目录
1.两数之和(easy)

V1暴力解法
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]
return []
结果:

- 时间复杂度:O(N2)。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。
V2哈希表
判断当前值是否在哈希表中,如果不在,将目标与该值的差值放入哈希表中。注意:将值存为key,索引存为value,这样才可以判断当前值是否在哈希表中。
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
i = 0
hashtable = {
}
while i < len(nums):
if nums[i] not in hashtable:
hashtable[target - nums[i]] = i
i += 1
else:
return [i, hashtable[nums[i]]]
结果:

- 时间复杂度:O(N)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N)。
217.存在重复元素(easy)
给定一个整数数组,判断是否存在重复元素。
如果存在一值在数组中出现至少两次,函数返回 true 。如果数组中每个元素都不相同,则返回 false 。
V1(用列表存储)
class Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
table = []
for i in nums:
if i not in table:
table.append(i)
else:
return True
return False
结果:

V2(用集合存储)
class Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
table = set()
for i in nums:
if i not in table:
table.add(i)
else:
return True
return False
结果:

V3(set())
class Solution:
def containsDuplicate(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
return len(set(nums)) != len(nums)
set() 函数创建一个无序不重复元素集,可进行关系测试,删除重复数据,还可以计算交集、差集、并集等。
结果:

594.最长和谐子序列(easy)
和谐数组是指一个数组里元素的最大值和最小值之间的差别 正好是 1 。
现在,给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你在所有可能的子序列中找到最长的和谐子序列的长度。
数组的子序列是一个由数组派生出来的序列,它可以通过删除一些元素或不删除元素、且不改变其余元素的顺序而得到。
V1
用哈希表存储每个元素出现的次数,然后遍历哈希表。
class Solution:
def findLHS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
table = {
}
for i in nums:
if table.get(i) is None:
table[i] = 1
else:
table[i] += 1
print(table.keys())
print(table.values())
length = 0
for i in table.keys():
if i + 1 in table.keys():
if table[i] + table[i+1] > length:
length = table[i] + table[i+1]
return length
结果:

128.最长连续序列(hard)
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
V1
class Solution:
def longestConsecutive(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
if len(nums) == 1:
return 1
table = {
}
for i in nums:
if table.get(i) is None:
table[i] = 1
else:
table[i] += 1
print(table)
num = sorted(table.keys())
print(num)
count = 1
max_count = 1
for i in range(len(num)-1):
if num[i+1] == num[i] + 1:
count += 1
if count > max_count:
max_count = count
else:
count = 1
return max_count
V2
class Solution:
def longestConsecutive(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
table = set(nums)
max_count = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] - 1 not in table:
count = 1
cur = nums[i]
while cur + 1 in table:
count += 1
cur += 1
max_count = max(count, max_count)
return max_count
349.两个数组的交集(easy)

V1(我的)
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
table = set()
out = set()
for i in nums1:
if i not in table:
table.add(i)
for j in nums2:
if j in table:
out.add(j)
return list(out)

V2(官方)
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
set1 = set(nums1)
set2 = set(nums2)
return self.set_intersection(set1, set2)
def set_intersection(self, set1, set2):
if len(set1) > len(set2):
return self.set_intersection(set2, set1)
return [x for x in set1 if x in set2]

V3(按照官方的简化)
简化的过程中才明白官方版本比较两个集合长度的意义,按照短的集合来循环,速度更快。
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
if not nums1 or not nums2: return []
set1 = set(nums1)
set2 = set(nums2)
return [x for x in set1 if x in set2]

350. 两个数组的交集 II(easy)

注意到本题和上一题的区别,这道题不仅需要找到交集包含哪些数,还要知道这些数重复了几次。
V1(我的)
思路:对两个列表各做一次循环,将出现的值以及对应的次数存储在字典里,然后找两个字典keys的交集,根据对应value的最小值循环append。
class Solution:
def intersect(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
table1 = {
}
table2 = {
}
out = []
for i in nums1:
table1[i] = table1.get(i, 0) + 1
for j in nums2:
table2[j] = table2.get(j, 0) + 1
key = [i for i in table1.keys() if i in table2.keys()]
for k in key:
for t in range(min(table1[k], table2[k])):
out.append(k)
return out

V2(按照官方修改)
只需对两个列表各循环一次。
class Solution:
def intersect(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
table1 = {
}
out = []
for i in nums1:
table1[i] = table1.get(i, 0) + 1
for j in nums2:
if j in table1.keys() and table1[j] > 0:
out.append(j)
table1[j] -= 1
return out

242. 有效的字母异位词(easy)

V1(我的)
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
table = {
}
for i in s:
table[i] = table.get(i, 0) + 1
for j in t:
if j in table.keys():
if table[j] == 0:
return False
table[j] -= 1
else:
return False
if sum(table.values()) == 0:
return True
return False

V2(我的)
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
table1 = {
}
table2 = {
}
for i in s:
table1[i] = table1.get(i, 0) + 1
for j in t:
table2[j] = table2.get(j, 0) + 1
return table1 == table2

V3(题解里看到的解法,使用Counter)
from collections import Counter
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
s_ = Counter(s)
t_ = Counter(t)
return s_ == t_

Counter 是 dictionary 对象的子类。collections 模块中的 Counter() 函数会接收一个诸如 list 或 tuple 的迭代器,然后返回一个 Counter dictionary。这个 dictionary 的键是该迭代器中的唯一元素,每个键的值是迭代器元素的计数。(来源:https://www.jianshu.com/p/cfb14ebcf371)
202. 快乐数(easy)

V1(我的)
难点在于何时输出False,如果在一个死循环里不停判断平方和是否为1,会出现执行时间NAN的情况。这里设置了一个集合,将所有出现过的平方和结果都放进去,当当前计算结果在这个集合中出现过时,则意味着结果进入循环状态,没有必要继续计算下去,此时输出False。
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
table = set()
while 1:
out = 0
n = str(n)
for i in n:
out += int(i) * int(i)
if out == 1:
return True
elif out in table:
return False
n = out
table.add(n)

V2(快慢指针)
看了题解中有用快慢指针做的。
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
if n == 1:
return True
slow = sum([int(i)**2 for i in str(n)])
fast = sum([int(i)**2 for i in str(slow)])
while slow != fast:
slow = sum([int(i)**2 for i in str(slow)])
fast = sum([int(i)**2 for i in str(fast)])
fast = sum([int(i)**2 for i in str(fast)])
if slow == 1:
return True
else:
return False

- 好像突然明白快慢指针中快指针和慢指针每次移动的距离不同的原因,大概是为了保证两个指针之间的距离可以取到任意值?这样才能够找出循环,否则两指针的距离始终不变的话未必能发现循环。
- 速度变慢的原因猜测是:一旦出现重复元素,V1采用集合判断的方式一下子就能判断出来,而使用V2快慢指针的方式,指针不一定正好分别指到两个重复元素,因此需要更长的循环时间等到指针指到特定位置。
判断循环就用快慢指针!
205. 同构字符串(easy)

V1(我的)
对应元素比较,s中的值作为字典的key,t中的值作为字典中的value。
class Solution:
def isIsomorphic(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
if len(s) != len(t):
return False
length = len(s)
table = {
}
for i in range(length):
if s[i] not in table.keys():
if t[i] in table.values():
return False
table[s[i]] = t[i]
else:
if table[s[i]] != t[i]:
return False
return True

V2(来源于题解)
比较对应元素的索引,一行代码搞定。
class Solution:
def isIsomorphic(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
return all(s.index(s[i]) == t.index(t[i]) for i in range(len(s)))

451. 根据字符出现频率排序(medium)


注意区分大小写。
V1(我的)
把字符串s出现的元素和次数存储在字典中,然后对字典的value进行排序,使用列表构建新的字符串。
class Solution:
def frequencySort(self, s: str) -> str:
table = {
}
s_new = []
for i in s:
table[i] = table.get(i,0) + 1
new_table = sorted(table.items(), key=lambda d: d[1], reverse=True)
for i in new_table:
for times in range(i[1]):
s_new.append(i[0])
return ''.join(s_new)

V2(在V1的基础上改进)
与V1的区别在于没有使用列表来存储新的字符串,注意到在字符串中重复某元素可以通过 字符串*出现次数 来获得,并使用 + 来连接。
使用乘法而非循环的效率更高。
class Solution:
def frequencySort(self, s: str) -> str:
table = {
}
s_new = ''
for i in s:
table[i] = table.get(i,0) + 1
new_table = sorted(table.items(), key=lambda d: d[1], reverse=True)
for i in new_table:
s_new += i[0] * i[1] ### 只修改了这一行
return s_new

V3(使用Counter)
from collections import Counter
class Solution:
def frequencySort(self, s: str) -> str:
return "".join(i[0] * i[1] for i in Counter(s).most_common(len(s)))

15. 三数之和(medium)

V1(我的,不通过)
我想的是把列表分为正、负、零三个小列表,输出的结果要么是两正一负,要么是两负一正,要么是零和一正一负或者全零。结果不通过,不想想了。
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
negative = []
positive = []
zero = []
out = []
for i in nums:
if i > 0:
positive.append(i)
elif i < 0:
negative.append(i)
else:
zero.append(i)
for i in range(len(positive)):
for j in range(i+1, len(positive)):
if -(positive[i] + positive[j]) in negative:
t = [positive[i],positive[j],-(positive[i]+positive[j])]
if t not in out:
out.append(t)
if zero!=[] and -positive[i] in negative:
t = [positive[i],0,-positive[i]]
if t not in out:
out.append(t)
for i in range(len(negative)):
for j in range(i+1, len(negative)):
if -(negative[i] + negative[j]) in positive:
t = [negative[i],negative[j],-(negative[i]+negative[j])]
if t not in out:
out.append(t)
if len(zero) >= 3:
out.append([0,0,0])
return out
V2(参考题解)
排序后采用对撞指针。
重点在于多处判断重复值,尽可能地缩小搜索范围。
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
nums.sort()
out = []
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
if nums[i] > 0:
break
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
i += 1
continue
j, k = i + 1, len(nums) - 1
while j < k:
s = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]
if s == 0:
out.append([nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]])
j += 1
k -= 1
while j < k and nums[j] == nums[j-1]:
j += 1
while j < k and nums[k] == nums[k+1]:
k -= 1
elif s < 0:
j += 1
while j < k and nums[j] == nums[j-1]:
j += 1
else:
k -= 1
while j < k and nums[k] == nums[k+1]:
k -= 1
return out

18. 四数之和(medium)

V1(参照上题 三数之和 的解法)
首先固定a,然后固定d,两头固定之后将该问题转化为上题“三数之和”的问题。
class Solution:
def fourSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
out = []
nums.sort()
for a in range(len(nums) - 3):
for d in range(len(nums)-1, a+2, -1):
b = a + 1
c = d - 1
while b < c:
s = nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d]
if s == target:
m = [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]]
if m not in out:
out.append(m)
b += 1
c -= 1
elif s < target:
b += 1
else:
c -= 1
return out

V2(在V1的基础上缩小搜索范围)
增加了四行代码,执行时间大为缩短。
class Solution:
def fourSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
out = []
nums.sort()
for a in range(len(nums) - 3):
#### 缩小搜索范围
if nums[a] + nums[a+1] + nums[a+2] + nums[a+3] > target:
break
####
for d in range(len(nums)-1, a+2, -1):
#### 缩小搜索范围
if nums[a] + nums[d-2] + nums[d-1] + nums[d] < target:
break
####
b = a + 1
c = d - 1
while b < c:
s = nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d]
if s == target:
m = [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]]
if m not in out:
out.append(m)
b += 1
c -= 1
elif s < target:
b += 1
else:
c -= 1
return out
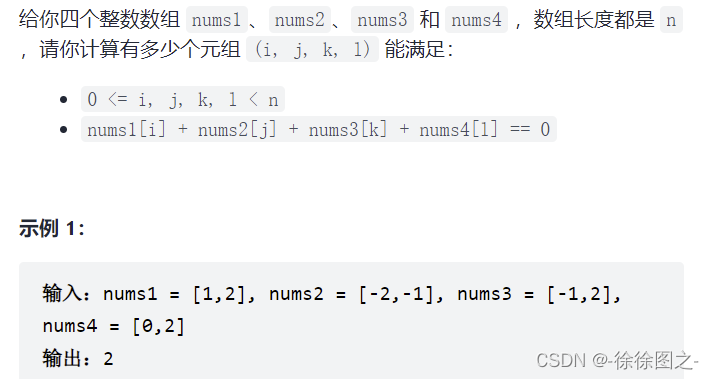
454. 四数相加 II
V1(超出时间限制)
直接四次循环,肯定超出时间限制
class Solution:
def fourSumCount(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], nums3: List[int], nums4: List[int]) -> int:
count = 0
nums1.sort()
nums2.sort()
nums3.sort()
nums4.sort()
if nums1[0] + nums2[0] + nums3[0] + nums4[0] > 0:
return 0
elif nums1[-1] + nums2[-1] + nums3[-1] + nums4[-1] < 0:
return 0
n = len(nums1)
for i in range(n):
if nums1[i] + nums2[0] + nums3[0] + nums4[0] > 0 or nums1[i] + nums2[-1] + nums3[-1] + nums4[-1] < 0:
continue
for j in range(n):
if nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[0] + nums4[0] > 0 or nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[-1] + nums4[-1] < 0:
continue
for k in range(n):
if nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[k] + nums4[0] > 0 or nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[k] + nums4[-1] < 0:
continue
for l in range(n):
if nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[k] + nums4[l] == 0:
count += 1
return count
V2(超出时间)
试图通过仅对唯一值做循环来减少循环次数,但还是超出时间限制
class Solution:
def fourSumCount(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], nums3: List[int], nums4: List[int]) -> int:
import numpy as np
count = 0
nums1, nums1_count = np.unique(nums1, return_counts=True)
nums2, nums2_count = np.unique(nums2, return_counts=True)
nums3, nums3_count = np.unique(nums3, return_counts=True)
nums4, nums4_count = np.unique(nums4, return_counts=True)
if nums1[0] + nums2[0] + nums3[0] + nums4[0] > 0:
return 0
elif nums1[-1] + nums2[-1] + nums3[-1] + nums4[-1] < 0:
return 0
for i in range(len(nums1)):
if nums1[i] + nums2[0] + nums3[0] + nums4[0] > 0 or nums1[i] + nums2[-1] + nums3[-1] + nums4[-1] < 0:
continue
for j in range(len(nums2)):
if nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[0] + nums4[0] > 0 or nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[-1] + nums4[-1] < 0:
continue
for k in range(len(nums3)):
if nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[k] + nums4[0] > 0 or nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[k] + nums4[-1] < 0:
continue
for l in range(len(nums4)):
if nums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[k] + nums4[l] == 0:
count += nums1_count[i]*nums2_count[j]*nums3_count[k]*nums4_count[l]
return int(count)
V3(题解,把四数之和变形为两数之和)
class Solution:
def fourSumCount(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], nums3: List[int], nums4: List[int]) -> int:
hashmap = dict()
count = 0
for i in nums1:
for j in nums2:
hashmap[i+j] = hashmap.get(i+j, 0) + 1
for k in nums3:
for l in nums4:
if -k-l in hashmap:
count += hashmap[-k-l]
return count

V4(collections.Counter)
class Solution:
def fourSumCount(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], nums3: List[int], nums4: List[int]) -> int:
from collections import Counter
dic = Counter(a+b for a in nums1 for b in nums2)
return sum(dic.get(-c-d, 0) for c in nums3 for d in nums4)
作者:QQqun902025048
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum-ii/solution/2-xing-python-by-qqqun902025048-2/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

小结
- 集合增加元素用add,列表增加元素用append。
- 循环尽量短。
- 在循环中通过增加判断条件尽可能地缩小搜索范围。
- 判断循环就用快慢指针。
- 统计字符串(或者其他可哈希的对象)中出现的所有元素及其出现次数时可以使用
collections.Counter()函数。 - 需要重复字符串时用乘法代替循环,效率更高。