4-UI自动化-selenium三大等待方式
上篇介绍了3-UI自动化-八大元素定位,xpath定位方式和相关的常问面试题
本篇来学习三大等待方式
♡ \color{red}{\heartsuit} ♡
在UI自动化测试中,脚本一定要加入等待来增强脚本的健壮性。因为基本上会遇到环境不稳定,网络慢的情况,如果不做任何等待处理的话,代码会由于没有找到元素而报错。另外,一种情况就是页面使用ajax异步加载机制。这时我们就要用到 wait。
selenium三大等待方式
timd.sleep(强制等待)
implicitly_wait(隐式等待)
WebDriverWait(显式等待)
强制等待timd.sleep
强制等待,最简单了,直接time.sleep(3),强制等待3s。哪里需要等待就在哪里设置
代码如下
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
class WaitSample:
def __init__(self):
self.driver = webdriver.Firefox()
# 在打开浏览器驱动等待3s,再去输入url
time.sleep(3)
self.driver.get('http://baidu.com')
def force_wait(self):
"""强制等待"""
# 输入关键词查询
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'kw').send_keys('强制等待selenium')
# 在点击百度一下前先等待2s
time.sleep(2)
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'su').click()
# 在输出浏览器的标题前,先等待3s,防止浏览器还未
time.sleep(3)
print(self.driver.title)
# 关闭窗口
self.driver.close()
# 退出浏览器
self.driver.quit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ws = WaitSample()
# 强制等待
ws.force_wait()
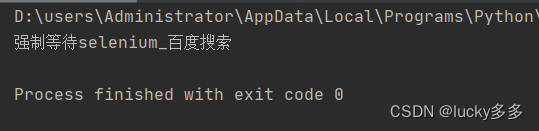
运行后控制台会输出浏览器标题
隐式等待implicitly_wait
implicitly_wait(隐式等待),每个元素在隐性等待设定好的等待时间上限内存在都不会报错,超出时间
上限就会抛超时异常。
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
class WaitSample:
def __init__(self):
self.driver = webdriver.Firefox()
# 在打开浏览器驱动等待3s,再去输入url
time.sleep(3)
self.driver.get('http://baidu.com')
def imp_wait(self):
"""隐式等待"""
# 隐式等待3s
self.driver.implicitly_wait(3)
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'kw').send_keys('隐式等待selenium')
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'su').click()
time.sleep(3)
print(self.driver.title)
# 关闭窗口
self.driver.close()
# 退出浏览器
self.driver.quit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ws = WaitSample()
# 隐式等待
ws.imp_wait()
注意隐式等待作用于整个driver周期,只需要在最开始设置一次就可以了,强制等待是哪里需要就在哪里设置。
显式等待WebDriverWait
显性等待需要指定
- 等待的条件 expected_conditions
- 定位元素的方式(也就是八大元素定位方式)
- 等待的时间上限(自定义)
- 等待的间隔(默认每隔0.5秒调用一次,可以不传)
显是等待会根据等待的条件判断,如果成立则往下执行,否则一直检查条件,直到达到最长等待时间。该方法是最常用的。
需要导入WebDriverWait模块和expected_conditions
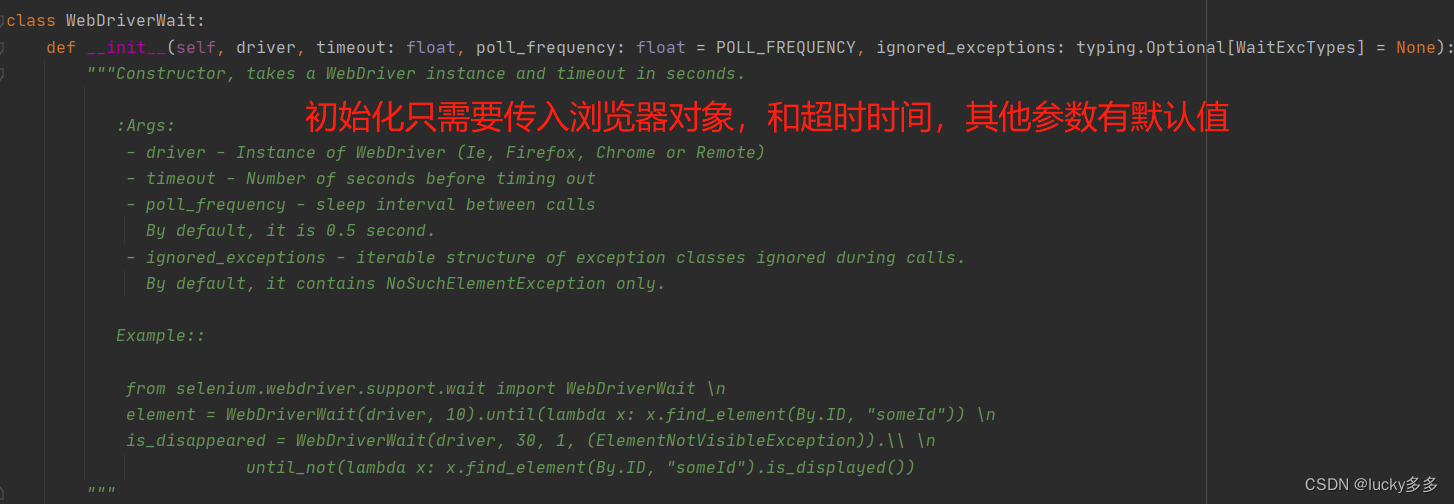
先看WebDriverWait类的源码,初始化只需要传入浏览器对象和超时时间。POLL_FREQUENCY是调用until()/until_not()方法间隔时间,默认是0.5s
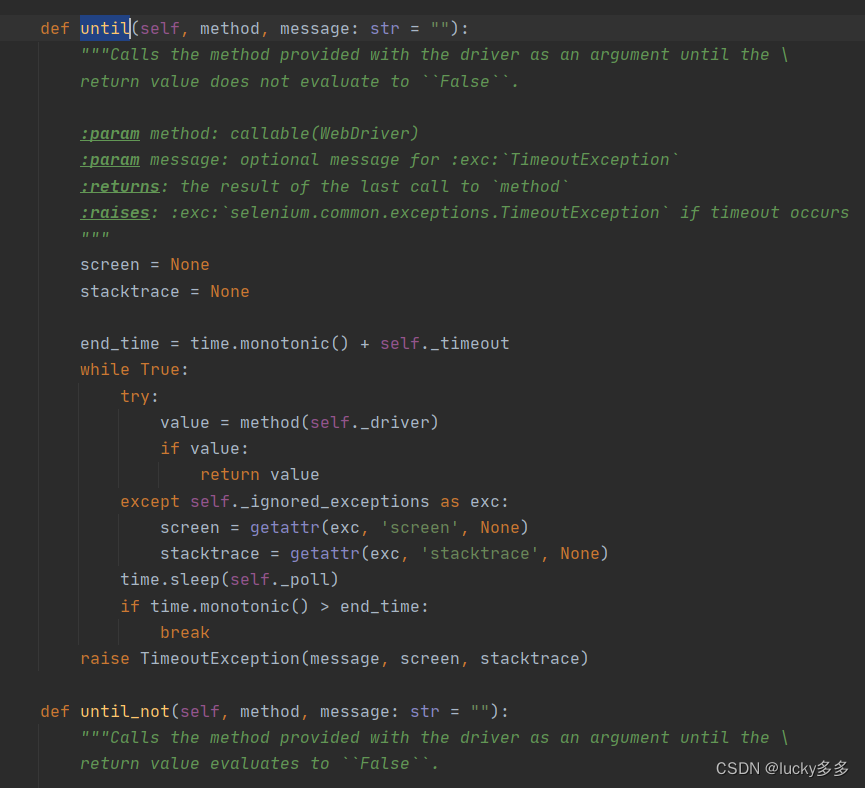
再看下WebDriverWait类有什么方法,可以看到有until()方法和until_not()方法,等待直到…,等待直到不…怎么怎么样。
比如说如果我们想要等待元素被加载后,才会进行下一步,用显示等待如何完成?
看下expectd_condictions的源码,它提供了很多方法,有标题等于,标题包含,当前文本元素值为…等方法,就不一一列举了。
主要列出几个常用的方法:
presence_of_element_located等待元素被加载,visibility_of_element_located等待元素可见,frame_to_be_available_and_switch_to_it等待窗口可见并切换到窗口,element_to_be_clickable等待元素可被点击。
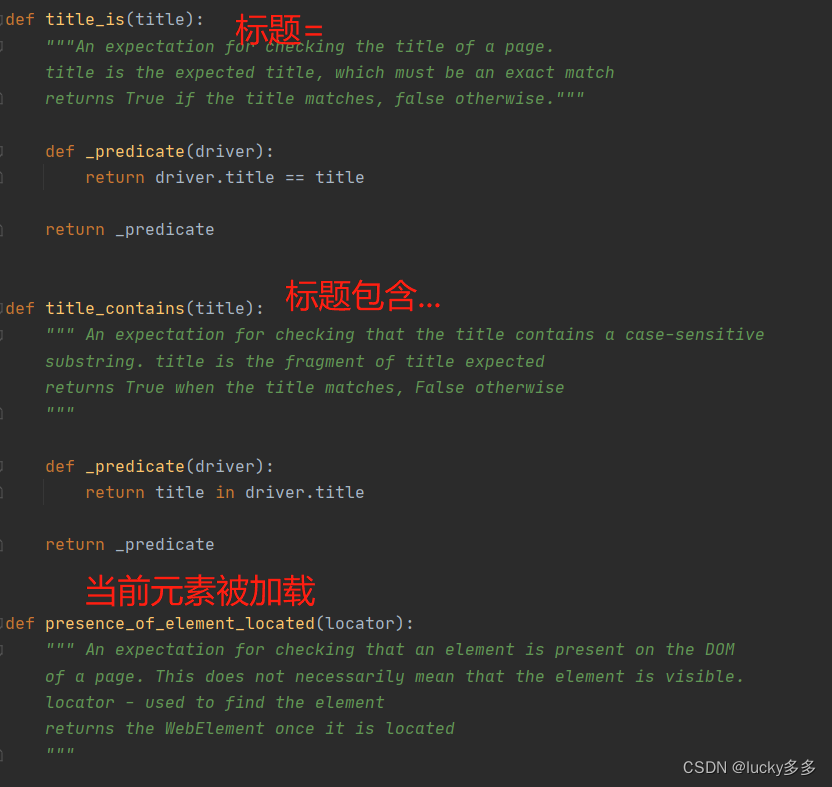
截取了presence_of_element_located()方法源码,可以看到传入的是一个locator对象,该对象用于查找元素,那么查找元素需要有元素定位方式和表达式,也就是locator=[By.ID, 'kw']是这种形式的。
def presence_of_element_located(locator):
""" An expectation for checking that an element is present on the DOM
of a page. This does not necessarily mean that the element is visible.
locator - used to find the element
returns the WebElement once it is located
"""
def _predicate(driver):
return driver.find_element(*locator)
return _predicate
示例代码:
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
class WaitSample:
def __init__(self):
self.driver = webdriver.Firefox()
# 在打开浏览器驱动等待3s,再去输入url
time.sleep(3)
self.driver.get('http://baidu.com')
def util_wait(self):
"""显式等待"""
# 先拿到显示等待对象
explicitly_wait = WebDriverWait(self.driver, 3)
# 等待直到元素可被加载
locator = [By.ID, 'kw']
explicitly_wait.until(expected_conditions.presence_of_element_located(locator)).send_keys('显示等待selenium')
# self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'kw').send_keys('隐式等待selenium')
# 等待 直到元素可见
locator2 = [By.ID, 'su']
explicitly_wait.until(expected_conditions.visibility_of_element_located(locator2)).submit()
# self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'su').click()
# time.sleep(3)
explicitly_wait.until(expected_conditions.title_contains('显示等待selenium'))
print(self.driver.title)
# 关闭窗口
self.driver.close()
# 退出浏览器
self.driver.quit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ws = WaitSample()
# 显式等待
ws.explicitly_wait()
显式等待和隐式等待的区别
隐式等待可以全局设置,在整个浏览器对象内有用,但是它只能等待元素是否出现,元素的各种状态不能控制,而显式等待应用更广,更灵活,显式等待可以根据元素的状态条件决定执行下一步,如元素被加载,元素可见、元素可被点击等。
一般来说,现设置隐式等待,因为它可以作用于整个driver对象,然后根据实际情况设置强制等待或显示等待,如果想让自己的代码更智能推荐用显示等待。
三种等待方式最终的代码
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
class WaitSample:
def __init__(self):
self.driver = webdriver.Firefox()
# 在打开浏览器驱动等待3s,再去输入url
time.sleep(3)
self.driver.get('http://baidu.com')
def force_wait(self):
"""强制等待"""
# 输入关键词查询
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'kw').send_keys('强制等待selenium')
# 在点击百度一下前先等待2s
time.sleep(2)
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'su').click()
# 在输出浏览器的标题前,先等待3s,防止浏览器还未
time.sleep(3)
print(self.driver.title)
# 关闭窗口
self.driver.close()
# 退出浏览器
self.driver.quit()
def imp_wait(self):
"""隐式等待"""
# 隐式等待3s
self.driver.implicitly_wait(3)
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'kw').send_keys('隐式等待selenium')
time.sleep(3)
self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'su').click()
print(self.driver.title)
# 关闭窗口
self.driver.close()
# 退出浏览器
self.driver.quit()
def util_wait(self):
"""显式等待"""
# 先拿到显示等待对象
explicitly_wait = WebDriverWait(self.driver, 5)
# 等待直到元素可被加载
locator = [By.ID, 'kw']
explicitly_wait.until(expected_conditions.presence_of_element_located(locator)).send_keys('显示等待selenium')
# self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'kw').send_keys('隐式等待selenium')
# 等待 直到元素可见
locator2 = [By.ID, 'su']
explicitly_wait.until(expected_conditions.visibility_of_element_located(locator2)).submit()
# self.driver.find_element(By.ID, 'su').click()
# time.sleep(3)
explicitly_wait.until(expected_conditions.title_contains('显示等待selenium'))
print(self.driver.title)
# 关闭窗口
self.driver.close()
# 退出浏览器
self.driver.quit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ws = WaitSample()
# 强制等待
# ws.force_wait()
# 隐式等待
# ws.imp_wait()
# 显式等待
ws.util_wait()
下篇学习