文章目录
http模块
引入http内置模块
var http = require("http")
创建服务器
http.createServer(()=>{})
回调函数一般传递两个参数:req和res
- req 接收浏览器传递的参数
- res 返回渲染的内容
listen(端口号,()=>{})监听端口号的内容,即监听对应浏览器页面的内容,行为,监听到了就执行回调函数中的内容
var http = require("http")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req,res) => {
// 接受浏览器传递的参数,返回渲染的内容
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
另一种写法:
将创建和处理内容分开写
var http = require("http")
var server = http.createServer()
server.on("request", (req, res) => {
// 接受浏览器传递的参数,返回渲染的内容
})
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
res 属性——返回结果
res返回渲染的内容
res.write(内容):将内容进行写入,write方法可以调用多次res.end():关闭浏览器写入。如果打开了浏览器写入,不关闭的话,浏览器会认为你要一直写入,一直等待。所以要使用 res.end() 将浏览器进行关闭。end中也可以传递参数,最终显示在页面。
注意 : 传递的参数必须是json字符串。不能直接传递一个数据,如数组。直接传递数组,前端不能进行解析,但是前端可以解析传递的json字符串。
eg:
01.server.js
var http = require("http")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req,res) => {
// 接受浏览器传递的参数,返回渲染的内容
res.write("hello world\n")
res.write("hello world2222\n")
res.end("[1,2,3]")
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
终端启动
node .\01.server.js
浏览器输出:
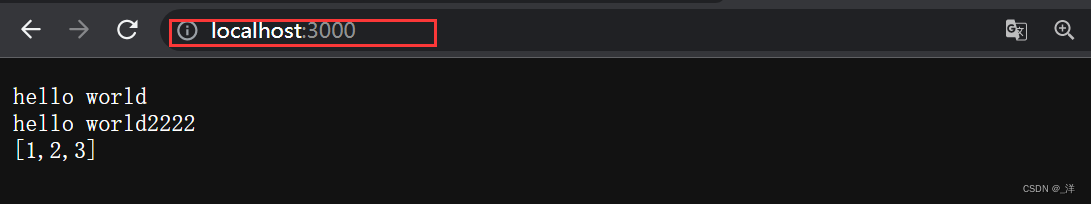
res.writeHead
服务器可能返回html标签内容,那如何确保它不被解析成字符串而被解析成html标签呢?就需要使用res.writeHead的Content-Type属性。
如,做如下限制:
res.writeHead(200,{
"Content-Type":"text/html"})
-
200:代表返回的状态码。eg:200代表成功,404代表失败。 -
Content-Type- text/html:代表解析成html内容
- text/plain:代表解析成普通字符串
(虽然现在node进行了更新如果是html标签默认解析成html的内容,但是还是写上"Content-Type"比较保险)
-
可以设置输入的编码属性。如果要输入中文要将编码格式设置为
utf-8
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=utf-8"})
eg:示例
var http = require("http")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200,{
"Content-Type":"text/html"})
// 接受浏览器传递的参数,返回渲染的内容
res.write(`
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
</head>
<body>
<b>hello world</b>
<p>我是一个段落</p>
</body>
</html>
`)
res.end()
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
输出:
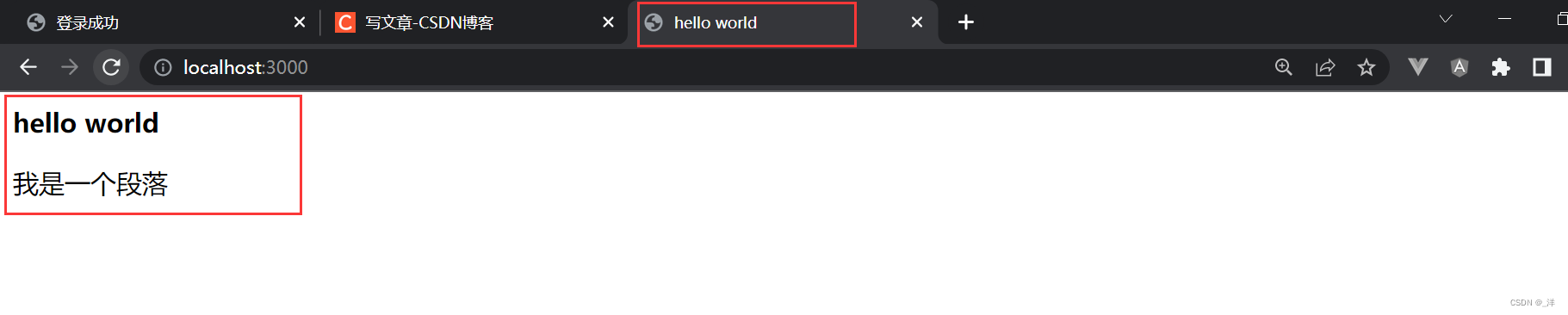
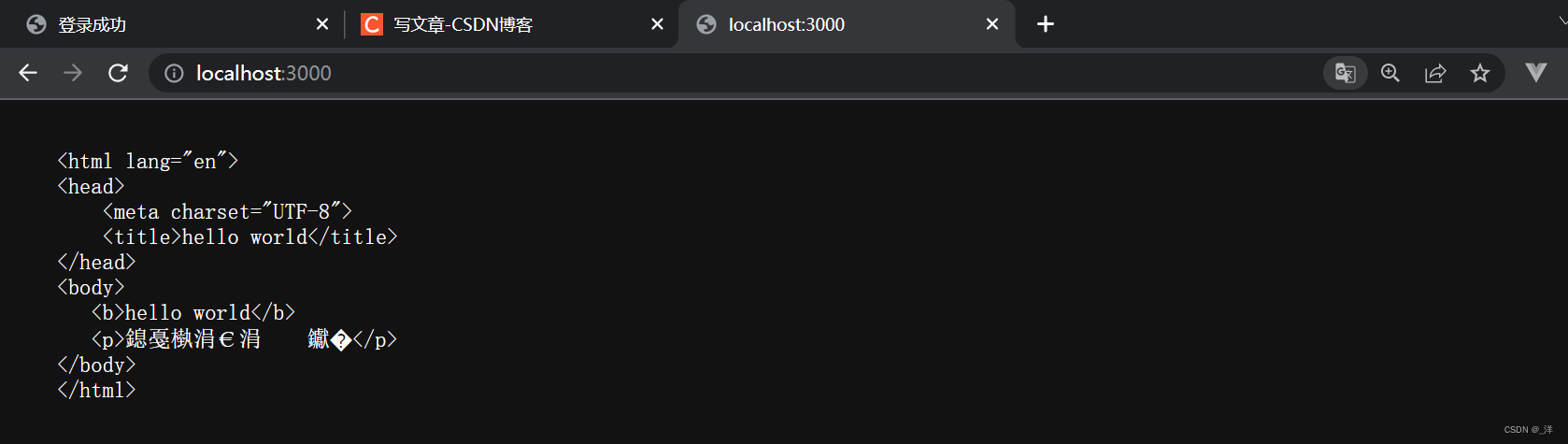
如果设置成
res.writeHead(200,{
"Content-Type":"text/plain"})
req 属性——处理请求
req代表浏览器的请求,其中包括很多内容
eg:
http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log(req)
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
包含很多内容,这里截取一下Server的内容:
_server: Server {
maxHeaderSize: undefined,
insecureHTTPParser: undefined,
_events: [Object: null prototype],
_eventsCount: 2,
_maxListeners: undefined,
_connections: 1,
_handle: [TCP],
_usingWorkers: false,
_workers: [],
_unref: false,
allowHalfOpen: true,
pauseOnConnect: false,
noDelay: false,
keepAlive: false,
keepAliveInitialDelay: 0,
httpAllowHalfOpen: false,
timeout: 0,
keepAliveTimeout: 5000,
maxHeadersCount: null,
maxRequestsPerSocket: 0,
headersTimeout: 60000,
requestTimeout: 0,
_connectionKey: '6::::3000',
[Symbol(IncomingMessage)]: [Function: IncomingMessage],
[Symbol(ServerResponse)]: [Function: ServerResponse],
[Symbol(kCapture)]: false,
[Symbol(async_id_symbol)]: 2
},
parser: HTTPParser {
'0': [Function: bound setRequestTimeout],
'1': [Function: parserOnHeaders],
'2': [Function: parserOnHeadersComplete],
'3': [Function: parserOnBody],
'4': [Function: parserOnMessageComplete],
'5': [Function: bound onParserExecute],
'6': [Function: bound onParserTimeout],
_headers: [],
_url: '',
socket: [Circular *1],
incoming: [Circular *2],
outgoing: null,
maxHeaderPairs: 2000,
_consumed: true,
onIncoming: [Function: bound parserOnIncoming],
[Symbol(resource_symbol)]: [HTTPServerAsyncResource]
},
- req.url
通过req.url获取请求路径
var http = require("http")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log(req.url)
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
输出:
server start
/
/favicon.ico
/当前页页面的路径
/favicon.ico是默认请求该端口的图标的路径
如果我们处理不了/favicon.ico,不想要访问该路径直接return即可
http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.url == "/favicon.ico")
return
console.log(req.url)
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
输出:
server start
/
同时在浏览器访问的路径和也会在服务器端实时显示。
http://localhost:3000/hello
服务器端
server start
/
/
/hello
- 处理路径请求,可以根据
req.url捕获路径,然后在函数中进行处理
var http = require("http")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.url == "/favicon.ico")
return
console.log(req.url)
res.writeHead(renderStatus(req.url), {
"Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf-8" })
res.write(renderHTML(req.url))
res.end()
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
function renderStatus(url) {
var arr = ["/home","/list"]
return arr.includes(url)?200:404
}
function renderHTML(url){
switch(url){
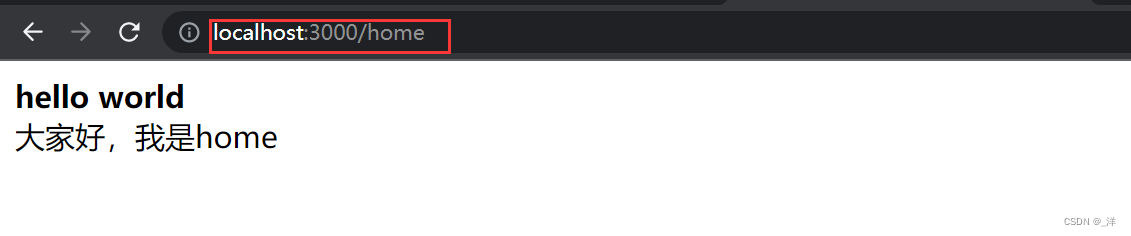
case "/home":
return `
<html>
<b>hello world</b>
<div>大家好,我是home</div>
</html>
`
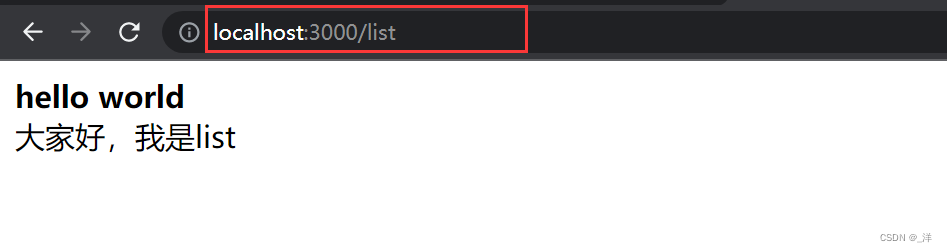
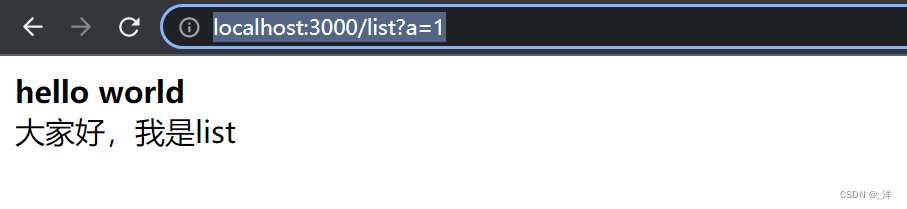
case "/list":
return `
<html>
<b>hello world</b>
<div>大家好,我是list</div>
</html>
`
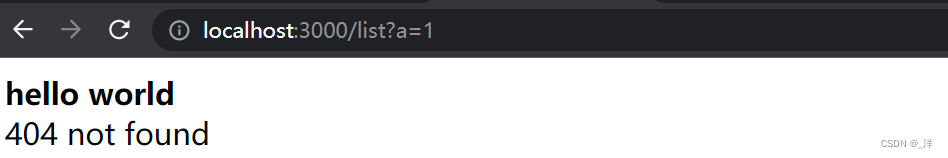
default:
return `
<html>
<b>hello world</b>
<div>404 not found</div>
</html>
`
}
}
url模块
问题产生:当我们处理请求路径的时候,路径后面完全可能携带参数,在?后面就是携带的参数。
所以处理路径的时候就需要将路径截取之后再进行处理。
url模块引入
var url = require("url")
url.parse解析路径
console.log(url.parse(req.url))
url.js
var http = require("http")
var url = require("url")
var renderStatus = require("../http模块.js/module/renderStatus")
var renderHTML = require("../http模块.js/module/renderHTML")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.url == "/favicon.ico")
return
console.log(url.parse(req.url))
res.writeHead(renderStatus.renderStatus(req.url), {
"Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf-8" })
res.write(renderHTML.renderHTML(req.url))
res.end()
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
控制台内容
server start
Url {
protocol: null,
slashes: null,
auth: null,
host: null,
port: null,
hostname: null,
hash: null,
search: '?a=1',
query: 'a=1',
pathname: '/list',
path: '/list?a=1',
href: '/list?a=1'
}
所以我们通过url.parse(req.url)的pathname属性就可以访问不带参数的请求路径
同时我们发现query中放的是传递过来的参数,但是他是一个字符串,要是一个json对象就好了
只需要给解析的方法添加一个true参数即可:console.log(url.parse(req.url,true))
输出:
query: [Object: null prototype] {
a: '1' },
那么就可以直接通过url.parse(req.url,true).query访问a
例子:
var http = require("http")
var url = require("url")
var renderStatus = require("../http模块.js/module/renderStatus")
var renderHTML = require("../http模块.js/module/renderHTML")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.url == "/favicon.ico")
return
var urlobjt = url.parse(req.url, true)
console.log(urlobjt.query.a)
var pathname =urlobjt.pathname
res.writeHead(renderStatus.renderStatus(pathname), {
"Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf-8" })
res.write(renderHTML.renderHTML(pathname))
res.end()
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
浏览器访问路径:http://localhost:3000/list?a=1
控制台输出:
server start
1
页面可以正常访问
url.format合并路径
上面通过url.prase可以将一个完整的路径解析成为一个个片段,同样我们可以通过 url.format将一个个片段重新合并为一个路径
eg:
var url = require("url")
// const urlString = 'https://www.baidu.com:443/ad/index.html?id=8&name=mouse#tag=110'
// const parsedStr = url.parse(urlString)
// console.log(parsedStr)
const obj ={
protocol: 'https:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'www.baidu.com:443',
port: '443',
hostname: 'www.baidu.com',
hash: '#tag=110',
search: '?id=8&name=mouse',
query: 'id=8&name=mouse',
pathname: '/ad/index.html',
path: '/ad/index.html?id=8&name=mouse',
}
console.log(url.format(obj))
输出:
https://www.baidu.com:443/ad/index.html?id=8&name=mouse#tag=110
resolve
将两个url进行拼接
注意点:
- 路径后面加不加
/的区别 - http路径从那开始进行连接
eg:
var a1 = url.resolve('/one/two/three/', 'four ')
var a2 = url.resolve('/one/two/three', 'four ')
console.log(a1,"\n",a2)
var b1 = url.resolve("http://example.com/", "/one")
// 会将域名之后的所有内容进行替换
var b2 = url.resolve("http://example.com/aaaa","/one")
console.log(b1,"\n",b2)
输出:
/one/two/three/four
/one/two/four
http://example.com/one
http://example.com/one
url新版使用
新版url.js
var http = require("http")
var url = require("url")
var renderStatus = require("../http模块.js/module/renderStatus")
var renderHTML = require("../http模块.js/module/renderHTML")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 获取url,两个参数:一个url地址,一个url的端口号
const myURL = new URL(req.url,'http://127.0.0.1:3000')
console.log(myURL)
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
终端输出:
URL {
href: 'http://127.0.0.1:3000/list',
origin: 'http://127.0.0.1:3000',
protocol: 'http:',
username: '',
password: '',
host: '127.0.0.1:3000',
hostname: '127.0.0.1',
port: '3000',
pathname: '/list',
search: '',
searchParams: URLSearchParams {
},
hash: ''
}
pathname:存储的是请求路径。
searchParams:存储的是传递的参数对象。是一个迭代器支持循环遍历。
路径拼接直接使用 new URL("请求路径","http路径")
var http = require("http")
var url = require("url")
var renderStatus = require("../http模块.js/module/renderStatus")
var renderHTML = require("../http模块.js/module/renderHTML")
const {
CONNREFUSED } = require("dns")
const {
REPLServer } = require("repl")
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 获取url,两个参数:一个url地址,一个url的端口号
const myURL = new URL(req.url,'http://127.0.0.1:3000')
var pathname = myURL.pathname
var searchParams = myURL.searchParams
console.log(searchParams)
for (var obj of myURL.searchParams) {
console.log(obj)
}
// 解构
for (var [key,value] of myURL.searchParams) {
console.log(key,value)
}
res.writeHead(renderStatus.renderStatus(pathname), {
"Content-Type": "text/html;charset=utf-8" })
res.write(renderHTML.renderHTML(pathname))
res.end()
// 路径拼接
var b = new URL("/one", "http://example.com/aaa/bbb")
console.log(b)
console.log(b.href)
}).listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server start")
})
输出:
server start
URLSearchParams {
'a' => '1', 'b' => '2', 'c' => '3' }
[ 'a', '1' ]
[ 'b', '2' ]
[ 'c', '3' ]
a 1
b 2
c 3
URL {
href: 'http://example.com/one',
origin: 'http://example.com',
protocol: 'http:',
username: '',
password: '',
host: 'example.com',
hostname: 'example.com',
port: '',
pathname: '/one',
search: '',
searchParams: URLSearchParams {
},
hash: ''
}
http://example.com/one
format用法
格式化路径
url.format(URL[, options])
参数options:
auth:是否保留a:b格式的内容。 默认值: true。fragment是否保留#。 默认值: true。search是否显示参数。 默认值: true。unicode编码。 默认值: false,默认进行编码;为true时就不进行编码了。
EG:
const myURL = new URL('https://a:b@测试?abc#foo');
console.log(url.format(myURL))
console.log(url.format(myURL,{
unicode:true, auth:false,fragment:false,search:false}));
输出:
https://a:b@xn--0zwm56d/?abc#foo
https://测试/
url.fileURLToPath(url)
转化为绝对路径。
此函数可确保正确解码百分比编码字符,并确保跨平台有效的绝对路径字符串。
获取请求路径,比直接使用url更简单、方便地获取路径
eg:
import {
fileURLToPath } from 'url';
new URL('file:///C:/path/').pathname;// 错误: /C:/path/
fileURLToPath('file:///C:/path/');// 正确: C:\path\ (Windows)
url.pathToFileURL(path)
转换为文件网址
该函数确保 path 被绝对解析,并且在转换为文件网址时正确编码网址控制字符。
eg:
import {
pathToFileURL } from 'url';
new URL('/foo#1', 'file:'); // 错误: file:///foo#1
pathToFileURL('/foo#1'); // 正确: file:///foo%231 (POSIX)
注意使用这些方法是需要引入的。
querystring小模块
querystring模块提供了用于解析和格式化网址查询字符串(参数)的实用工具。
querystring格式转换
即使用querystring可以实现 对象格式 和 参数传递格式之间的转换
- querystring.parse(str):将 str 解析成对象
- querystring.stringify(number):将number编码成from格式对象,即参数传递格式。
eg:
var str = "name=yang&age=18&location=beijing"
var querystring = require("querystring")
var obj = querystring.parse(str)
console.log(obj)
var number = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3
}
var myNumber = querystring.stringify(number)
console.log(myNumber)
输出:
[Object: null prototype] {
name: 'yang',
age: '18',
location: 'beijing'
}
a=1&b=2&c=3
escape/unescape
编码和解码
escape 进行编码
unescape 进行解码
var str = "name=yang&age=18&url = http://www.baidu.com"
var querystring = require("querystring")
var escaped = querystring.escape(str)
console.log(escaped)
var escaped1 = querystring.unescape(escaped)
console.log(escaped1)
输出:
name%3Dyang%26age%3D18%26url%20%3D%20http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com
name=yang&age=18&url = http://www.baidu.com