
PyTorch入门
前言
Vue框架:从项目学Vue
OJ算法系列:神机百炼 - 算法详解
Linux操作系统:风后奇门 - linux
C++11:通天箓 - C++11
Python常用模块:通天箓 - Python
机器学习:Machine Learning
张量Tensor
- 等于Numpy中的Array + 梯度计算及其传播
- 在神经网络建模过程中,最常用的是torch.float 和 torch.long类型,其中float类型用于浮点数变量,long类型(64bit)用于整数变量。
| 数据类型 | dtype |
|---|---|
| 布尔类型 | torch.bool |
| 16bit浮点数 | torch.float16或torch.half |
| 32bit浮点数 | torch.float32或torch.float |
| 64bit浮点数 | torch.float64或torch.double |
| 8bit无符号整数 | torch.unit8 |
| 8bit有符号整数 | torch.int8 |
| 16bit有符号整数 | torch.int16或torch.short |
| 32bit有符号整数 | torch.int32或torch.int |
| 64bit有符号整数 | torch.int64或torch.long |
导入torch
# 导入PyTorch
import torch
import numpy as np
print(torch.__version__)
结果:
1.13.0
创建张量
- tensor()强制转换list和tuple为tensor
- from_numpy()强制转换array为tensor
- arange()生成器
- rand()随机生成器,均值为0,方差为1
#通过列表
t1 = torch.tensor([1, 2])
print('t1.shape :',t1.shape)
print('t1 :',t1)
print('*'*40)
#通过元组
t2 = torch.tensor((3, 4, 5))
print('t2.shape :',t2.shape)
print('t2 :',t2)
print('*'*40)
#通过元组列表
t3 = torch.tensor(([3, 4, 5], [3, 4, 5]))
print('t3.shape :',t3.shape)
print('t3 :',t3)
print('*'*40)
#通过列表元组
t4 = torch.tensor([(3, 4, 5), (3, 4, 5)])
print('t4.shape :',t4.shape)
print('t4 :',t4)
print('*'*40)
#通过Numpy数组
t5 = torch.tensor(np.array([np.arange(1,4),np.arange(4,7)]))
print('t5.shape :',t5.shape)
print('t5 :',t5)
print('*'*40)
#通过torch自带的生成器
t6 = torch.arange(9)
print('t6.shape :',t6.shape)
print('t6 :',t6)
print('*'*40)
#通过torch自带的randn(类似Numpy的rand)
#均值为0,方差&标准差为1
t7 = torch.rand(3, 4)
print('t7.shape :',t7.shape)
print('t7 :',t7)
print('*'*40)
t8 = torch.randn(4, 4)
print('t8.shape :',t8.shape)
print('t8 :',t8)
print('*'*40)
结果:
t1.shape : torch.Size([2])
t1 : tensor([1, 2])
****************************************
t2.shape : torch.Size([3])
t2 : tensor([3, 4, 5])
****************************************
t3.shape : torch.Size([2, 3])
t3 : tensor([[3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5]])
****************************************
t4.shape : torch.Size([2, 3])
t4 : tensor([[3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5]])
****************************************
t5.shape : torch.Size([2, 3])
t5 : tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
****************************************
t6.shape : torch.Size([9])
t6 : tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
****************************************
t7.shape : torch.Size([3, 4])
t7 : tensor([[0.8585, 0.7642, 0.2302, 0.0333],
[0.4206, 0.8841, 0.5200, 0.2278],
[0.9252, 0.9679, 0.6137, 0.2227]])
****************************************
t8.shape : torch.Size([4, 4])
t8 : tensor([[ 0.6837, 0.3894, -1.4908, 1.1544],
[ 0.0383, -0.2924, 0.0763, -0.4037],
[ 0.0150, -0.3598, 1.3893, 1.0635],
[ 0.1822, -1.9519, -0.0498, -0.2129]])
****************************************
返回numpy.ndarray
- object.numpy()强制转化
numpy.ndarray是一个类,array()是类中一个初始化方法
t9 = torch.rand(3, 4)
print('t9 :',type(t9))
t10 = t9.numpy()
print('t10 :',type(t10))
print('t9 :',type(t9))
print(t10)
t9 : <class 'torch.Tensor'>
t10 : <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
t9 : <class 'torch.Tensor'>
[[0.30557132 0.589663 0.91819024 0.8397739 ]
[0.7587973 0.93850935 0.77926093 0.37537104]
[0.03518718 0.9489069 0.79025054 0.45351315]]
tensor与list/ndarray/dataframe转化:
- 多种多维数组作用不同:
- PyTorch模型只接收tensor
- pandas便于读写csv,查看数据各种特征:isnull、sum…
- numpy利于计算
- list创建简单,且是前面类型的转化中枢
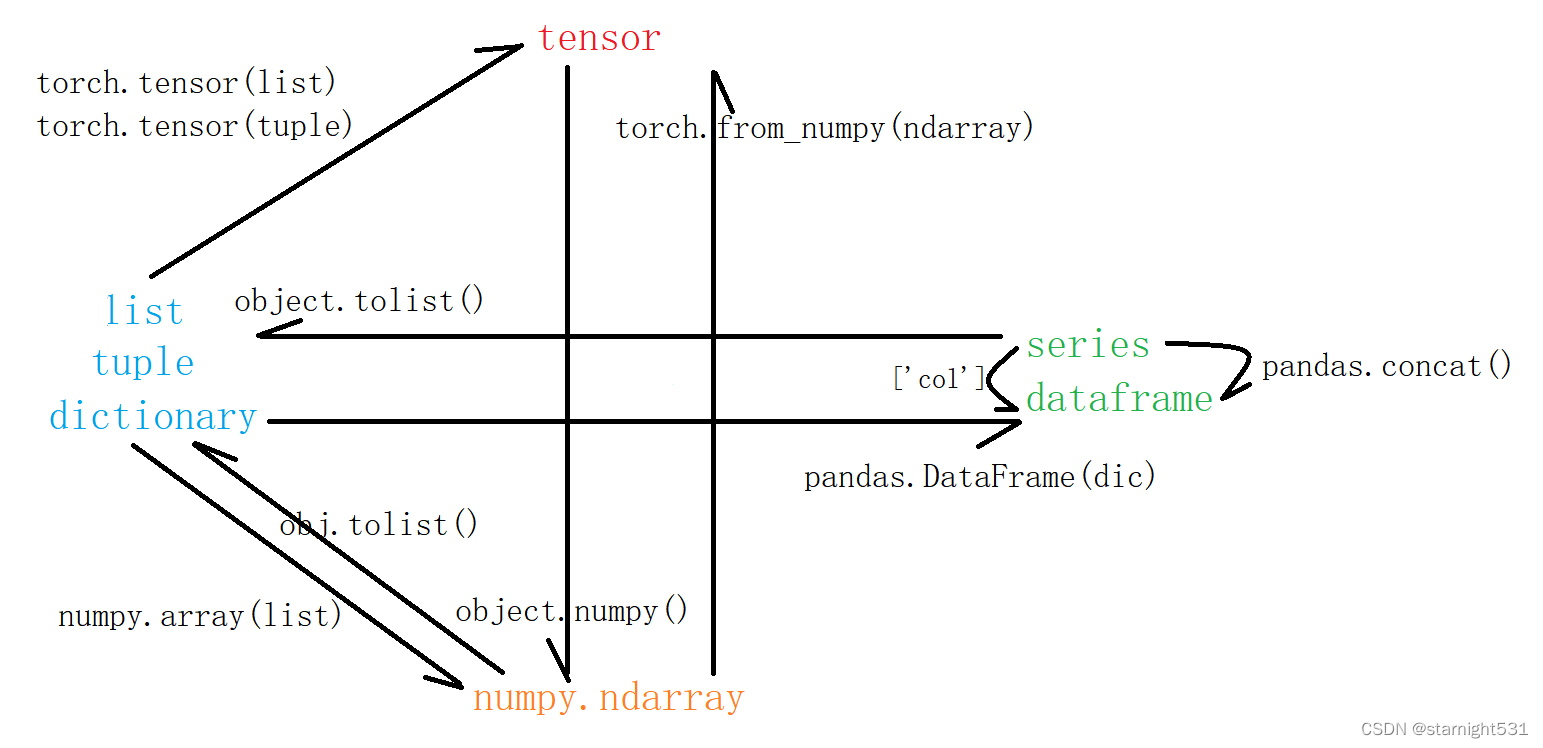
tensor内数据类型转化
- .dtype查看数据类型
- .类型(),转化为指定类型
- .type(torch.类型),转化为指定类型
# .dtype
a = torch.arange(10)
print('a :', a.dtype)
# .float() / .double() / .long()
b = a.float()
c = a.double()
print('b :', b.dtype)
print('c :', c.dtype)
# .type(torch.类型)
d = a.type(torch.long)
print('d :', d.dtype)
a : torch.int64
b : torch.float32
c : torch.float64
d : torch.int64
维度变换
-
查看:
- tensor.ndim,维度数目
- tensor.size() = tensor.shape,各维度数目
- tensor.numel(),总共有多少元素
-
转变:
- tensor.reshape(),同于numpy的reshape(),灵活调整
- tensor.squeeze(),同于numpy.squeeze(),舍弃维度
- tensor.unsqueeze(),同于numpy.expand_dims,添加维度
- tensor.transpose(),维度重新排序
0维item():
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(x.ndim) # 维度数量
print(x.shape) # 同size
print(x.size()) # 张量size
print(x.numel()) # 总共有多少的元素 num elements
结果:
2
torch.Size([2, 2])
torch.Size([2, 2])
4
reshape():
- 最好最高阶取值(-1,n,m,…)
# reshape
x = torch.rand(4, 3, 2) # 4个3行2列
x_reshape = x.reshape(4, 6) # 4个6行
print(x.shape,x)
print(x_reshape.shape,x_reshape)
结果:
torch.Size([4, 3, 2]) tensor([[[0.2527, 0.4964],
[0.2626, 0.9498],
[0.1045, 0.5866]],
[[0.8804, 0.3144],
[0.3867, 0.1342],
[0.0946, 0.4661]],
[[0.7645, 0.7955],
[0.1478, 0.1380],
[0.8725, 0.4701]],
[[0.6088, 0.5250],
[0.5597, 0.7713],
[0.0573, 0.5705]]])
torch.Size([4, 6]) tensor([[0.2527, 0.4964, 0.2626, 0.9498, 0.1045, 0.5866],
[0.8804, 0.3144, 0.3867, 0.1342, 0.0946, 0.4661],
[0.7645, 0.7955, 0.1478, 0.1380, 0.8725, 0.4701],
[0.6088, 0.5250, 0.5597, 0.7713, 0.0573, 0.5705]])
squeeze&unsqueeze:
- 减少/增加一维
# squeeze
x = torch.rand(4, 1) #4行1列
x_squeeze = x.squeeze() #1行
print(x.shape, x)
print(x_squeeze.shape, x_squeeze)
结果:
torch.Size([4, 1]) tensor([[0.8059],
[0.6073],
[0.5573],
[0.0338]])
torch.Size([4]) tensor([0.8059, 0.6073, 0.5573, 0.0338])
# unsqueeze
x = torch.rand(4) #1行4列
x_unsqueeze_0 = x.unsqueeze(0) #增加行
x_unsqueeze_1 = x.unsqueeze(1) #增加列
print(x.shape, x)
print(x_unsqueeze_0.shape, x_unsqueeze_0)
print(x_unsqueeze_1.shape, x_unsqueeze_1)
结果:
torch.Size([4]) tensor([0.6690, 0.7504, 0.3665, 0.8370])
torch.Size([1, 4]) tensor([[0.6690, 0.7504, 0.3665, 0.8370]])
torch.Size([4, 1]) tensor([[0.6690],
[0.7504],
[0.3665],
[0.8370]])
# transpose
x = torch.rand(4, 3, 2)
x_transpose_12 = x.transpose(1, 2)
x_transpose_02 = x.transpose(0, 2)
print(x.shape, x)
# 将dim=1, dim=2 维度互换
print(x_transpose_12.shape, x_transpose_12)
# 将dim=0, dim=2 维度互换
print(x_transpose_02.shape, x_transpose_02)
结果:
torch.Size([4, 3, 2]) tensor([[[0.2127, 0.0750],
[0.9866, 0.1007],
[0.3098, 0.7659]],
[[0.1835, 0.4821],
[0.2532, 0.3440],
[0.3932, 0.1854]],
[[0.2653, 0.9608],
[0.6539, 0.0693],
[0.1171, 0.4757]],
[[0.7080, 0.1878],
[0.1567, 0.4416],
[0.1667, 0.2108]]])
torch.Size([4, 2, 3]) tensor([[[0.2127, 0.9866, 0.3098],
[0.0750, 0.1007, 0.7659]],
[[0.1835, 0.2532, 0.3932],
[0.4821, 0.3440, 0.1854]],
[[0.2653, 0.6539, 0.1171],
[0.9608, 0.0693, 0.4757]],
[[0.7080, 0.1567, 0.1667],
[0.1878, 0.4416, 0.2108]]])
torch.Size([2, 3, 4]) tensor([[[0.2127, 0.1835, 0.2653, 0.7080],
[0.9866, 0.2532, 0.6539, 0.1567],
[0.3098, 0.3932, 0.1171, 0.1667]],
[[0.0750, 0.4821, 0.9608, 0.1878],
[0.1007, 0.3440, 0.0693, 0.4416],
[0.7659, 0.1854, 0.4757, 0.2108]]])
permute:
- 对换dim,重新排列
# permute
x = torch.rand(4, 3, 2)
x_permute = x.permute(1, 2, 0)
print(x.shape, x)
# 将原本的1,2,0维度按照顺序重新排列
print(x_permute.shape, x_permute)
结果:
torch.Size([4, 3, 2]) tensor([[[0.9426, 0.3520],
[0.1443, 0.4034],
[0.1542, 0.8090]],
[[0.3293, 0.3210],
[0.2344, 0.7441],
[0.9163, 0.9639]],
[[0.2973, 0.7787],
[0.2891, 0.6637],
[0.0113, 0.6871]],
[[0.7415, 0.9899],
[0.7431, 0.9398],
[0.8310, 0.0346]]])
torch.Size([3, 2, 4]) tensor([[[0.9426, 0.3293, 0.2973, 0.7415],
[0.3520, 0.3210, 0.7787, 0.9899]],
[[0.1443, 0.2344, 0.2891, 0.7431],
[0.4034, 0.7441, 0.6637, 0.9398]],
[[0.1542, 0.9163, 0.0113, 0.8310],
[0.8090, 0.9639, 0.6871, 0.0346]]])
张量相关操作
- item():获取0维张量内的唯一值
- zero(), ones():构建 全0/全1 张量
- cat():进行行扩展(对列数有要求) 或者 进行列扩展(对行数有要求)
- slice:()
item()
# 0维张量
zero_dim = torch.tensor(1.0)
print(zero_dim.shape)
print(zero_dim)
# item获取0维张量的值
print(type(zero_dim.item()), zero_dim.item())
结果:
torch.Size([])
tensor(1.)
<class 'float'> 1.0
zeros() & ones()
# 全0 & 全1 张量
zero = torch.zeros(2,3)
print(zero)
one = torch.ones(2,3)
print(one)
# 连接 np.concatenate
car_0 = torch.cat([zero, one], 0) #行扩展
print(car_0)
car_1 = torch.cat([zero, one], 1) #列扩展
print(car_1)
结果:
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1.]])
slice
# 切片和Numpy Array一致
x = torch.arange(0, 15)
print(x[0:6])
print(x[0:8:2])
print(x[0::3])
print()
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[1,2,3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(tensor1[:, 1])
print(tensor1[:, [1,2]])
print(tensor1[:-1, [2]])
结果:
tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
tensor([0, 2, 4, 6])
tensor([ 0, 3, 6, 9, 12])
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
tensor([2, 5])
tensor([[2, 3],
[5, 6]])
tensor([[3]])
张量计算
- 转秩:.T
- 加减乘除
- 矩阵乘法:@ 或 torch.mm()
- batch矩阵乘法:@ 或 torch.bmm()
+-*/
# + - * /
x = torch.randn(4, 3)
y = torch.randn(4, 3)
print(x)
print(y)
print((x + y).shape, (x + y))
print((x - y).shape, (x - y))
print((x * y).shape, (x * y))
print((x / y).shape, (x / y))
结果:
tensor([[-1.3878, -0.2911, -0.7524],
[ 0.4174, -0.9334, 1.0381],
[-1.2400, 1.1345, -1.3406],
[ 1.4062, 1.6843, -1.1564]])
tensor([[-0.2299, -0.4271, -0.5138],
[ 0.0280, -0.2743, 0.8372],
[ 1.6998, 1.3105, 0.1312],
[ 0.6012, 1.1933, 0.4462]])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([[-1.6177, -0.7182, -1.2662],
[ 0.4454, -1.2077, 1.8753],
[ 0.4598, 2.4450, -1.2094],
[ 2.0075, 2.8777, -0.7102]])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([[-1.1579, 0.1360, -0.2386],
[ 0.3894, -0.6592, 0.2009],
[-2.9397, -0.1760, -1.4718],
[ 0.8050, 0.4910, -1.6027]])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([[ 0.3190, 0.1243, 0.3866],
[ 0.0117, 0.2560, 0.8691],
[-2.1076, 1.4868, -0.1759],
[ 0.8455, 2.0100, -0.5160]])
torch.Size([4, 3]) tensor([[ 6.0366, 0.6815, 1.4643],
[ 14.9285, 3.4035, 1.2400],
[ -0.7295, 0.8657, -10.2192],
[ 2.3389, 1.4115, -2.5914]])
@ 或 mm
# @ 或 torch.mm
print(x.shape, y.T.shape)
print((x @ y.T).shape)
print((torch.mm(x, y.T).shape))
print(x @ y.T)
结果:
torch.Size([4, 3]) torch.Size([3, 4])
torch.Size([4, 4])
torch.Size([4, 4])
tensor([[ 0.8300, -0.5889, -2.8390, -1.5175],
[-0.2307, 1.1368, -0.3776, -0.3997],
[ 0.4893, -1.4682, -0.7967, 0.0101],
[-0.4485, -1.3908, 4.4459, 2.3394]])
batch@ 或 bmm
# batch@ 或 torch.bmm()
batch_size = 4
x = torch.rand(batch_size, 3, 2)
y = torch.rand(batch_size, 2, 3)
print((x@y).shape)
print((torch.bmm(x, y).shape))
结果:
torch.Size([4, 3, 3])
torch.Size([4, 3, 3])
后语:
- 博主专业其实是AI,但是花费的精力和时间较传统计算机软工短很多。
- 一周抽空写3or4小时的notebook来复习AI,防止复试被问到本专业。