学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(41-50天,查找与排序)_闵帆的博客-CSDN博客
选择排序
一、描述
选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法, 无论什么数据进去都是 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) 的时间复杂度. 所以用到它的时候, 数据规模越小越好. 唯一的好处可能就是不占用额外的内存空间了吧. 只需要两个额外的空间来存放最小数据的引用与下标, 因此空间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1).
与插入排序不同, 先做最麻烦的, 要进行 n − 1 n-1 n−1 次比较才能获得最小的数据.
二、具体代码
/**
*********************
* Selection sort. All data are valid.
*********************
*/
public void selectionSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
int tempIndexForSmallest;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
// Initialize.
tempNode = data[i];
tempIndexForSmallest = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
if (data[j].key < tempNode.key) {
tempNode = data[j];
tempIndexForSmallest = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// Change the selected one with the current one.
data[tempIndexForSmallest] = data[i];
data[i] = tempNode;
} // Of for i
}// Of selectionSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void selectionSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = {
5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = {
"if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.selectionSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of selectionSortTest
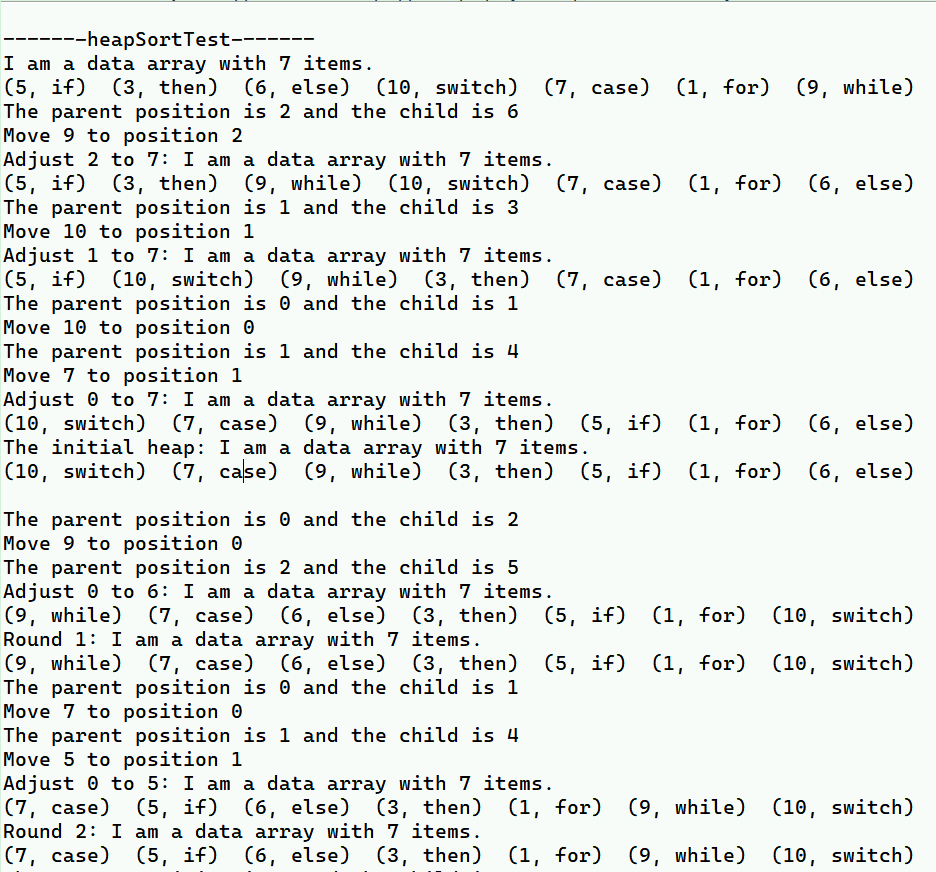
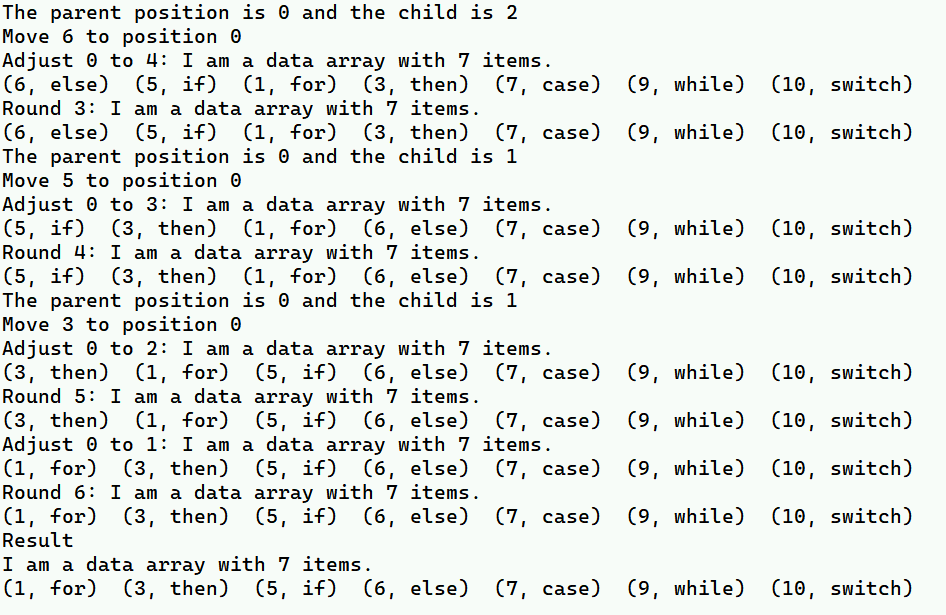
三、运行截图

堆排序
一、描述
堆排序 (heapsort) 是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法.
堆积是一个近似完全二叉树的结构, 并同时满足堆积的性质:即子结点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点.
堆排序可以说是一种利用堆的概念来排序的选择排序.
分为两种方法:
大顶堆: 每个节点的值都大于或等于其子节点的值, 在堆排序算法中用于升序排列;
小顶堆: 每个节点的值都小于或等于其子节点的值, 在堆排序算法中用于降序排列;
调整堆的时间复杂度为 O ( log n ) Ο(\log{n}) O(logn). 所以说堆排序的平均时间复杂度为 O ( n log n ) Ο(n\log{n}) O(nlogn).
它的空间复杂度只有 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
当然代码中没有使用引用的结构来表示二叉树, 而是使用的数组.
结合二叉树用数组表示时候的下标符合的数学表达式就能够很轻易地得到子树和父节点.
二、实现
1. 步骤
a. 创建一个大顶堆 H[0 … … n-1]
b. 把堆首(最大值)和堆尾互换
c. 把堆的尺寸缩小 1, 把新的数组顶端数据调整到相应位置
d. 重复步骤 2, 直到堆的尺寸为 1
2. 具体代码
/**
*********************
* Heap sort. Maybe the most difficult sorting algorithm.
*********************
*/
public void heapSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
// Step 1. Construct the initial heap.
for (int i = length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(i, length);
} // Of for i
System.out.println("The initial heap: " + this + "\r\n");
// Step 2. Swap and reconstruct.
for (int i = length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
tempNode = data[0];
data[0] = data[i];
data[i] = tempNode;
adjustHeap(0, i);
System.out.println("Round " + (length - i) + ": " + this);
} // Of for i
}// Of heapSort
/**
*********************
* Adjust the heap.
*
* @param paraStart The start of the index.
* @param paraLength The length of the adjusted sequence.
*********************
*/
public void adjustHeap(int paraStart, int paraLength) {
DataNode tempNode = data[paraStart];
int tempParent = paraStart;
int tempKey = data[paraStart].key;
for (int tempChild = paraStart * 2 + 1; tempChild < paraLength; tempChild = tempChild * 2 + 1) {
// The right child is bigger.
if (tempChild + 1 < paraLength) {
if (data[tempChild].key < data[tempChild + 1].key) {
tempChild++;
} // Of if
} // Of if
System.out.println("The parent position is " + tempParent + " and the child is " + tempChild);
if (tempKey < data[tempChild].key) {
// The child is bigger.
data[tempParent] = data[tempChild];
System.out.println("Move " + data[tempChild].key + " to position " + tempParent);
tempParent = tempChild;
} else {
break;
} // Of if
} // Of for tempChild
data[tempParent] = tempNode;
System.out.println("Adjust " + paraStart + " to " + paraLength + ": " + this);
}// Of adjustHeap
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void heapSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = {
5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = {
"if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.heapSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of heapSortTest
三、运行截图
总结
生成大顶堆地方式很值得注意, 他是利用自底向上来处理的数据. 之前我就一直在纠结于自顶向下处理数据.
然后就会发现有些大一点的数就不能够到上面去.
而且处理的时候不是从最后一层处理, 而是在倒数第二层做文章. 这个算法真的太精妙了.