我们知道我们可以专门检测一些对象。那么我们如何训练系统检测自定义对象呢?让我们一步一步来。
1. 创建数据集
机器是通过数据集学习的。数据集必须包含图像和标签。例如,让我的目标是创建一个检测坦克的系统。
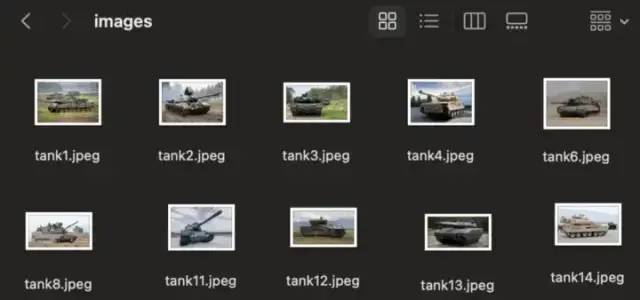
我准备了从网上下载的坦克图片。然后我们需要使用第三方工具对图像进行标记,例如;LabelImg、MakeSense 等。我们将在此示例中使用 MakeSense,可以在此处访问它:https://www.makesense.ai/
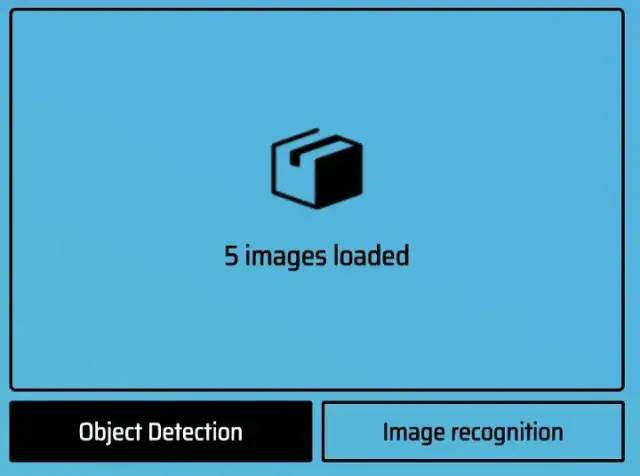
上传完所有图片后,点击 Object Detection 选择。你会看到你上传的照片。你需要标记对象的区域。

我们标记了对象的区域。(如果图像有很多对象,则必须标记所有对象。)然后查看页面右侧的“标签”。
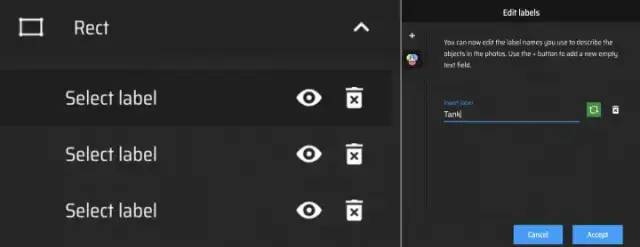
单击加号图标并在那里输入对象的名称。
现在我们的数据集准备好了!让我们下载数据集。
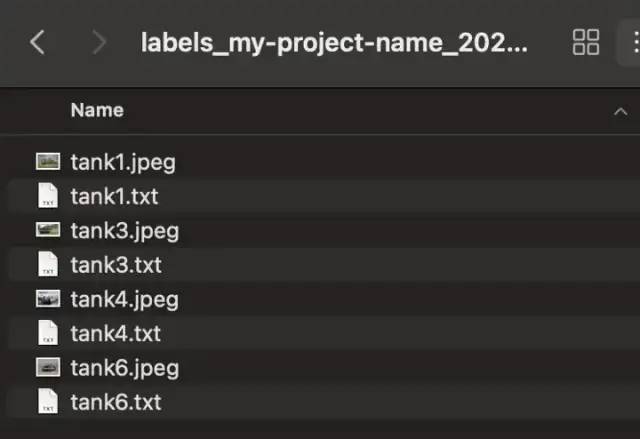
准备的数据集如上图。
2. 使用 Colab 进行训练
我们将使用 Google Colab 进行训练。

什么是 Colab?
Colaboratory,简称“Colab”,是谷歌研究院的一款产品。Colab 允许任何人通过浏览器编写和执行任意 python 代码,特别适合机器学习、数据分析和教育。
GPU 训练比 CPU 训练更快。
按照以下步骤进行训练
打开 Google Drive,创建一个名为“yolov3”的文件夹
将你的数据集上传为“images.zip”
从此处链接下载训练文件“Train_YoloV3.ipynb” :https://github.com/turgay2317/yolov3-training-files
打开 Colab:https://colab.research.google.com/
选择“上传”选项卡,并选择下载训练文件“Train_YoloV3.ipynb”
上传过程结束后,你会遇到如下页面。
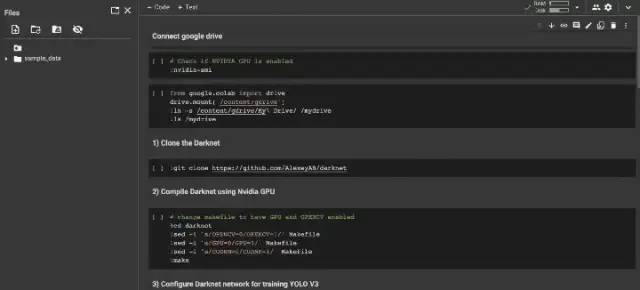
该文件应用了这些步骤;检查 Nvidia GPU,安装 Google Drive,克隆和编译 DarkNet,为标签创建 obj.names 文件,从 images.zip 中提取图像,开始训练
训练结束后可以查看Google Drive/yolov3目录下的权重文件。

我们将使用权重文件。下载它。
3. 准备所有检测文件
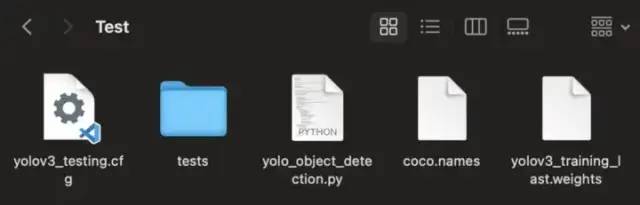
我们将使用这些文件:
yolov3_training_last.weights -> 训练文件
coco.names -> 包含特定对象的标签
yolo_object_detection.py -> 使用 OpenCV 进行对象检测
yolov3_testing.cfg -> 一些配置
你可以从这里下载其他文件:https://github.com/turgay2317/yolov3-training-files
4. 运行自定义对象检测
不要忘记安装 OpenCV 和所需的库。然后运行“yolo_object_detection.py”文件!
import cv2
import numpy as np
import glob
import random
net = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolov3_training_last.weights", "yolov3_testing.cfg")
classes = ["Tank"]
images_path = glob.glob(r"tests/*.jpeg")
layer_names = net.getLayerNames()
output_layers = [layer_names[i - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(classes), 3))
random.shuffle(images_path)
for img_path in images_path:
# Loading image
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=0.4, fy=0.4)
height, width, channels = img.shape
# Detecting objects
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 0.00392, (416, 416), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
outs = net.forward(output_layers)
# Showing informations on the screen
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
if confidence > 0.3:
# Object detected
print(class_id)
center_x = int(detection[0] * width)
center_y = int(detection[1] * height)
w = int(detection[2] * width)
h = int(detection[3] * height)
# Rectangle coordinates
x = int(center_x - w / 2)
y = int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.5, 0.4)
print(indexes)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
for i in range(len(boxes)):
if i in indexes:
x, y, w, h = boxes[i]
label = str(classes[class_ids[i]])
color = colors[class_ids[i]]
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
cv2.putText(img, label, (x, y + 30), font, 3, color, 2)
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
key = cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
检测实例
最后,你可以看到我们的检测成功了。现在我们的系统可以检测到坦克。
5. 视频中的自定义对象检测
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
# Load Yolo
net = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolov3_training_last.weights", "yolov3_testing.cfg")
classes = []
with open("coco.names", "r") as f:
classes = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
layer_names = net.getLayerNames()
output_layers = [layer_names[i - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(classes), 3))
# Loading image
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("tests/test.mp4")
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
starting_time = time.time()
frame_id = 0
while True:
_, frame = cap.read()
frame_id += 1
height, width, channels = frame.shape
# Detecting objects
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 0.00392, (416, 416), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
outs = net.forward(output_layers)
# Showing informations on the screen
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
if confidence > 0.1:
# Object detected
center_x = int(detection[0] * width)
center_y = int(detection[1] * height)
w = int(detection[2] * width)
h = int(detection[3] * height)
# Rectangle coordinates
x = int(center_x - w / 2)
y = int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.8, 0.3)
for i in range(len(boxes)):
if i in indexes:
x, y, w, h = boxes[i]
label = str(classes[class_ids[i]])
confidence = confidences[i]
color = colors[class_ids[i]]
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
cv2.putText(frame, label + " " + str(round(confidence, 2)), (x, y + 30), font, 3, color, 3)
elapsed_time = time.time() - starting_time
fps = frame_id / elapsed_time
cv2.putText(frame, "FPS: " + str(round(fps, 2)), (10, 50), font, 4, (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.imshow("Image", frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == 27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()6. 相机的自定义对象检测
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
# Load Yolo
net = cv2.dnn.readNet("yolov3_training_last.weights", "yolov3_testing.cfg")
classes = []
with open("coco.names", "r") as f:
classes = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
layer_names = net.getLayerNames()
output_layers = [layer_names[i - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(classes), 3))
# Loading image
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
starting_time = time.time()
frame_id = 0
while True:
_, frame = cap.read()
frame_id += 1
height, width, channels = frame.shape
# Detecting objects
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 0.00392, (416, 416), (0, 0, 0), True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
outs = net.forward(output_layers)
# Showing informations on the screen
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
if confidence > 0.1:
# Object detected
center_x = int(detection[0] * width)
center_y = int(detection[1] * height)
w = int(detection[2] * width)
h = int(detection[3] * height)
# Rectangle coordinates
x = int(center_x - w / 2)
y = int(center_y - h / 2)
boxes.append([x, y, w, h])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.8, 0.3)
for i in range(len(boxes)):
if i in indexes:
x, y, w, h = boxes[i]
label = str(classes[class_ids[i]])
confidence = confidences[i]
color = colors[class_ids[i]]
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
cv2.putText(frame, label + " " + str(round(confidence, 2)), (x, y + 30), font, 3, color, 3)
elapsed_time = time.time() - starting_time
fps = frame_id / elapsed_time
cv2.putText(frame, "FPS: " + str(round(fps, 2)), (10, 50), font, 4, (0, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.imshow("Image", frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == 27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()因此,你现在可以检测自定义对象!
☆ END ☆
如果看到这里,说明你喜欢这篇文章,请转发、点赞。微信搜索「uncle_pn」,欢迎添加小编微信「 woshicver」,每日朋友圈更新一篇高质量博文。
↓扫描二维码添加小编↓
