因为前面的总结都是分为不同模块的有基本知识还有代码块,这个就专门写所有面试常考的手写代码。
一. 查找
(1)二分查找
//二分查找 升序表
/**
*
* @param {Number[]} arr
* @param {Number} target
*/
function halfSearch(arr, target) {
let left = 0
let right = arr.length-1
let mid = Math.floor((right + left) / 2)
while (left <= right) {
mid = Math.floor((right + left) / 2)
if (arr[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1
} else if (arr[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1
} else {
return mid
}
}
return -1
}
console.log(halfSearch([3,5,7,9,11,14],11));二. 排序
(1)冒泡排序/简单排序
function BubbleSort(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
let temp = arr[j]
arr[j] = arr[i]
arr[i] = temp
}
}
}
return arr
}
console.log(BubbleSort([3,5,77,32,22,14]));(2)插入排序
function insertSort(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let key = arr[i]
let j = i - 1
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
arr[j] = key
j--
}
}
return arr
}
console.log(insertSort([3,6,22,31,14,9,5,7]));(3)选择排序
function selectSort(arr) {
let res = []
while (arr.length !== 0) {
let min = Math.min(...arr)
let index = arr.indexOf(min)
res.push(min)
arr.splice(index, 1)
}
return res
}
console.log(selectSort([3, 76, 33, 22, 16, 21, 5]));(4)快速排序
/**
*
* @param {Number[]} arr
*/
function quickSort(arr) {
if (arr.length === 0) {
return arr
}
let refer = arr.shift()
let right = []
let left = []
for (let item of arr) {
if (item < refer) {
left.push(item)
} else {
right.push(item)
}
}
return quickSort(left).concat(refer, quickSort(right))
}
console.log(quickSort([3, 6, 88, 22, 14, 12, 46]));(5)归并排序
function mergerSort(arr) {
function merger(leftArray, rightArray) {
let n = leftArray && leftArray.length
let m = rightArray && rightArray.length
let backs = []
let i = 0
let j = 0
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (leftArray[i] < rightArray[j]) {
backs.push(leftArray[i++])
} else {
backs.push(rightArray[j++])
}
}
while (i < n) {
backs.push(leftArray[i++])
}
while (j < m) {
backs.push(rightArray[j++])
}
return backs
}
if (arr.length === 1) return arr
let mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2)
let left = arr.slice(0, mid)
let right = arr.slice(mid)
return merger(mergerSort(left), mergerSort(right))
}
console.log(mergerSort([11, 2, 6, 87, 4, 6]));三. 数组全排列
/**
*
* @param {Array} arr
*/
function permute(arr) {
let res = []
/**
*
* @param {Array} path
* @returns
*/
function dfs(path) {
if (path.length === arr.length) {
res.push([...path])
return
}
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (path.includes(arr[i]))
continue
path.push(arr[i])
dfs(path)
path.pop()
}
}
dfs([])
return res
}
console.log(permute(["a", 1, "c"]));四. 防抖节流
(1)防抖
function fd(fun, delay) {
let timer
return function () {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => { fun() }, delay)
} else {
clearTimeout(timer)
}
}
}(2)节流
function jl(fun, delay) {
let flag = true
let timer
return function () {
if (!flag) {
return
}
flag = false
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fun()
flag = true
}, delay)
}
}五. 深度克隆
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function deepClone(target) {
let res = undefined
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(target) === "[object Array]") {
res = []
} else if (Object.prototype.toString.call(target) === "[object Object]") {
res = {}
} else {
return target
}
for (let key in target) {
let value = target[key]
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Array]"
|| Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Object]") {
res[key] = deepClone(value)
} else {
res[key] = value
}
}
return res
}
let obj1 = { a: 1, b: { c: 2, d: { f: 56 } } }
let obj2 = deepClone(obj1)
</script>
</body>
</html>六. 深度冻结
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function deepFreeze(target) {
Object.freeze(target)
for (let key in target) {
let value = target[key]
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Object]" ||
Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Array]") {
deepFreeze(value)
}
}
}
}
let obj1 = { a: 1, b: 2, c: [1, 4, 6], d: { aa: 1 } }
deepFreeze(obj1)
</script>
</body>
</html>七. vue数据代理
(1)vue2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let proxy = {}
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: { aa: 11 } }
Object.defineProperty(proxy, "a", {
get() {
return obj[key]
},
set(newValue) {
obj[key] = newValue
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>(2)vue3
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: { dd: 11 } }
let p = new Proxy(obj, {
get(target, propName) {
Reflect.get(target, propName)
},
set(target, propName, value) {
Reflect.set(target, propName, value)
},
deleteProperty(target, propName) {
Reflect.deleteProperty(target, propName)
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>(3)双向绑定模拟(vue2为例)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 为什么要在标签里直接定义输入事件呢,其实v-modal本身就是个语法糖 -->
<input type="text" id="dom1" />
<input type="text" id="dom2" />
<script>
class Watcher {
constructor(dom, msg) {
this.dom = dom
this.msg = msg
}
update(data) {
this.dom.value = data
}
}
//其实就是个发布订阅
class Def {
constructor() {
this.subs = {}
}
//发布消息
publish(msg, data) {
if (this.subs[msg]) {
this.notice(msg, data)
}
}
subscribe(item) {
if (!this.subs[item.msg]) {
this.subs[item.msg] = []
}
this.subs[item.msg].push(item)
}
notice(msg, data) {
for (let item of this.subs[msg]) {
item.update(data)
}
}
}
class VM {
constructor(data, Watchers) {
this.data = data
this.def = new Def()
this.Watchers = Watchers
}
Observe() {
for (let key in this.data) {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
get() {
this.def.subscribe(this.WillUpdate)
return this.data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
//修改数据相同也会触发set,过滤一下。
if (newValue !== this.data[key]) {
this.data[key] = newValue
this.def.publish(key, this.data[key])
}
}
})
}
}
default() {
for (let item of this.Watchers) {
this.WillUpdate = item
item.dom.value = this[item.msg]
//就是v-modal语法糖的原理
item.dom.addEventListener("input", (e) => {
this[item.msg] = e.target.value
})
}
}
}
function data() {
return {
a: 111,
b: 222,
c: 'test',
}
}
const Watcher1 = new Watcher(document.getElementById("dom1"), "a")
const Watcher2 = new Watcher(document.getElementById("dom2"), "b")
let Watchers = [Watcher1, Watcher2]
const vm = new VM(data(), Watchers)
vm.Observe()
vm.default()
</script>
</body>
</html>八. localStorage设置过期时间
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="test()">getItem</button>
<script>
function mySet(key, value, expire) {
let nowTime = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000)
let expireTime = nowTime + expire
localStorage.setItem(key, value)
localStorage.setItem(`${key}__expire`, expireTime)
}
function myGet(key) {
let nowTime = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000)
if (localStorage.getItem(`${key}__expire`) > nowTime) {
return localStorage.getItem(key)
} else {
localStorage.removeItem(key)
localStorage.removeItem(`${key}__expire`)
return false
}
}
localStorage.__proto__.mySet = mySet
localStorage.__proto__.myGet = myGet
//按秒来的
localStorage.mySet("test", "mememe", 3)
function test() {
console.log(localStorage.myGet("test"));
}
</script>
</body>
</html>九. 手写call、apply
(1)call
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var name = "window"
var obj = { name: "obj" }
Function.prototype.mycall = function (target) {
let obj = (target === Object(target)) ?
target : window
let param = []
for (let i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
param.push(arguments[i])
}
obj.fn = this
obj.fn(...param)
}
let showName = function (test1, test2) {
console.log(this.name, test1, test2);
}
showName.mycall(obj, "test1", "test2")
</script>
</body>
</html>(2) apply
其实和call原理差不多。主要就是接收参数变成了数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var name = "window"
var obj = { name: "obj" }
Function.prototype.MyApply = function (target) {
let obj = (Object(target) === target) ? target : window
obj.fn = this
let param = arguments[1]
obj.fn(...param)
}
function showName(test1, test2) {
console.log(this.name,test1,test2);
}
showName.MyApply(obj, ["123", "abc"])
</script>
</body>
</html>(3)当然可以写一手bind
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
Function.prototype.MyBind = function (target) {
let obj = (Object(target) === target) ? target : window
obj.fn = this
return function () {
obj.fn(...arguments)
}
}
var name = "window"
var obj = { name: "obj" }
function showName(test1, test2) {
console.log("name:", this.name, "test:", test1, test2);
}
let objShow = showName.MyBind(obj)
objShow("123", "abc")
</script>
</body>
</html>十. 手写instanceof
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function MyInstanceof(target, construct) {
let targetProto = Object.getPrototypeOf(target)
while (targetProto !== null) {
if (construct.prototype !== targetProto) {
targetProto = Object.getPrototypeOf(targetProto)
}
else {
return true
}
}
return false
}
class dog {
}
class person {
}
class student extends person {
}
class smallStudent extends student {
}
let sS = new smallStudent()
console.log(MyInstanceof(sS, person));
console.log(MyInstanceof(sS, student));
console.log(MyInstanceof(sS, dog));
</script>
</body>
</html>十一. 合并两个有序链表
(1)使用的链表类(一个简化版,非常好用)
function ListNode(val) {
this.val = val
this.next = null
}
ListNode.prototype.set = function (node) {
this.next = node
}
let setListNode = function (arr) {
if (arr.length > 0) {
let ln = null
// let res = null;
while (arr.length > 0) {
let temp = new ListNode(arr.pop())
temp.set(ln)
ln = temp
}
return ln
}
return false
}
let l1 = setListNode([4, 8, 10])
let l2 = setListNode([1, 3, 5, 22])(2)合并有序链表
2个
function mergeTwoLists(l1, l2) {
// write code here
const pHead = { //定义一个新的链表,此时指向为null
next: null
};
var pre = pHead;
while (l1 || l2) {
if (!l2 || (l1 && l1.val < l2.val)) { //比较这两个链表值
pre.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next; //l1放入后 往后移
} else {
pre.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
return pHead.next;
}
console.log(mergeTwoLists(l1, l2));k个(其实就是把k个拆分成两两合并,和上面一个道理)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
if(lists.length===0){
return null
}
let res=lists.shift()
function mergeTowList(l1,l2){
let pHead={
next:null
}
let cur=pHead
while(l1||l2){
if(!l2||(l1&&l1.val<l2.val)){
cur.next=l1
l1=l1.next
}else{
cur.next=l2
l2=l2.next
}
cur=cur.next
}
return pHead.next
}
while(lists.length>0){
let list=lists.shift()
res=mergeTowList(res,list)
}
return res
};(3)翻转链表
let l1 = setListNode([4, 8, 10])
let l2 = setListNode([1, 3, 5, 22])
var reverseList = function(head) {
let prev = null;
let curr = head;
while (curr) {
const next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
};
console.log(reverseList(l1));(4)删除倒数第n个节点
//快慢指针法
function DeleteNthNode(head, n) {
let res = new ListNode()
res.next = head
// 首先声明三个指针,对应倒数第n个节点的前一个地址,倒数第n个节点的地址,最后的地址。
let p0 = res, p1 = res.next, p2 = res.next
//快慢指针 让p2先跑n
while (n) {
p2 = p2.next
n--
}
// 因为p2为尾指针,那就让大家一起移动直到p2移到尾,这时对应的p2与p1就差了n个,也就是p1
// 就是倒数第n个
while (p2) {
p0 = p0.next;
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next
}
// 然后让倒数前n个的前一为直接指向n+1个就行
p0.next = p1.next
return res.next
}删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(js)_一枚小银子的博客-CSDN博客
(5) 反转中间的链表其余的不变
leecode原题 力扣![]() https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/submissions/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/submissions/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} left
* @param {number} right
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseBetween = function (head, left, right) {
let res = new ListNode()
res.next = head
let prev = res
for (let i = 0; i < left - 1; ++i) {
prev = prev.next;
}
let cur = prev.next
for (let i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {
const next = cur.next;
cur.next = next.next;
next.next = prev.next;
prev.next = next;
}
return res.next
}; (6) 链表删除重复元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
let prev=null
let curr=head
while(curr){
const next=curr.next
if(prev&&prev.val===curr.val){
prev.next=next
curr=next
}else{
prev=curr
curr=curr.next
}
}
return head
};(7)k个一组反转链表
var reverseKGroup = function (head, k) {
let phead = head
let length = 0
while (phead !== null) {
length++
phead = phead.next
}
function reverse(head, left, right) {
console.log(left, right);
let res = new ListNode()
res.next = head
let prev = res
for (let i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
prev = prev.next
}
let curr = prev.next
for (let i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {
const next = curr.next
curr.next = next.next
next.next = prev.next
prev.next = next
}
return res.next
}
for (let i = 0; (i + k) <= length; i = i + k) {
head = reverse(head, i + 1, i + k)
console.log(head);
}
return head
};十三.promise封装AJAX
封装get为例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="send()">send</button>
<script>
function GetHttp(url, param) {
return new Promise((reslove, reject) => {
let query = ""
for (let key in param) {
if (query === "") {
query = query + `${key}=${param[key]}`
} else {
query = query + `&${key}=${param[key]}`
}
}
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open("GET", url + "?" + query)
xhr.send()
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState == 4) {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
reslove(xhr.response)
} else {
reject(xhr.status)
}
}
}
})
}
function send() {
GetHttp("http://127.0.0.1:8000/test", { a: 1, b: 2 }).then((res) => {
console.log(res);
}).catch((err) => {
console.warn(err);
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>这是我的测试服务器
const express = require('express')
const cors = require('cors')
const app = express()
app.use(cors())
app.use((request, response, next) => {
console.log("有人请求了该服务器");
console.log(`HOST:${request.get("Host")}`);
next()
})
app.get("/test", (req, res) => {
res.send({ msg: "成功了恭喜" })
})
const port = 8000
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://127.0.0.1:${port}`);
})十四. 图片懒加载
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
img {
display: block;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid palevioletred;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<img alt="加载中" data-src="../../imgs/back.png" />
<img alt="加载中" data-src="../../imgs/girl.jpg" />
<img alt="加载中" data-src="../../imgs/background.jpg" />
<img alt="加载中" data-src="../../imgs/sitgril.jpg" />
<img alt="加载中" data-src="../../imgs/flygirl.jpg" />
<img alt="加载中" data-src="../../imgs/yes.jpg" />
<img alt="加载中" data-src="../../imgs/testfloat.jpg" />
</div>
<script>
var images = document.getElementsByTagName("img");
function callback(entries) {
for (let i of entries) {
if (i.isIntersecting) {
let img = i.target;
let trueSrc = img.getAttribute("data-src");
img.setAttribute("src", trueSrc);
observer.unobserve(img);
}
}
}
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(callback);
for (let i of images) {
observer.observe(i);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>解释一下IntersectionObserver
这是window自带的构造函数,创建一个监视器,当我们监视的元素在可视范围内出现时调用回调函数。(原因是与根元素交点的问题,详细参考下面)
十五. 手写jsonp
客户端代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="http://127.0.0.1:8000/jsonp"></script>
<script>
console.log(obj);
</script>
</body>
</html>服务器
const express = require("express")
const app = express()
app.get("/jsonp", (req, res) => {
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/javascript")
res.send("var obj = { a: 11, b: { test: 'test' } }")
})
const port = 7000
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://127.0.0.1:${port}`);
})十六. 判断数组层级
/**
*
* @param {Array} arr
*/
function JudgeFloors(arr) {
let str = JSON.stringify(arr)
let floors = 0
let nowfloor = 0
let i = 0
while (i < str.length) {
if (str.charAt(i) == "[") {
nowfloor++
} else if (str.charAt(i) == "]") {
floors = Math.max(floors, nowfloor)
nowfloor = 1
}
i++
}
return floors
}
console.log(JudgeFloors([1, 3, 4, [4, [5, [2, 5], 6], 3, 2], 9]));十七. 数组扁平化
/**
*
* @param {Array} arr
*/
function flat(arr) {
arr = arr.flat()
for (let item of arr) {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(item) === "[object Array]") {
arr = flat(arr)
}
}
return arr
}
let arr = [3, [5], 6, [3, 4, [2, 3], 6, 7]]
console.log(flat(arr));十八. 对象扁平化
function flatObj(obj) {
let res = {}
function flat(target, prekey) {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(target) === "[object Object]" ||
Object.prototype.toString.call(target) === "[object Array]") {
for (let key in target) {
let newkey = (prekey == "") ? `${key}` : `${prekey}.${key}`
let value = target[key]
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Object]"
|| Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Array]") {
flat(value, newkey)
} else {
res[newkey] = value
}
}
}
}
flat(obj, "")
return res
}
let obj = {
a: 1, b: 2, c: { cc: "test", dd: [1, 3, 5, { afg: "afg" }] }
}
console.log(flatObj(obj))
十九. 最长不重复子串
/**
*
* @param {String} str
*/
function maxLengthSubStr(str) {
let res = []
let length = 0
let i = 0
while (i < str.length) {
if (!res.includes(str.charAt(i))) {
res.push(str.charAt(i))
i++
} else {
length = Math.max(res.length, length)
res.shift()
}
}
console.log(res);
length = Math.max(length, res.length)
return length
}
console.log(maxLengthSubStr("fwqefg"));二十. 判断对象为空
function judgeNull1(obj) {
if (JSON.stringify(obj) == "{}")
return true
else
return false
}
function judgeNull2(obj) {
for (let key in obj) {
return false
}
return true
}
function judgeNull3(obj) {
if (Object.keys(obj).length == 0) {
return true
}
return false
}
let obj = {}
console.log(judgeNull1(obj), judgeNull2(obj), judgeNull3(obj));二十一.有效括号长度
/**
*
* @param {String} s
*/
function maxLength(s) {
let res = []
let length = 0
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) === "(") {
res.push("(")
} else if (s.charAt(i) === ")") {
if (res.length > 0) {
res.pop()
length++
}
}
}
return length
}
console.log(maxLength("((())"));二十三. 手写promise.all
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function MypromiseAll(arr) {
let resArray = []
return new Promise((reslove, reject) => {
for (let item of arr) {
item.then((res) => {
resArray.push(res)
if (resArray.length === arr.length)
reslove(resArray)
}).catch((err) => {
reject(err)
})
}
})
}
let p1 = new Promise((reslove, reject) => {
reslove("p1成功了")
})
let p2 = new Promise((reslove, reject) => {
reslove("p2成功了")
})
let p3 = new Promise((reslove, reject) => {
reject("p3失败了")
})
let p4 = new Promise((reslove, reject) => {
reject("p4失败了")
})
MypromiseAll([p1, p2]).then((res) => {
console.log(res);
}).catch((err) => {
console.warn(err);
})
MypromiseAll([p1, p2, p3, p4]).then((res) => {
console.log(res);
}).catch((err) => {
console.warn(err);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>二十三. 手写new
function myNew(fn, ...args) {
if (typeof (fn) !== 'function') {
throw 'fn must be a function'
}
//将obj的原型指向fn的原型
var obj = Object.create(fn.prototype)
// 执行fn,改变fn指针为obj
var res = fn.apply(obj, args)
return res instanceof Object ? res : obj
}这个前面看注释都好理解,重要讲一下最后一行,为什么res如果是对象就返回res,如果不是对象就返回实例对象呢。
这是因为在构造函数中如果我们返回一个值,若该值是非对象的值,那么不会对我们创建的实例对象有任何影响。但是如何构造函数返回的是一个对象,那么我们会发现我们创建的实例对象将不在是实例对象,而是构造函数的返回对象。
一个例子直接说明一切
function Dog1(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
return "123456"
}
function Dog2(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
return {
a: 1, b: 2
}
}
function Dog3(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
let dog1 = new Dog1("xiaohuang", 5)
let dog2 = new Dog2("xiao hua", 18)
let dog3 = new Dog3("xiao yu", 28)
console.log(dog1);
console.log(dog2);
console.log(dog3);那么结果为
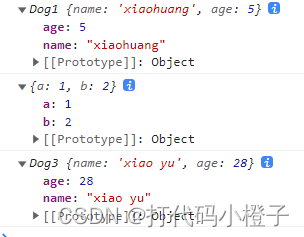
二十四. css实现各种图形
三角形 扇形 平行四边形
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#demo1 {
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-top: 100px solid transparent;
border-left: 100px solid transparent;
border-right: 100px solid transparent;
border-bottom: 100px red solid;
}
#demo2 {
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-top: 100px solid transparent;
border-left: 100px solid transparent;
border-right: 100px solid transparent;
border-bottom: 100px palegreen solid;
border-radius: 100px;
}
#demo3 {
margin-top: 20px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(45, 31, 177);
transform: skewX(45deg);
}
div{
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="demo1"></div>
<div id="demo2"></div>
<div id="demo3"></div>
</body>
</html>二十五. 实现环形进度条
我个人的实现比较复杂,我看他们好像有更简单的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.main {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
.back {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
/* background-color: rgb(38, 154, 221); */
border: 20px solid rgb(56, 183, 233);
border-radius: 200px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
color: aqua;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border-radius: 200px;
border: 20px solid royalblue;
border-color: transparent transparent royalblue royalblue;
transform: rotateZ(45deg);
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
z-index: 1;
}
.right {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border-radius: 200px;
border: 20px solid royalblue;
border-color: royalblue royalblue transparent transparent;
transform: rotateZ(45deg);
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
z-index: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div class="back"></div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
<script>
let degree = 0
function rotate() {
degree = degree + 10
let left = document.getElementsByClassName("left")[0]
let right = document.getElementsByClassName("right")[0]
if (degree <= 180) {
right.style.transform = `rotateZ(${45 + degree}deg)`
}
else if (degree > 180 && degree <= 360) {
right.style.borderColor = "rgb(56, 183, 233) rgb(56, 183, 233) transparent transparent"
right.style.zIndex = "999"
right.style.transform = `rotateZ(45deg)`
left.style.transform = `rotateZ(${45 + degree - 180}deg)`
} else if (degree >= 360) {
degree = 0
right.style.borderColor = "royalblue royalblue transparent transparent"
right.style.zIndex = "1"
left.style.transform = `rotateZ(45deg)`
}
document.getElementsByClassName("back")[0].innerHTML = `${((degree / 360) * 100).toPrecision(3)}%`
}
setInterval(() => {
rotate()
}, 1000)
</script>
</body>
</html>效果图

二十六. 实现一个定时器,执行一定次数
/**
*
* @param {Function} fn
* @param {Number} times
* @param {Number} delay
*/
function myTimer(fn, times, delay, ...args) {
let nowTime = Math.floor(times)
return function () {
let timer = setInterval(
function () {
fn(...args)
nowTime--
if (nowTime <= 0) {
clearInterval(timer)
}
}, delay
)
}()
}
function showName(name) {
console.log(name);
}
myTimer(showName, 5, 1000, "test")二十七. 二叉树
二叉树(js实现)_SQCTM810的博客-CSDN博客_js 二叉树
(1)二叉树实现类
class BiTree {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
apendLeft(node) {
this.left = node
}
apendRight(node) {
this.right = node
}
}
let tree = new BiTree("A")
let nodeB = new Node("B")
let nodeC = new Node("C")
let nodeD = new Node("D")
let nodeE = new Node("E")
tree.left = nodeB
tree.right = nodeC
nodeB.apendLeft(nodeD)
nodeC.apendLeft(nodeE)
console.log(tree);
(2)二叉树遍历
1.先序,后序,中序
function preOrder(root) {
if (!root) {
return
}
console.log(root.val);
preOrder(root.left)
preOrder(root.right)
}
function midOrder(root) {
if (!root) {
return
}
preOrder(root.left)
console.log(root.val);
preOrder(root.right)
}
function postOrder(root) {
if (!root) {
return
}
preOrder(root.left)
preOrder(root.right)
console.log(root.val);
}分别对应先序 中序 后序 即根左右 左根右 左右根
2. 层级遍历
var levelOrder = function (root) {
if (!root) return []
let res = []
let queue = [root]
while (queue.length) {
let length = queue.length
let arr = []
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
let node = queue.shift()
arr.push(node.val)
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left)
if (node.right) queue.push(node.right)
}
res.push(arr)
}
return res
}