm
t:=2^n div 2^tt;
for j:=0 to 2^tt-1 by 2 do
for l:=1 to t by 1 do
a[t*j+l]:=a[t*j+l]+a[t*(j+1)+l];
a[t*(j+1)+l]:=a[t*j+l]-2*a[t*(j+1)+l];
end for;
end for;
end for;
b:=[Abs (a[i]):i in [1..2^n]];
nl:=2^(n-1)-Max(b) div 2;
nl;
//Write("input.txt",f);
end for;#此为sagemath代码
#/usr/bin/env sage
import gc
from sage.crypto.boolean_function import BooleanFunction
k=13
n=2*k
u=[0]*(2^n)
F.<w>=GF(2^n)
for tt in range(0,2^n-1):
fv=0
k1=(w^tt).integer_representation()
a=str('{0:b}'.format(k1))
#变成二进制数,不带‘0b’格式
b=list(a.rjust(n,'0'))
#补足n位,以进行点积运算
b=[int(x) for x in b]
#转换为int型
for i in range(0,k):
fv=fv+b[i]*b[i+k]
#进行点积运算
fv=fv%2
u[k1]=fv
#del b
#gc.collect()
B=BooleanFunction(u)
#B.nonlinearity()
from brial import *
k=7
m=1
s=k/2
#构造第一部分
ring1 = BooleanPolynomialRing(k,'x')
x=[]
for i in range(0,k):
x.append(ring1.gen(i))
p1=(x[0]*x[1]+0)
for t in range(4,k+1):
p1=p1+(x[t-2]*x[t-1]+0)
B1=BooleanFunction(p1)
f1=list(B1.truth_table(format='int'))
#del p1, x,ring1
#gc.collect()
#构造第二部分
ring2 = declare_ring([Block('y',k-2*m),Block('x',k)],globals())
x=[]
for i in range(k-2*m,2*k-2*m):
x.append(ring2.gen(i))
y=[]
for i in range(0,k-2*m):
y.append(ring2.gen(i))
p2=x[0]*x[1]
for i in range(0,k-2*m):
p2=p2+y[i]*x[i+2*m]
B2=BooleanFunction(p2)
#B2.nonlinearity()
f2=list(B2.truth_table(format='int'))
F=f1+f2[2^k:]
B=BooleanFunction(F)
fx=B.algebraic_normal_form()
#del ring2,x,y,p2,B2,f2,F
#gc.collect()
n=2*k-2*m+1
ring3 = BooleanPolynomialRing(n,'x')
x=[]
for i in range(0,n):
x.append(ring3.gen(i))
fx1=1
for i in range(0,n-1):
fx1=fx1*(1+x[i])
fx2=x[n-1]
for i in range(k,n-1):
fx2=fx2*(1+x[i])
fx=fx+fx1+fx2
B=BooleanFunction(fx)
v=list(B.truth_table(format='int'))
F=v+u[2^n:]
B1=BooleanFunction(F)
#B.nonlinearity()
U=F
#del ring3,x,fx1,fx2,fx,B,v,F
#gc.collect()
#x*y(2^(k-1)+1)
k=13
n=2*k
g.<w>=GF(2^k)
g=[0]*(2^k)
for tt in range(0,2^(k-1)):
g[(w^tt).integer_representation()]=1
f.<v>=GF(2^n)
f=[0]*(2^n)
#x!=0,y!=0
for tt in range(0,2^k-1):
for dd in range(0,2^k-1):
k1=((w^tt)*(w^(dd*(2^k-2)))).integer_representation()
# k1=(w^(tt+dd)).integer_representation()
k2=((w^tt).integer_representation())*(2^k)+(w^dd).integer_representation()
f[k2]=g[k1]
#x=0
for tt in range(0,2^k-1):
k3=(w^tt).integer_representation()
f[k3]=U[k3]
#f[0]=U[0]
B2=BooleanFunction(f)
#del g,f
#gc.collect()
B2.nonlinearity()
程序计算结果

11 .construction2 Immunity against fast algebraic attacks(取s=0)
n=4: (1,1)
n=6: (1,3)
n=8: (1,5),(2,4),(3,3)
n=10: (1,7),(2,6),(3,5),(4,4)
n=12: (1,9),(2,8),(3,7),(4,6),(5,5)
n=14: (1,11),(2,11),(3,10),(4,8)