前言
公司项目要连接第三方公司的血压计,由于从来没有做过和蓝牙有关的项目,好奇的心驱使下下也想顺便了解一下这方面的知识,于是主动向领导请求开发这个功能,经过4天的折腾,终于弄好了,(为什么要4天呢?TMD第三天才搞明白原来不是我代码不行,是他们给错文档了,MDZZ,强忍住骂娘的冲动。。。
蓝牙基础知识:
- BLE:(Bluetooth low energy)蓝牙4.0设备因为低耗电,也叫BLE
- peripheral,central:外设和中心设备,发起链接的是central(一般是指手机),被链接的设备是peripheral(运动手环)
- service and characteristic:(服务和特征)每个设备会提供服务和特征,类似于服务端的API,但是结构不同.
每个设备会有很多服务,每个服务中包含很多字段,这些字段的权限一般分为读(read),写(write),通知(notify)几种,就是我们连接设备后具体需要操作的内容
- Description:每个characteristic可以对应一个或者多个Description用于描述characteristic的信息或属性(eg.范围,计量单位)
蓝牙开发主要有2种模式:
- 中心模式:就是以你的app作为中心,连接其他的外设的场景(本次项目使用,个人认为大部分的情况下都是这种模式)
- 外设模式:使用
手机作为外设连接其他中心设备操作的场景
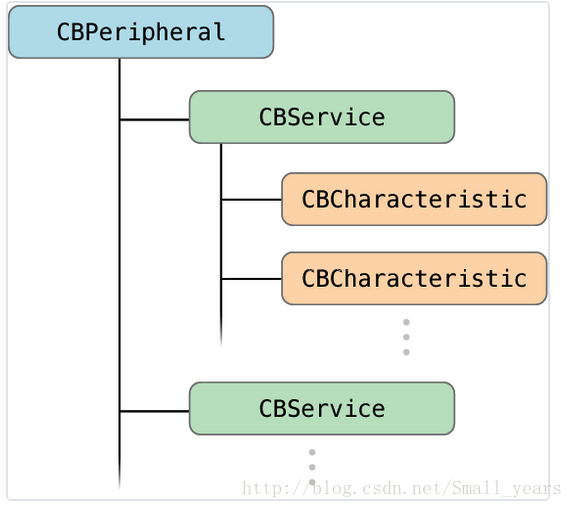
服务和特征(service and characteristic)
- 每个设备都会有1个or多个服务
- 每个服务里都会有1个or多个特征
- 特征就是具体键值对,提供数据的地方
- 每个特征属性分为:读,写,通知等等
- 外设(Peripheral)、服务(service)和特征(characteristic)的关系:

建议需要蓝牙开发的小伙伴,先去App Store下载LightBlue这个软件,他的主要作用就是连接上蓝牙外设,并且告诉你,这个蓝牙设备都支持什么服务,每个服务下面有哪些特征,甚至还可以持续监听蓝牙设备发出的数据,你也可以向蓝牙设备写数据(经个人验证,本次开发血压计,写数据、监听数据都没有用,不知道是设备的问题,还是LightBlue的问题,但都无所谓了,毕竟有了服务和特征的UUID,它的任务就完成了……)
开发:
主要流程思路:
- 建立一个Central Manager实例进行蓝牙管理
- 搜索外围设备
- 连接外围设备
- 获得外围设备的服务
- 获得服务的特征
- 从外围设备读数据
- 给外围设备发送数据
上代码:
注:本来想好好写写集成过程的代码,但是回头一想,集成代码出现在踩坑的文章中,好不专业,而且集成代码在网上
搜索能搜索出一大堆,非常完整、全面,瞬间没有了写下去的动力,回头想想那就不重复造轮子了吧,附上一篇文章,
过程大概就是这样:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/87c30628ddaa
作者辛苦!
坑:
下面主要说一下过程中遇到的坑:
1、搞准CBService的UUID
连接好设备后,搜索CBService时候的UUID,开始做之前最好知道哪个服务的UUID是你需要的,这个第三方设备合作方或者蓝牙设备文档上面会告诉你。如果不知道服务的UUID,需要自己一个个试的话,那就要注意啦,因为设备上面有很多服务,可能有多个服务都具备读写属性甚至都支持通知,在这一步找到正确的UUID是十分关键的,如果这一步错了,后面肯定错。。。
2、查看特征支持
找到服务之后要查看该服务下面的特征都支持什么属性,有了特征支持,就可以针对每个特征进行相应的操作。
提供一个打印特征支持的方法:
-(void)logCharacteristicProperties:(CBCharacteristicProperties)properties {//查看特征支持
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyBroadcast) {//广播
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyBroadcast");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyRead) {//读
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyRead");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyWriteWithoutResponse) {//写-没有响应
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyWriteWithoutResponse");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyWrite) {//写
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyWrite");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyNotify) {//通知
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyNotify");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyIndicate) {//声明
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyIndicate");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyAuthenticatedSignedWrites) {//通过验证的
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyAuthenticatedSignedWrites");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyExtendedProperties) {//拓展
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyExtendedProperties");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyNotifyEncryptionRequired) {//需要加密的通知
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyNotifyEncryptionRequired");
}
if (properties &CBCharacteristicPropertyIndicateEncryptionRequired) {//需要加密的申明
NSLog(@"CBCharacteristicPropertyIndicateEncryptionRequired");
}
}
3、发送数据,无响应
有些设备发送指令的时候会发现没有响应,甚至didWriteValueForCharacteristic
回调的值都是空,这种情况的一个原因是:有些设备需要先建立连接,才能执行后续操作,这个链接不是之前的已经链接好的蓝牙,是需要向外设发送一个连接指令,就比如我这次做的血压计开发,踩了好久的坑,直接发送开始测量指令是不好使的,必须得先发送链接指令,等血压计响应之后,再发开始测量指令。。。
一般情况下,我们发送的指令都是从字符串开始的,想发送给蓝牙,必须是NSData型,但好像转化的时候不是
常见的转换方法,
附上发送的指令转换方法:
-(NSData*)stringToByte:(NSString*)string{
NSString *hexString=[[stringuppercaseString] stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@" "withString:@""];
if ([hexString length]%2!=0) {
return nil;
}
Byte tempbyt[1]={0};
NSMutableData* bytes=[NSMutableDatadata];
for(int i=0;i<[hexStringlength];i++)
{
unichar hex_char1 = [hexStringcharacterAtIndex:i]; ////两位16进制数中的第一位(高位*16)
int int_ch1;
if(hex_char1 >= '0' && hex_char1 <='9')
int_ch1 = (hex_char1-48)*16; //// 0 的Ascll - 48
else if(hex_char1 >= 'A' && hex_char1 <='F')
int_ch1 = (hex_char1-55)*16;//// A 的Ascll - 65
else
return nil;
i++;
unichar hex_char2 = [hexStringcharacterAtIndex:i]; ///两位16进制数中的第二位(低位)
int int_ch2;
if(hex_char2 >= '0' && hex_char2 <='9')
int_ch2 = (hex_char2-48);//// 0 的Ascll - 48
else if(hex_char2 >= 'A' && hex_char2 <='F')
int_ch2 = hex_char2-55;//// A 的Ascll - 65
else
return nil;
tempbyt[0] = int_ch1+int_ch2; ///将转化后的数放入Byte数组里
[bytes appendBytes:tempbytlength:1];
}
return bytes;
}
//NSData类型转换成NSString
- (NSString*)hexadecimalString:(NSData *)data{
NSString* result;
const unsignedchar* dataBuffer = (const unsigned char*)[data bytes];
if(!dataBuffer){
return nil;
}
NSUInteger dataLength = [datalength];
NSMutableString* hexString = [NSMutableStringstringWithCapacity:(dataLength * 2)];
for(int i =0; i < dataLength; i++){
[hexString appendString:[NSStringstringWithFormat:@"%02lx", (unsignedlong)dataBuffer[i]]];
}
result = [NSString stringWithString:hexString];
return result;
}
4、处理蓝牙接收的信息
一般收到的信息都是十六进制的数值,具体代表什么意思,相信蓝牙开发文档已经都写好了,如果没有的话,我
也不知道怎么办了
十六进制转为十进制的方法:
/**
十六进制转化为十进制
@param aHexString 需要转化的str
@return 十进制数
*/
- (NSNumber *) numberHexString:(NSString *)aHexString{
// 为空,直接返回.
if (nil == aHexString){
return nil;
}
NSScanner * scanner = [NSScannerscannerWithString:aHexString];
unsigned long long longlongValue;
[scanner scanHexLongLong:&longlongValue];
//将整数转换为NSNumber,存储到数组中,并返回.
NSNumber * hexNumber = [NSNumbernumberWithLongLong:longlongValue];
return hexNumber;
}