vuex官方解释
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式 + 库。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
简单理解
vuex就是把组件共享状态抽取出来以一个全局单例模式管理,把共享的数据函数放进vuex中,任何组件都可以进行使用。
什么时候我们该使用它?
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。确实是如此——如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex。一个简单的 store 模式就足够您所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
使用
1、 安装Vex
npm install --save vuex2、配置Vuex文件
新建文件夹 store 新建文件 index.js ,在index.js文件进行配置vuex文件——相当于数据库,只不过是在前端。所有状态(数据都放在state中)比如:counter就相当于数据库的一个字段,0就是字段值。
import { createStore } from "vuex";
// const store = createStore({
// })
// export default store;
//或者简写如下
export default createStore({
state:{
counter:0
}
})3、在全局进行引入,在main.js文件添加以下代码,重点是引入和挂载。
import store from './store'
const app = createApp(App);
app.use(store)
app.mount('#app')
4、在组件中读取状态,在任意一个组件页面中使用,都可以获取到存储在state下的值
第一种
<p> counter = {
{$store.state.counter}} </p>
第二种 在任意一个组件页面中使用以下代码,只不过是放在了computed下,computed专门读取vuex的数据。
<template>
<p>{
{ counter }}</p>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
//专门读取vuex的数据
//如有多个 则: ...mapState(["counter",“age"])
...mapState(["counter"])
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
核心概念
vuex中一共有五个状态 State Getter Mutation Action Module
▣State
提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据统一放到store的state进行储存,相似与data
在vuex中state中定义数据,可以在任何组件中进行调用
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
//数据,相当于data
state: {
name:"张三",
age:12,
count:0
},
})调用:
方法一:
在标签中直接使用
<p>{
{$store.state.count}}</p>
<p>{
{$store.state.name}}</p>
<p>{
{$store.state.age}}</p>方法二:
this.$store.state.全局数据名称方法三:从vuex中按需导入mapstate函数
注意:当前组件需要的全局数据,映射为当前组件computed属性
<template>
<p>{
{ counter }}</p>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
//专门读取vuex的数据
//如有多个 则: ...mapState(["counter",“age"])
...mapState(["counter"])
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>▣ Mutation
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type)和一个回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
import { createStore } from "vuex";
// const store = createStore({
// })
// export default store;
//或者简写如下
export default createStore({
state:{
//所有状态(数据都放在state中)
counter:0
},
getters:{
getCount(state){
return state.counter >0 ?state.counter : "此时的counter<=0"
}
},
mutations:{
addCount(state){
state.counter=state.counter+1;
}
}
})调用方法:
<template>
<h1>主页</h1>
<p>counter : {
{$store.state.counter}}</p>
<p>counter : {
{$store.getters.getCount}}</p>
<p>{
{getCount}}</p>
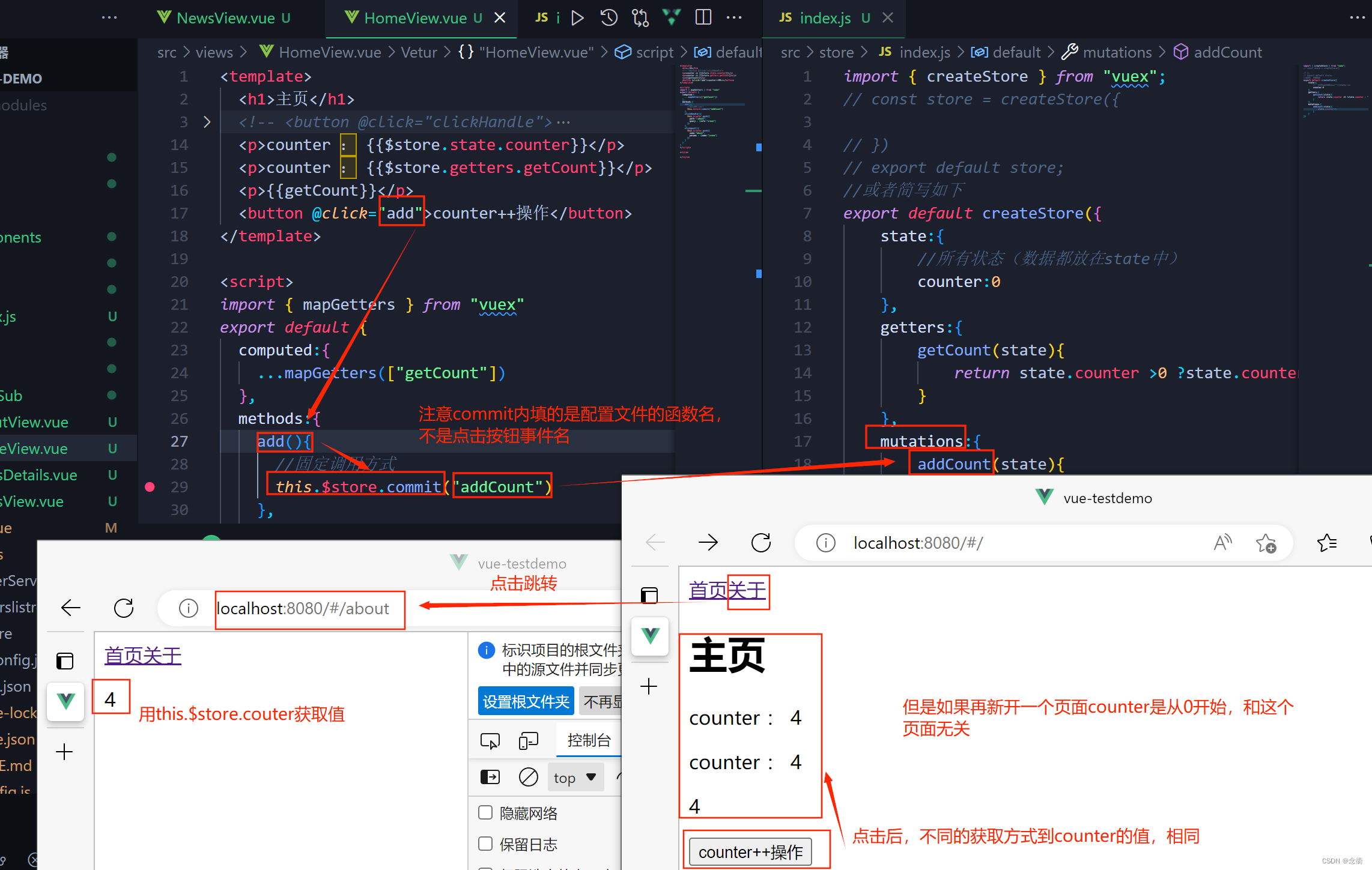
<button @click="add">counter++操作</button>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["getCount"])
},
methods:{
add(){
//固定调用方式
this.$store.commit("addCount")
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>分析:任何对counter引入的组件都会得到相同的变化,即counter值相同。但新开一个页面,counter不会得到相同的变化,依旧从index文件中获取到初始值:0 。
使用二 :带参数传递
例子:点击一次,增加15
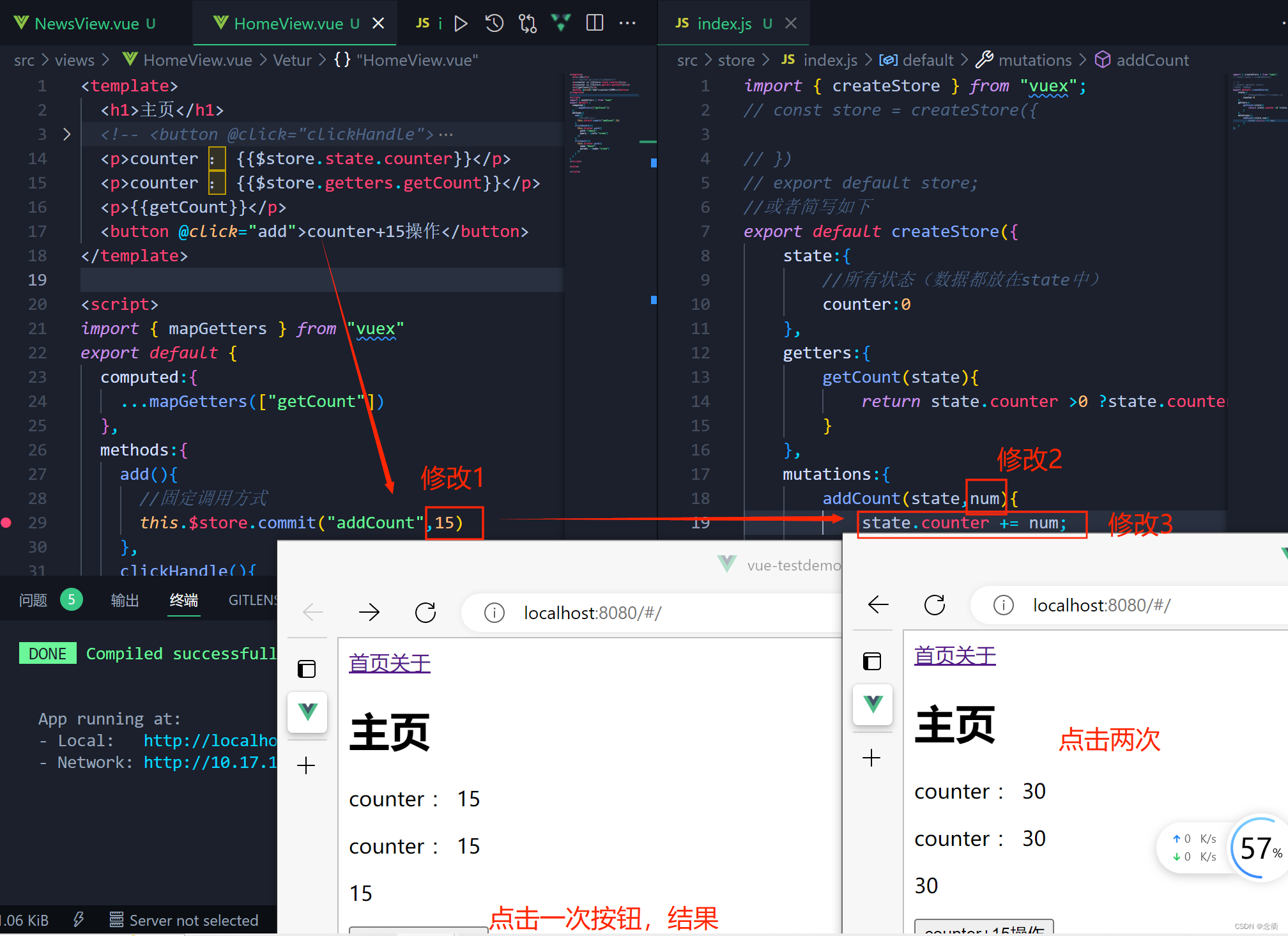
例子升级:调用方法使用mapMutations获取,即修改methods方法中如下:效果一样。
<template>
<p>counter : {
{$store.state.counter}}</p>
<p>counter : {
{$store.getters.getCount}}</p>
<p>{
{getCount}}</p>
<button @click="add">counter+15操作</button>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapMutations} from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["getCount"])
},
methods:{
...mapMutations(["addCount"]),
add(){
this.addCount(15)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>▣Action
Action和Mutation相似,Mutation 不能进行异步操作,若要进行异步操作,就得使用Action
Action 提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
import axios from "axios";
import { createStore } from "vuex";
export default createStore({
state:{
//所有状态(数据都放在state中)
counter:0
},
getters:{
getCount(state){
return state.counter >0 ?state.counter : "此时的counter<=0"
}
},
mutations:{
addCount(state,num){
state.counter += num;
}
},
actions:{
//({}) 加上花括号代表对象结构赋值
asyncAdd({commit}){
axios.get("http://iwenwiki.com/api/FingerUnion/list.php")
.then(res => {
commit("addCount",res.data[0])
})
}
}
})调用方法一:
<template>
<p>counter : {
{$store.state.counter}}</p>
<p>counter : {
{$store.getters.getCount}}</p>
<p>{
{getCount}}</p>
<button @click="add">counter+15操作</button>
<button @click="addAsyn">异步增加counter操作</button>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapMutations} from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["getCount"])
},
methods:{
...mapMutations(["addCount"]),
addAsyn(){
this.$store.dispatch("asyncAdd")
},
add(){
//固定调用方式
// this.$store.commit("addCount",15)
this.addCount(15)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
调用方法二:使用mapMutations获取,即引入后修改methods方法中如下:效果一样
tips: ({}) 加上花括号代表对象结构赋值

▣Getter
对vuex中数据进行过滤。
类似于vue中的computed,进行缓存,对于Store中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据。
第一种
import { createStore } from "vuex";
// const store = createStore({
// })
// export default store;
//或者简写如下
export default createStore({
state:{
//所有状态(数据都放在state中)
counter:0
},
getters:{
getCount(state){
return state.counter >0 ?state.counter : "此时的counter<=0"
}
}
})调用方法一:
<p> counter : {
{$store.getters.getCount}} </p>调用方法二: 使用mapGetters
<template>
<p>{
{getCount}}</p>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from "vuex"
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["getCount"])
}
}
</script>
<style></style>结果:
![]()
▣Modules
当遇见大型项目时,数据量大,store就会显得很臃肿
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:

引用:
this.$store.state.cityModules.cityname