pandas深入理解
Pandas是一个Python库,旨在通过“标记”和“关系”数据以完成数据整理工作,库中有两个主要的数据结构Series和DataFrame
In [1]: import numpy as np In [2]: import pandas as pd In [3]: from pandas import Series,DataFrame In [4]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
本文主要说明完成数据整理的几大步骤:
1.数据来源
1)加载数据
2)随机采样
2.数据清洗
0)数据统计(贯穿整个过程)
1)处理缺失值
2)层次化索引
3)类数据库操作(增、删、改、查、连接)
4)离散面元划分
5)重命名轴索引
3.数据转换
1)分组
2)聚合
3)数据可视化
数据来源
1.加载数据
pandas提供了一些将表格型数据读取为DataFrame对象的函数,其中用的比较多的是read_csv和read_table,参数说明如下:
参数 |
说明 |
| path | 表示文件位置、URL、文件型对象的字符串 |
| sep或delimiter | 用于将行中的各字段进行拆分的字符串或正则表达式 |
| head | 用作列名的行号 |
| index_col | 用作行索引的列编号或列名 |
| skiprows | 需要跳过的行号列表(从0开始) |
| na_value | 一组用户替换的值 |
| converters | 由列号/列名跟函数之间的映射关系组成的字典 |
| chunksize | 文件快的大小 |
举例:
In [2]: result = pd.read_table('C:\Users\HP\Desktop\SEC-DEBIT_0804.txt',sep = '\s+') In [3]: result Out[3]: SEC-DEBIT HKD0002481145000001320170227SECURITIES BUY ON 23Feb2017 0 10011142009679 HKD00002192568083002000 NaN NaN NaN 1 20011142009679 HKD00004154719083002000 NaN NaN NaN 2 30011142005538 HKD00000210215083002300 NaN NaN NaN 3 40011142005538 HKD00000140211083002300 NaN NaN NaN
延展:
DataFrame写文件:data.to_csv('*.csv')
Series写文件:data.to_csv('*.csv')
Series读文件:Series.from_csv('*.csv')
2.随机采样
利用numpy.random.permutation函数可以实现对Series和DataFrame的列随机重排序工作
In [18]: df = DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(5,4)) In [19]: df Out[19]: 0 1 2 3 0 0 1 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 2 8 9 10 11 3 12 13 14 15 4 16 17 18 19 In [20]: sample = np.random.permutation(5) In [21]: sample Out[21]: array([0, 1, 4, 2, 3]) In [22]: df.take(sample) Out[22]: 0 1 2 3 0 0 1 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 4 16 17 18 19 2 8 9 10 11 3 12 13 14 15 In [25]: df.take(np.random.permutation(5)[:3]) Out[25]: 0 1 2 3 2 8 9 10 11 4 16 17 18 19 3 12 13 14 15
数据清洗
0.数据统计
In [31]: df = DataFrame({'A':np.random.randn(5),'B':np.random.randn(5)})
In [32]: df
Out[32]:
A B
0 -0.635732 0.738902
1 -1.100320 0.910203
2 1.503987 -2.030411
3 0.548760 0.228552
4 -2.201917 1.676173
In [33]: df.count() #计算个数
Out[33]:
A 5
B 5
dtype: int64
In [34]: df.min() #最小值
Out[34]:
A -2.201917
B -2.030411
dtype: float64
In [35]: df.max() #最大值
Out[35]:
A 1.503987
B 1.676173
dtype: float64
In [36]: df.idxmin() #最小值的位置
Out[36]:
A 4
B 2
dtype: int64
In [37]: df.idxmax() #最大值的位置
Out[37]:
A 2
B 4
dtype: int64
In [38]: df.sum() #求和
Out[38]:
A -1.885221
B 1.523419
dtype: float64
In [39]: df.mean() #平均数
Out[39]:
A -0.377044
B 0.304684
dtype: float64
In [40]: df.median() #中位数
Out[40]:
A -0.635732
B 0.738902
dtype: float64
In [41]: df.mode() #众数
Out[41]:
Empty DataFrame
Columns: [A, B]
Index: []
In [42]: df.var() #方差
Out[42]:
A 2.078900
B 1.973661
dtype: float64
In [43]: df.std() #标准差
Out[43]:
A 1.441839
B 1.404871
dtype: float64
In [44]: df.mad() #平均绝对偏差
Out[44]:
A 1.122734
B 0.964491
dtype: float64
In [45]: df.skew() #偏度
Out[45]:
A 0.135719
B -1.480080
dtype: float64
In [46]: df.kurt() #峰度
Out[46]:
A -0.878539
B 2.730675
dtype: float64
In [48]: df.quantile(0.25) #25%分位数
Out[48]:
A -1.100320
B 0.228552
dtype: float64
In [49]: df.describe() #描述性统计指标
Out[49]:
A B
count 5.000000 5.000000
mean -0.377044 0.304684
std 1.441839 1.404871
min -2.201917 -2.030411
25% -1.100320 0.228552
50% -0.635732 0.738902
75% 0.548760 0.910203
max 1.503987 1.676173
1.处理缺失值
In [50]: string = Series(['apple','banana','pear',np.nan,'grape']) In [51]: string Out[51]: 0 apple 1 banana 2 pear 3 NaN 4 grape dtype: object In [52]: string.isnull() #判断是否为缺失值 Out[52]: 0 False 1 False 2 False 3 True 4 False dtype: bool In [53]: string.dropna() #过滤缺失值,默认过滤任何含NaN的行 Out[53]: 0 apple 1 banana 2 pear 4 grape dtype: object In [54]: string.fillna(0) #填充缺失值 Out[54]: 0 apple 1 banana 2 pear 3 0 4 grape dtype: object In [55]: string.ffill() #向前填充 Out[55]: 0 apple 1 banana 2 pear 3 pear 4 grape dtype: object In [56]: data = DataFrame([[1. ,6.5,3],[1. ,np.nan,np.nan],[np.nan,np.nan,np.nan],[np.nan,7,9]]) #DataFrame操作同理 In [57]: data Out[57]: 0 1 2 0 1.0 6.5 3.0 1 1.0 NaN NaN 2 NaN NaN NaN 3 NaN 7.0 9.0
2.层次化索引
In [6]: data = Series(np.random.randn(10),index=[['a','a','a','b','b','b','c','c','d','d'],[1,2,3,1,2,3,1,2,2,3]]) In [7]: data Out[7]: a 1 0.386697 2 0.822063 3 0.338441 b 1 0.017249 2 0.880122 3 0.296465 c 1 0.376104 2 -1.309419 d 2 0.512754 3 0.223535 dtype: float64 In [8]: data.index Out[8]: MultiIndex(levels=[[u'a', u'b', u'c', u'd'], [1, 2, 3]], labels=[[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3], [0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2]]) In [10]: data['b':'c'] Out[10]: b 1 0.017249 2 0.880122 3 0.296465 c 1 0.376104 2 -1.309419 dtype: float64 In [11]: data[:,2] Out[11]: a 0.822063 b 0.880122 c -1.309419 d 0.512754 dtype: float64 In [12]: data.unstack() Out[12]: 1 2 3 a 0.386697 0.822063 0.338441 b 0.017249 0.880122 0.296465 c 0.376104 -1.309419 NaN d NaN 0.512754 0.223535 In [13]: data.unstack().stack() Out[13]: a 1 0.386697 2 0.822063 3 0.338441 b 1 0.017249 2 0.880122 3 0.296465 c 1 0.376104 2 -1.309419 d 2 0.512754 3 0.223535 dtype: float64 In [14]: df = DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(4,3),index=[['a','a','b','b'],[1,2,1,2]],columns=[['Ohio','Ohio','Colorad ...: o'],['Green','Red','Green']]) In [15]: df Out[15]: Ohio Colorado Green Red Green a 1 0 1 2 2 3 4 5 b 1 6 7 8 2 9 10 11 In [16]: df.index.names = ['key1','key2'] In [17]: df.columns.names = ['state','color'] In [18]: df Out[18]: state Ohio Colorado color Green Red Green key1 key2 a 1 0 1 2 2 3 4 5 b 1 6 7 8 2 9 10 11 In [19]: df['Ohio'] #降维 Out[19]: color Green Red key1 key2 a 1 0 1 2 3 4 b 1 6 7 2 9 10 In [20]: df.swaplevel('key1','key2') Out[20]: state Ohio Colorado color Green Red Green key2 key1 1 a 0 1 2 2 a 3 4 5 1 b 6 7 8 2 b 9 10 11 In [21]: df.sortlevel(1) #key2 Out[21]: state Ohio Colorado color Green Red Green key1 key2 a 1 0 1 2 b 1 6 7 8 a 2 3 4 5 b 2 9 10 11 In [22]: df.sortlevel(0) #key1 Out[22]: state Ohio Colorado color Green Red Green key1 key2 a 1 0 1 2 2 3 4 5 b 1 6 7 8 2 9 10 11
3.类sql操作
In [5]: dic = {'Name':['LiuShunxiang','Zhangshan','ryan'],
...: 'Sex':['M','F','F'],
...: 'Age':[27,23,24],
...: 'Height':[165.7,167.2,154],
...: 'Weight':[61,63,41]}
In [6]: student = pd.DataFrame(dic)
In [7]: student
Out[7]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63
2 24 154.0 ryan F 41
In [8]: dic1 = {'Name':['Ann','Joe'],
...: 'Sex':['M','F'],
...: 'Age':[27,33],
...: 'Height':[168,177.2],
...: 'Weight':[51,65]}
In [9]: student1 = pd.DataFrame(dic1)
In [10]: Student = pd.concat([student,student1]) #插入行
In [11]: Student
Out[11]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63
2 24 154.0 ryan F 41
0 27 168.0 Ann M 51
1 33 177.2 Joe F 65
In [14]: pd.DataFrame(Student,columns = ['Age','Height','Name','Sex','Weight','Score']) #新增列
Out[14]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight Score
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61 NaN
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63 NaN
2 24 154.0 ryan F 41 NaN
0 27 168.0 Ann M 51 NaN
1 33 177.2 Joe F 65 NaN
In [16]: Student.ix[Student['Name']=='ryan','Height'] = 160 #修改某个数据
In [17]: Student
Out[17]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63
2 24 160.0 ryan F 41
0 27 168.0 Ann M 51
1 33 177.2 Joe F 65
In [18]: Student[Student['Height']>160] #删选
Out[18]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63
0 27 168.0 Ann M 51
1 33 177.2 Joe F 65
In [21]: Student.drop(['Weight'],axis = 1).head() #删除列
Out[21]:
Age Height Name Sex
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F
2 24 160.0 ryan F
0 27 168.0 Ann M
1 33 177.2 Joe F
In [22]: Student.drop([1,2]) #删除行索引为1和2的行
Out[22]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
0 27 168.0 Ann M 51
In [24]: Student.drop(['Age'],axis = 1) #删除列索引为Age的列
Out[24]:
Height Name Sex Weight
0 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
1 167.2 Zhangshan F 63
2 154.0 ryan F 41
0 168.0 Ann M 51
1 177.2 Joe F 65
In [26]: Student.groupby('Sex').agg([np.mean,np.median]) #等价于SELECT…FROM…GROUP BY…功能
Out[26]:
Age Height Weight
mean median mean median mean median
Sex
F 26.666667 24 168.133333 167.20 56.333333 63
M 27.000000 27 166.850000 166.85 56.000000 56
In [27]: series = pd.Series(np.random.randint(1,20,5)) #排序
In [28]: series
Out[28]:
0 9
1 17
2 17
3 13
4 15
dtype: int32
In [29]: series.order() #默认升序
C:/Anaconda2/Scripts/ipython-script.py:1: FutureWarning: order is deprecated, use sort_values(...)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Out[29]:
0 9
3 13
4 15
1 17
2 17
dtype: int32
In [30]: series.order(ascending = False) #降序
C:/Anaconda2/Scripts/ipython-script.py:1: FutureWarning: order is deprecated, use sort_values(...)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Out[30]:
2 17
1 17
4 15
3 13
0 9
dtype: int32
In [31]: Student.sort_values(by = ['Height']) #按值排序
Out[31]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight
2 24 160.0 ryan F 41
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63
0 27 168.0 Ann M 51
1 33 177.2 Joe F 65
In [32]: dict2 = {'Name':['ryan','LiuShunxiang','Zhangshan','Ann','Joe'],
...: 'Score':['89','90','78','60','53']}
In [33]: Score = pd.DataFrame(dict2)
In [34]: Score
Out[34]:
Name Score
0 ryan 89
1 LiuShunxiang 90
2 Zhangshan 78
3 Ann 60
4 Joe 53
In [35]: stu_score = pd.merge(Student,Score,on = 'Name') #表连接
In [36]: stu_score
Out[36]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight Score
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61 90
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63 78
2 24 160.0 ryan F 41 89
3 27 168.0 Ann M 51 60
4 33 177.2 Joe F 65 53
注:student1以dic形式转DataFrame对象和直接新建DataFrame对象,连接结果不同
In [71]:student1 = DataFrame({'name';['Ann','Joe'],'Sex':['M','F'],'Age':[27,33],'Height':[168,177.2],'Weight':[51,65 ...: ]}) In [72]: student Out[72]: Age Height Name Sex Weight 0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61 1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63 2 24 154.0 ryan F 41 In [73]: student1 Out[73]: Age Height Sex Weight name 0 27 168.0 M 51 Ann 1 33 177.2 F 65 Joe In [74]: Student = pd.concat([student,student1]) In [75]: Student Out[75]: Age Height Name Sex Weight name 0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61 NaN 1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63 NaN 2 24 154.0 ryan F 41 NaN 0 27 168.0 NaN M 51 Ann 1 33 177.2 NaN F 65 Joe
延伸表连接,merge函数参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 说明 |
| left | 参与合并的左侧DataFrame |
| right | 参与合并的右侧DataFrame |
| how | "inner"、"outer"、"left"、"right"其中之一,默认为inner |
| on | 用于连接的列名 |
| left_on | 左侧DataFrame中用作连接键的列 |
| right_on | 右侧DataFrame中用作连接键的列 |
| left_index | 将左侧DataFrame中的行索引作为连接的键 |
| right_index | 将右侧DataFrame中的行索引作为连接的键 |
| sort | 根据连接键对合并后的数据进行排序 |
举例如下
In [5]: df1 = DataFrame({'key':['b','b','a','c','a','a','b'],'data1':range(7)})
In [6]: df1
Out[6]:
data1 key
0 0 b
1 1 b
2 2 a
3 3 c
4 4 a
5 5 a
6 6 b
In [7]: df2 = DataFrame({'key':['a','b','d'],'data2':range(3)})
In [8]: df2
Out[8]:
data2 key
0 0 a
1 1 b
2 2 d
In [9]: pd.merge(df1,df2) #默认内链接,合并相同的key即a,b
Out[9]:
data1 key data2
0 0 b 1
1 1 b 1
2 6 b 1
3 2 a 0
4 4 a 0
5 5 a 0
In [10]: df3 = DataFrame({'lkey':['b','b','a','c','a','a','b'],'data1':range(7)})
In [11]: df4 = DataFrame({'rkey':['a','b','d'],'data2':range(3)})
In [12]: df3
Out[12]:
data1 lkey
0 0 b
1 1 b
2 2 a
3 3 c
4 4 a
5 5 a
6 6 b
In [13]: df4
Out[13]:
data2 rkey
0 0 a
1 1 b
2 2 d
In [14]: print pd.merge(df3,df4,left_on = 'lkey',right_on = 'rkey')
data1 lkey data2 rkey
0 0 b 1 b
1 1 b 1 b
2 6 b 1 b
3 2 a 0 a
4 4 a 0 a
5 5 a 0 a
In [15]: print pd.merge(df3,df4,left_on = 'lkey',right_on = 'data2')
Empty DataFrame
Columns: [data1, lkey, data2, rkey]
Index: []
In [16]: print pd.merge(df1,df2,how = 'outer')
data1 key data2
0 0.0 b 1.0
1 1.0 b 1.0
2 6.0 b 1.0
3 2.0 a 0.0
4 4.0 a 0.0
5 5.0 a 0.0
6 3.0 c NaN
7 NaN d 2.0
In [17]: df5 = DataFrame({'key':list('bbacab'),'data1':range(6)})
In [18]: df6 = DataFrame({'key':list('ababd'),'data2':range(5)})
In [19]: df5
Out[19]:
data1 key
0 0 b
1 1 b
2 2 a
3 3 c
4 4 a
5 5 b
In [20]: df6
Out[20]:
data2 key
0 0 a
1 1 b
2 2 a
3 3 b
4 4 d
In [21]: print pd.merge(df5,df6,on = 'key',how = 'left')
data1 key data2
0 0 b 1.0
1 0 b 3.0
2 1 b 1.0
3 1 b 3.0
4 2 a 0.0
5 2 a 2.0
6 3 c NaN
7 4 a 0.0
8 4 a 2.0
9 5 b 1.0
10 5 b 3.0
In [22]: left = DataFrame({'key1':['foo','foo','bar'],'key2':['one','two','one'],'lval':[1,2,3]})
In [23]: right = DataFrame({'key1':['foo','foo','bar','bar'],'key2':['one','one','one','two'],'rval':[4,5,6,7]})
In [24]: left
Out[24]:
key1 key2 lval
0 foo one 1
1 foo two 2
2 bar one 3
In [25]: right
Out[25]:
key1 key2 rval
0 foo one 4
1 foo one 5
2 bar one 6
3 bar two 7
In [26]: print pd.merge(left,right,on = ['key1','key2'],how = 'outer')
key1 key2 lval rval
0 foo one 1.0 4.0
1 foo one 1.0 5.0
2 foo two 2.0 NaN
3 bar one 3.0 6.0
4 bar two NaN 7.0
In [27]: print pd.merge(left,right,on = 'key1')
key1 key2_x lval key2_y rval
0 foo one 1 one 4
1 foo one 1 one 5
2 foo two 2 one 4
3 foo two 2 one 5
4 bar one 3 one 6
5 bar one 3 two 7
In [28]: print pd.merge(left,right,on = 'key1',suffixes = ('_left','_right'))
key1 key2_left lval key2_right rval
0 foo one 1 one 4
1 foo one 1 one 5
2 foo two 2 one 4
3 foo two 2 one 5
4 bar one 3 one 6
5 bar one 3 two 7
4.离散化面元划分
In [17]: age = [20,22,25,27,21,23,37,31,61,45,41,32] In [18]: bins = [18,25,35,60,100] In [19]: cats = pd.cut(age,bins) In [20]: cats Out[20]: [(18, 25], (18, 25], (18, 25], (25, 35], (18, 25], ..., (25, 35], (60, 100], (35, 60], (35, 60], (25, 35]] Length: 12 Categories (4, object): [(18, 25] < (25, 35] < (35, 60] < (60, 100]] In [26]: group_names = ['YoungAdult','Adult','MiddleAged','Senior'] In [27]: pd.cut(age,bins,labels = group_names) #设置面元名称 Out[27]: [YoungAdult, YoungAdult, YoungAdult, Adult, YoungAdult, ..., Adult, Senior, MiddleAged, MiddleAged, Adult] Length: 12 Categories (4, object): [YoungAdult < Adult < MiddleAged < Senior] In [28]: data = np.random.randn(10) In [29]: cats = pd.qcut(data,4) #qcut提供根据样本分位数对数据进行面元划分 In [30]: cats Out[30]: [(0.268, 0.834], (-0.115, 0.268], (0.268, 0.834], [-1.218, -0.562], (-0.562, -0.115], [-1.218, -0.562], (-0.115, 0.268], [-1.218, -0.562], (0.268, 0.834], (-0.562, -0.115]] Categories (4, object): [[-1.218, -0.562] < (-0.562, -0.115] < (-0.115, 0.268] < (0.268, 0.834]] In [33]: pd.value_counts(cats) Out[33]: (0.268, 0.834] 3 [-1.218, -0.562] 3 (-0.115, 0.268] 2 (-0.562, -0.115] 2 dtype: int64 In [35]: pd.qcut(data,[0.1,0.5,0.9,1.]) #自定义分位数,[0-1]的数值 Out[35]: [(-0.115, 0.432], (-0.115, 0.432], (0.432, 0.834], NaN, [-0.787, -0.115], [-0.787, -0.115], (-0.115, 0.432], [-0.787, -0.115], (-0.115, 0.432], [-0.787, -0.115]] Categories (3, object): [[-0.787, -0.115] < (-0.115, 0.432] < (0.432, 0.834]]
5.重命名轴索引
In [36]: data = DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index = ['Ohio','Colorado','New York'],columns = ['one','two','thr ...: ee','four']) In [37]: data Out[37]: one two three four Ohio 0 1 2 3 Colorado 4 5 6 7 New York 8 9 10 11 In [38]: data.index = data.index.map(str.upper) In [39]: data Out[39]: one two three four OHIO 0 1 2 3 COLORADO 4 5 6 7 NEW YORK 8 9 10 11 In [40]: data.rename(index = str.title,columns=str.upper) Out[40]: ONE TWO THREE FOUR Ohio 0 1 2 3 Colorado 4 5 6 7 New York 8 9 10 11 In [41]: data.rename(index={'OHIO':'INDIANA'},columns={'three':'ryana'}) #对部分轴标签更新 Out[41]: one two ryana four INDIANA 0 1 2 3 COLORADO 4 5 6 7 NEW YORK 8 9 10 11
数据转换
1.分组
In [42]: df = DataFrame({'key1':['a','a','b','b','a'],'key2':['one','two','one','two','one'],'data1':np.random.randn(5)
...: ,'data2':np.random.randn(5)})
In [43]: df
Out[43]:
data1 data2 key1 key2
0 0.762448 0.816634 a one
1 1.412613 0.867923 a two
2 0.899297 -1.049657 b one
3 0.912080 0.628012 b two
4 -0.549258 -1.327614 a one
In [44]: grouped = df['data1'].groupby(df['key1']) #按key1列分组,计算data1列的平均值
In [45]: grouped
Out[45]: <pandas.core.groupby.SeriesGroupBy object at 0x00000000073C97F0>
In [46]: grouped.mean()
Out[46]:
key1
a 0.541935
b 0.905688
Name: data1, dtype: float64
In [48]: df['data1'].groupby([df['key1'],df['key2']]).mean()
Out[48]:
key1 key2
a one 0.106595
two 1.412613
b one 0.899297
two 0.912080
Name: data1, dtype: float64
In [49]: df.groupby('key1').mean() #根据列名分组
Out[49]:
data1 data2
key1
a 0.541935 0.118981
b 0.905688 -0.210822
In [50]: df.groupby(['key1','key2']).mean()
Out[50]:
data1 data2
key1 key2
a one 0.106595 -0.255490
two 1.412613 0.867923
b one 0.899297 -1.049657
two 0.912080 0.628012
In [51]: df.groupby('key1')['data1'].mean() #选取部分列进行聚合
Out[51]:
key1
a 0.541935
b 0.905688
Name: data1, dtype: float64
In [52]: df.groupby(['key1','key2'])['data1'].mean()
Out[52]:
key1 key2
a one 0.106595
two 1.412613
b one 0.899297
two 0.912080
Name: data1, dtype: float64
In [53]: people = DataFrame(np.random.randn(5,5),columns = ['a','b','c','d','e'],index = ['Joe','Steve','Wes','Jim','Tr
...: avis'])
In [54]: people
Out[54]:
a b c d e
Joe 0.223628 -0.282831 0.368583 0.246665 -0.815742
Steve 0.662181 0.187961 0.515883 -2.021429 -0.624596
Wes -1.009086 0.450082 -0.819855 -1.626971 0.632064
Jim 1.593881 0.803760 -0.209345 -1.295325 -0.553693
Travis -0.041911 1.115285 -1.648207 0.521751 -0.414183
In [55]: mapping = {'a':'red','b':'red','c':'blue','d':'blue','e':'red','f':'orange'}
In [56]: map_series = Series(mapping)
In [57]: map_series
Out[57]:
a red
b red
c blue
d blue
e red
f orange
dtype: object
In [58]: people.groupby(map_series,axis = 1).count() #根据series分组
Out[58]:
blue red
Joe 2 3
Steve 2 3
Wes 2 3
Jim 2 3
Travis 2 3
In [59]: by_columns = people.groupby(mapping,axis =1) #根据字典分组
In [60]: by_columns.sum()
Out[60]:
blue red
Joe 0.615248 -0.874945
Steve -1.505546 0.225546
Wes -2.446826 0.073060
Jim -1.504670 1.843948
Travis -1.126456 0.659191
In [61]: people.groupby(len).sum() #根据函数分组
Out[61]:
a b c d e
3 0.808423 0.971012 -0.660617 -2.675632 -0.737371
5 0.662181 0.187961 0.515883 -2.021429 -0.624596
6 -0.041911 1.115285 -1.648207 0.521751 -0.414183
In [63]: columns = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays([['US','US','US','JP','JP'],[1,3,5,1,3]],names = ['city','tennor'])
In [65]: df1 = DataFrame(np.random.randn(4,5),columns = columns)
In [66]: df1
Out[66]:
city US JP
tennor 1 3 5 1 3
0 1.103548 1.087425 0.717741 -0.354419 1.294512
1 -0.247544 -1.247665 1.340309 1.337957 0.528693
2 2.168903 -0.124958 0.367158 0.478355 -0.828126
3 -0.078540 -3.062132 -2.095675 -0.879590 -0.020314
In [67]: df1.groupby(level = 'city',axis = 1).count() #根据索引级别分组
Out[67]:
city JP US
0 2 3
1 2 3
2 2 3
3 2 3
2.透视表
pandas为我们提供了实现数据透视表功能的函数pivot_table(),该函数参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 说明 |
| data | 需要进行透视的数据 |
| value | 指定需要聚合的字段 |
| index | 指定值为行索引 |
| columns | 指定值为列索引 |
| aggfunc | 聚合函数 |
| fill_value | 常量替换缺失值,默认不替换 |
| margins | 是否合并,默认否 |
| dropna | 是否观测缺失值,默认是 |
举例:
In [68]: dic = {'Name':['LiuShunxiang','Zhangshan','ryan'],
...: ...: 'Sex':['M','F','F'],
...: ...: 'Age':[27,23,24],
...: ...: 'Height':[165.7,167.2,154],
...: ...: 'Weight':[61,63,41]}
...:
In [69]: student = pd.DataFrame(dic)
In [70]: student
Out[70]:
Age Height Name Sex Weight
0 27 165.7 LiuShunxiang M 61
1 23 167.2 Zhangshan F 63
2 24 154.0 ryan F 41
In [71]: pd.pivot_table(student,values = ['Height'],columns = ['Sex']) #'Height'作为数值变量,'Sex'作为分组变量
Out[71]:
Sex F M
Height 160.6 165.7
In [72]: pd.pivot_table(student,values = ['Height','Weight'],columns = ['Sex','Age'])
Out[72]:
Sex Age
Height F 23 167.2
24 154.0
M 27 165.7
Weight F 23 63.0
24 41.0
M 27 61.0
dtype: float64
In [73]: pd.pivot_table(student,values = ['Height','Weight'],columns = ['Sex','Age']).unstack()
Out[73]:
Age 23 24 27
Sex
Height F 167.2 154.0 NaN
M NaN NaN 165.7
Weight F 63.0 41.0 NaN
M NaN NaN 61.0
In [74]: pd.pivot_table(student,values = ['Height','Weight'],columns = ['Sex'],aggfunc = [np.mean,np.median,np.std])
Out[74]:
mean median std
Sex F M F M F M
Height 160.6 165.7 160.6 165.7 9.333810 NaN
Weight 52.0 61.0 52.0 61.0 15.556349 NaN
3.数据可视化
plot参数说明
| Series.plot()方法 | DataFrame.plot()方法 | ||
| 参数 | 说明 | 参数 | 说明 |
| label | 用于图例的标签 | subplot | 将各个DataFrame对象绘制到各subplot中 |
| ax | matplotlib.subplot对象 | sharex | 若subplot = True,则共用同一X轴,包括刻度和界限 |
| style | 风格字符串 | sharey | 若subplot = True,则共用同一X轴,包括刻度和界限 |
| alpha | 图表填充的不透明度 | figsize | 表示图像大小的元组 |
| kind | 可以是'line','bar','barh','kde' | title | 表示图像标题的字符串 |
| xtick | 用作X轴刻度的值 | legend | 添加一个subplot图例,默认True |
| Ytick | 用作Y轴刻度的值 | sort_columns | 以字母表顺序绘制各列,默认使用当前列顺序 |
| Xlim | X轴的界限 | ||
| Ylim | Y轴的界限 | ||
1)线性图
In [76]: s = Series(np.random.randn(10).cumsum(),index = np.arange(0,100,10))
In [77]: s.plot()
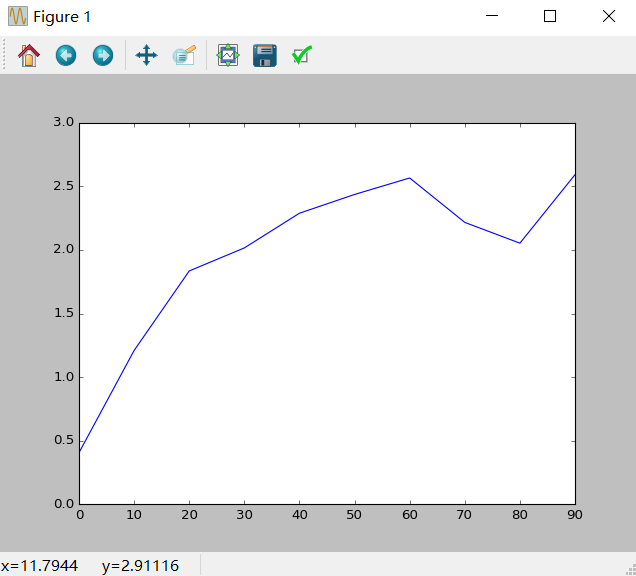
In [78]: df = DataFrame(np.random.randn(10,4).cumsum(0),columns = ['A','B','C','D'],index = np.arange(0,100,10)) In [79]: df.plot()

2)柱状图
In [80]:fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,1) In [81]:data = Series(np.random.rand(16),index=list('abcdefghijklmnop')) In [82]:data.plot(kind = 'bar',ax = axes[0],color = 'k',alpha = 0.7) In [83]:data.plot(kind = 'barh',ax = axes[1],color = 'k',alpha = 0.7)
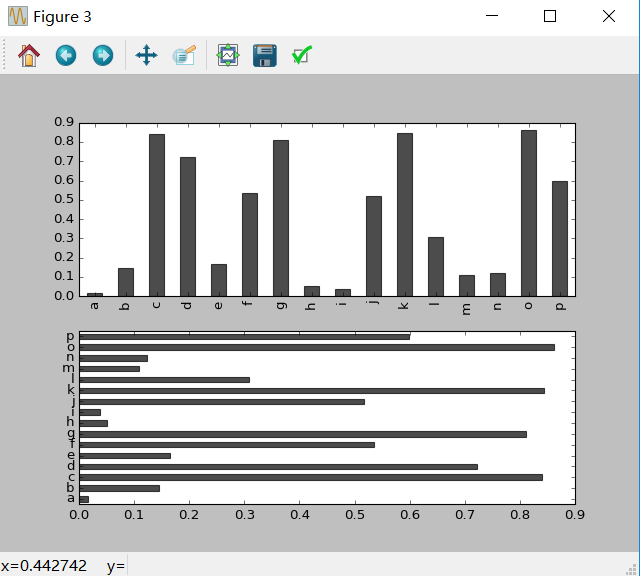
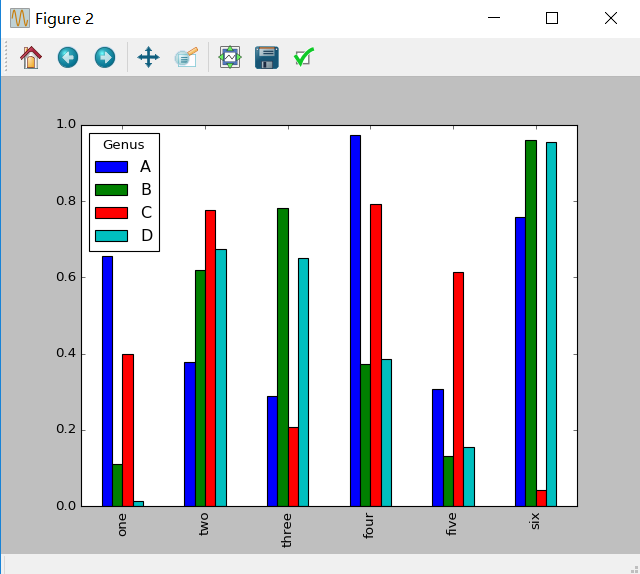
In [84]:df = DataFrame(np.random.rand(6,4),index = ['one','two','three','four','five','six'],columns = pd.Index(['A','B','C','D'],name = 'Genus')) In [85]:df.plot(kind = 'bar')
3)密度图
In [87]:comp1 = np.random.normal(0,1,size = 100) In [88]:comp2 = np.random.normal(10,2,size = 100) In [89]:values = Series(np.concatenate([comp1,comp2])) In [90]:values.hist(bins = 50,alpha = 0.3,color = 'r',normed = True) In [91]:values.plot(kind = 'kde',style = 'k--')

4)散点图
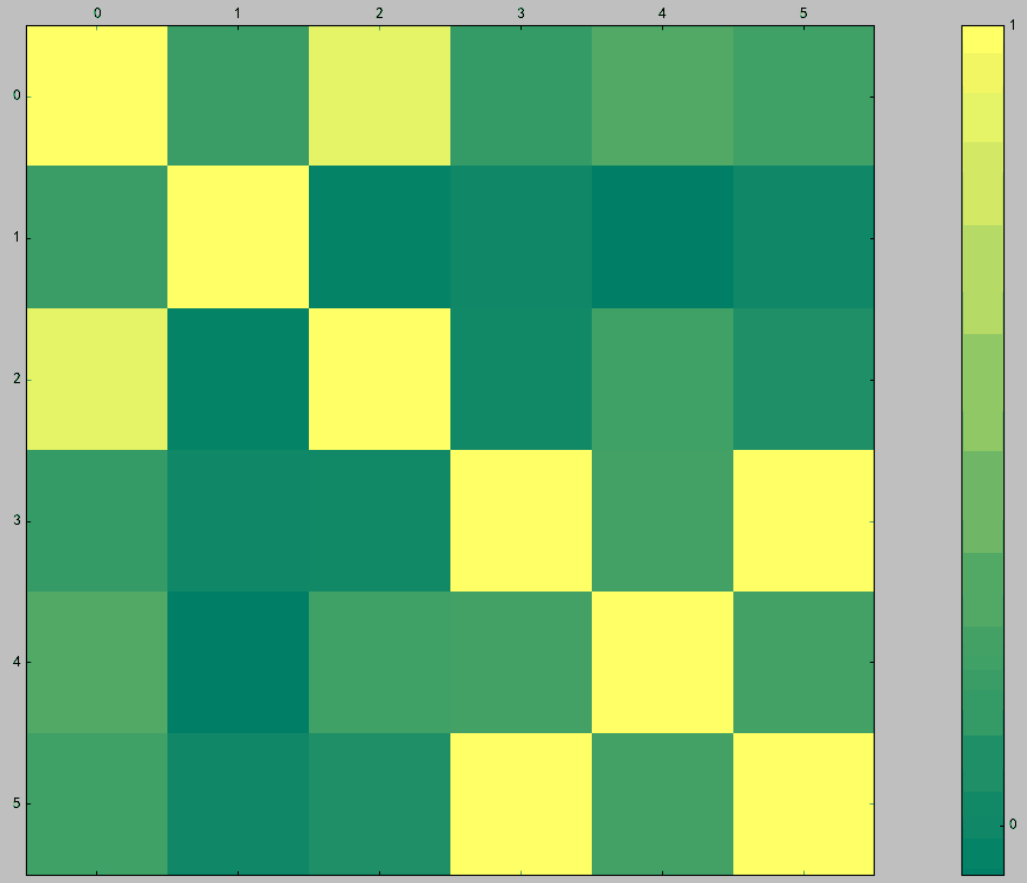
In [7]: import tushare as ts In [8]: data = ts.get_hist_data('300348',start='2017-08-15') In [9]: pieces = data[['close', 'price_change', 'ma20','volume', 'v_ma20', 'turnover']] In [10]: pd.scatter_matrix(pieces)
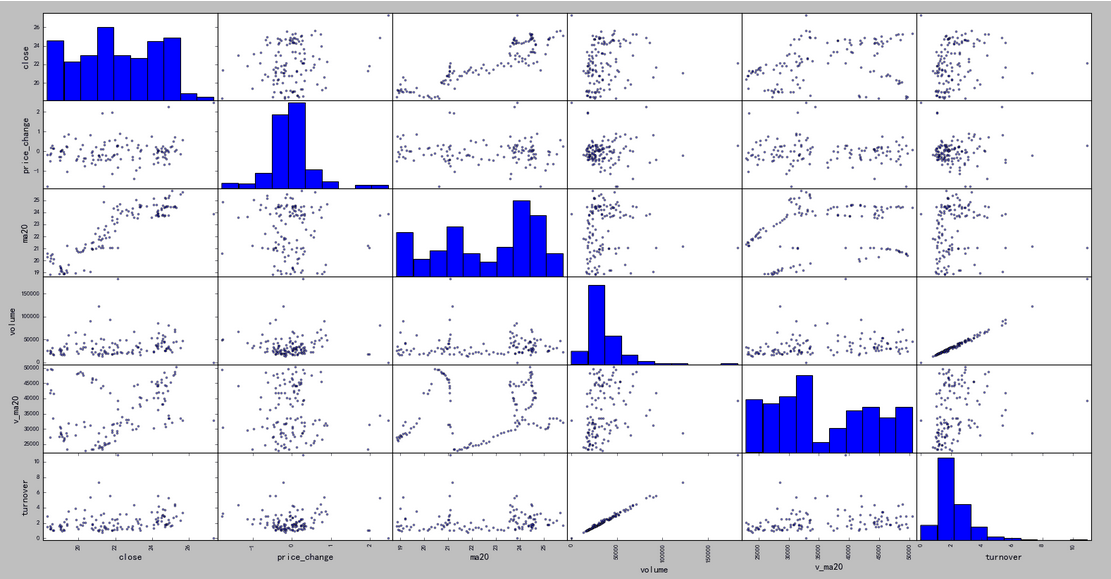
5)热力图
In [11]: cov = np.corrcoef(pieces.T) In [12]: img = plt.matshow(cov,cmap=plt.cm.summer) In [13]: plt.colorbar(img, ticks=[-1,0,1])