- dup/dup2系统调用
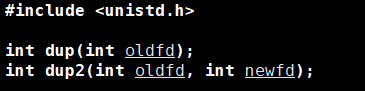
函数原型如下:
- 使用dup将标准输出重定向到文件中
#include <stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main(){
int fd = open("./log",O_CREAT | O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
close(1);
int new_fd = dup(fd);
if(new_fd != 1){
perror("dup");
return 2;
}
printf("new_fd : %d\n",new_fd);
close(fd);
for(;;){
char buf[1024] = {0};
ssize_t num = read(0,buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(num < 0){
perror("read");
continue;
}
printf("%s",buf);
fflush(stdout);
}
close(new_fd);
return 0;
}
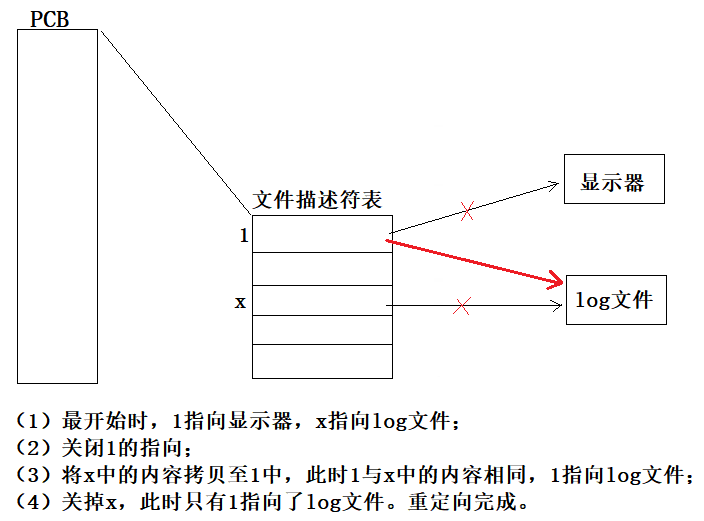
为了帮助理解,我们可以来画一张图:
其实这个方法是利用了dup分配文件描述符是从最小的开始分配这样的机制,来完成这个重定向。
- 使用dup2将标准输出重定向至文件中
#include <stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main(){
int fd = open("./log",O_CREAT | O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
close(1);
dup2(fd,1);
for(;;){
char buf[1024] = {0};
ssize_t num = read(0,buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(num < 0){
perror("read");
continue;
}
printf("%s",buf);
fflush(stdout);
}
return 0;
}
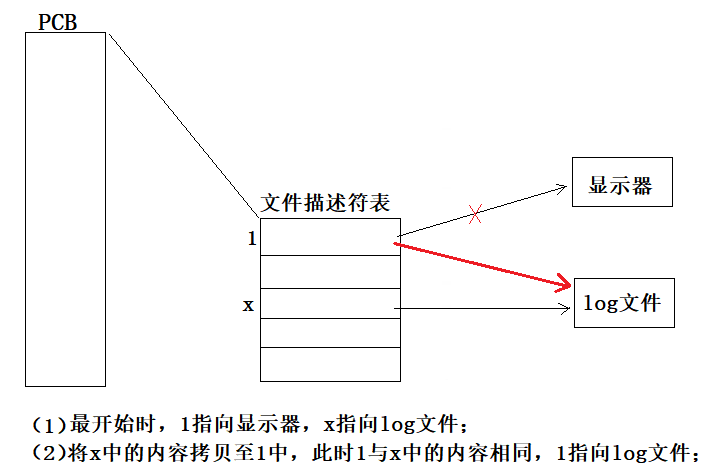
相同的,我们也可以画一张图来理解这个过程: