Vuex全局管理的基本代码结构及其使用
一、代码结构及其使用
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
//提供唯一的公共数据源
state: {
list:[]
},
//用于变更state中的数据,必须是同步函数
mutations: {
},
//用于变更state中的数据,不能直接修改,需要通过context.commit()操作mutation,
//但是可以写异步操作
actions: {
},
//模块化,可以导入其他的store
modules: {
}
})
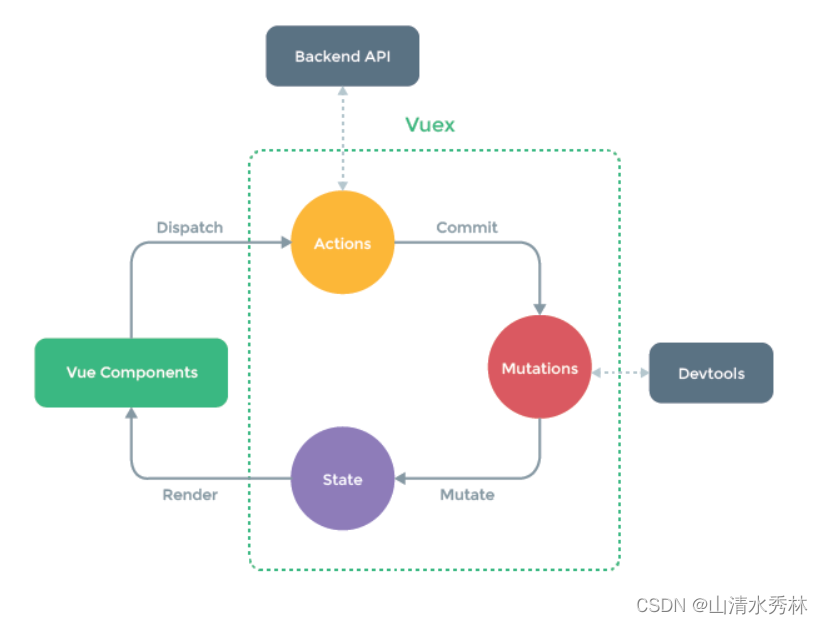
官方图示:
1. state :提供唯一的公共数据源
所有共享的数据都要统一放在Store的 state 中进行存储;
组件访问 state 中数据的第一种方式:this.$store.state.全局数据名称
组件访问 state 中数据的第二种方式 - mapState函数:
①从vuex中按需导入mapState函数:import { mapState} from 'vuex'
②通过 mapState 函数,将当前组件需要的全局数据映射为当前组件的computed计算属性:
import {
mapState } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapState({
// 三种写法:
// list: state => state.list
// list: "list" 这个写法慎用,可能有问题
list: state => {
return state.list;
}
})
},
2. mutations :用于变更state中的数据,必须是同步函数
①Vuex中应该通过mutation变更state中的数据,而不是直接操作state中的数据。
②通过这种方式虽然操作起来繁琐一些,但是可以集中监控所有数据的变化。
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
num:1
},
mutations: {
add(state){
state.num++
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
调用mutations中函数的第一种方式:this.$store.commit(‘函数名’)
methods:{
handle1(){
this.$store.commit('add')
}
}
如果需要传递参数,则在mutations中定义时写入形参,调用时传入实参:
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
num:1
},
mutations: {
add(state){
state.num++
},
addN(state,step){
state.num += step
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
调用时传入实参:
methods:{
handle2(){
this.$store.commit('addN',50)
}
}
调用mutations中函数的第二种方式 - mapMutations函数:
①从 Vuex 中按需导入 mapMutations 函数:import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
②通过 mapMutations 函数将需要的 mutations 中的函数映射为当前组件的 methods 方法:...mapMutations(['函数名'])
③映射完毕后,可以直接当作 methods 中的方法通过 this 调用(当然也可以直接作为绑定事件的处理函数):
import {
mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods:{
...mapMutations(['add','addN']),
handler1(){
this.addN(12345)
}
}
3. actions:用于变更state中的数据,但不能直接修改,需要通过context.commit()调用mutation,且可以包含任意的异步操作
Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态(state):
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
num:1
},
mutations: {
add(state){
state.num++
},
addN(state,step){
state.num += step
}
},
actions: {
async(context){
context.commit('add')
}
},
modules: {
}
})
在组件中调用Action的第一种方式:this.$store.dispatch(‘action名称’)
methods:{
asyncHandler1(){
this.$store.dispatch('async')
}
}
如果需要包含异步操作和传参:
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
num:1
},
mutations: {
add(state){
state.num++
},
addN(state,step){
state.num += step
}
},
actions: {
async2(context,step){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('addN',step)
},1000)
}
},
modules: {
}
})
methods:{
asyncHandler2(){
this.$store.dispatch('async2',123)
}
}
在组件中调用Action的第二种方式 - mapActions函数:
①从 Vuex 中按需导入 mapActions 函数:import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
②通过 mapActions 函数将需要的 actions 函数映射为当前组件的 methods 方法:...mapActions (['函数名'])
③映射完毕后,可以直接当作 methods 中的方法通过 this 调用(当然也可以直接作为绑定事件的处理函数):
import {
mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods:{
...mapActions (['async','async2']),
asyncHandler3(){
this.async2(123456)
}
}
4. modules :用于模块化导入其他store
例如新建了一个js文件,里面定义了一个storeA:
const storeA= {
state: {
storeANum:999
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
getters: {
}
}
export {
storeA}
导出后即可再另一个store中导入此模块:
import {
storeA} from "@/store/storeA";
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
num:1
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
storeA
}
})
二、Getter
Getter用于对 store 中的数据进行加工处理后形成新的数据,类似 Vue 中的计算属性。
Getter不会修改store中的数据,而是起到一个包装的作用。
Store 中的数据发生变化,Getter的数据也会跟着变化。
在 Store 中配置 getters(和 actions 等平级):
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count : 0
},
getters:{
showNum : state => {
return '当前最新的数量是:' + state.count
}
}
})
使用 getters 的第一种方式:this.$store.getters.名称
<h3>{
{
$store.getters.showNum }}</h3>
<button @click="handler1"> num + 1 </button>
<button @click="asyncHandler1"> num + 1 </button>
使用 getters 的第二种方式 - mapGetters函数:
①从 Vuex 中按需导入 mapGetters 函数:import { mapGetters} from 'vuex'
②通过 mapGetters 函数将需要的 getter 映射为当前组件的 computed 计算属性:
import {
mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['showNum'])
},