目录
前言
Vuex是Vue.js的一个状态管理库,它可以帮助我们更好地管理应用程序的状态。在Vue.js中,组件之间的通信往往需要借助于props和emit来完成,但是当应用程序的状态变得比较复杂时,这种方式就变得比较麻烦。Vuex可以帮助我们更好地管理状态,以及在组件之间共享状态。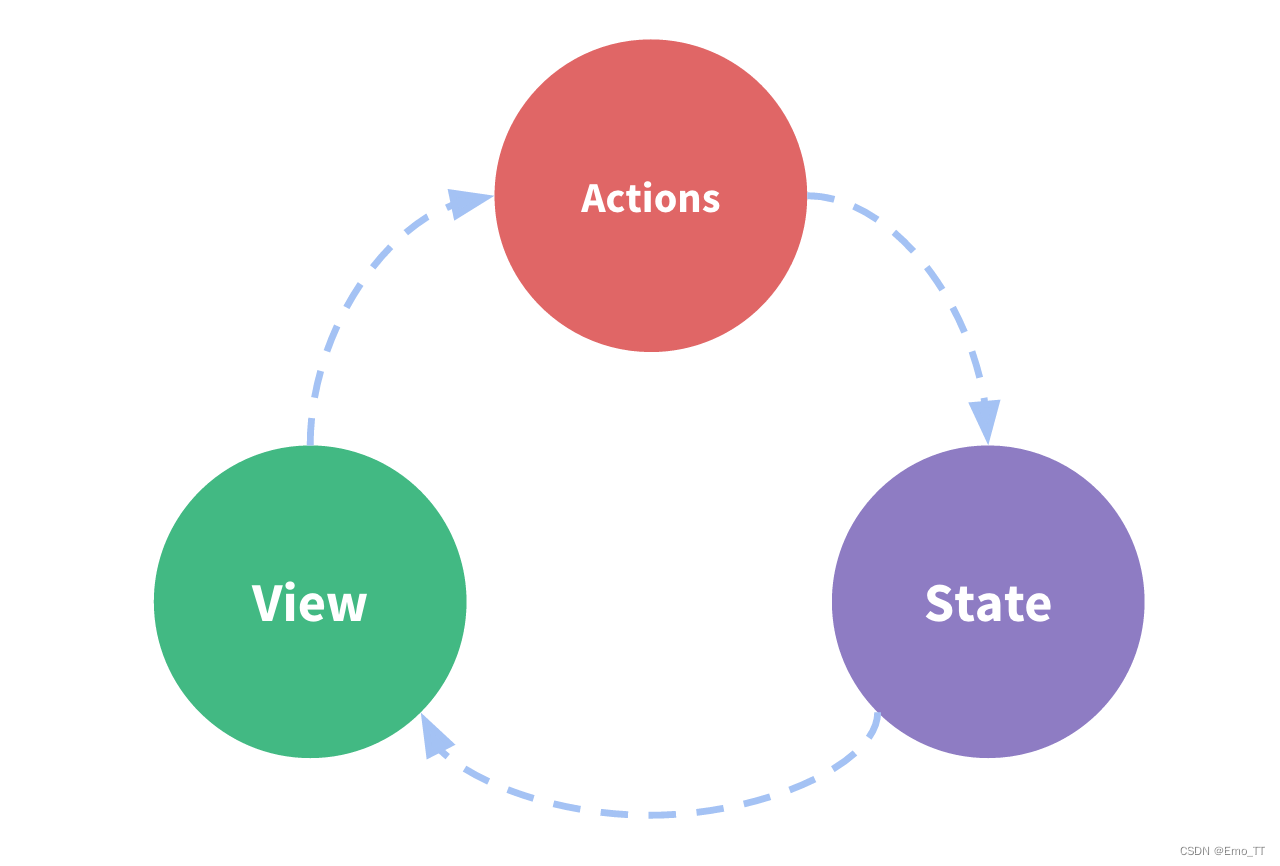
本篇教程将介绍Vuex的基本概念、使用方法和常见应用场景。我们将通过一个简单的计数器示例来演示如何使用Vuex,并且通过不同的场景,逐步深入Vuex的使用。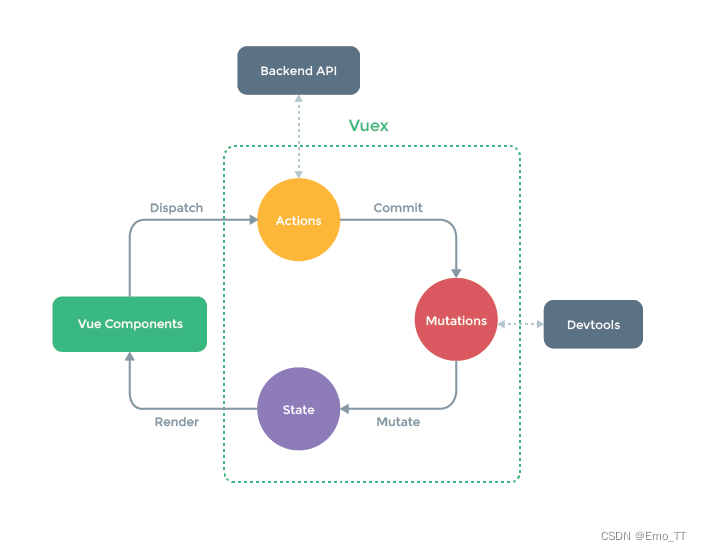
1. 安装和配置Vuex
在开始使用Vuex之前,我们需要先安装它。可以使用npm或yarn来安装:
npm install vuex --save
或
yarn add vuex
安装完成之后,我们需要在Vue.js中使用Vuex。为了使用Vuex,我们需要在Vue.js实例中进行一些配置,具体来说,我们需要:
- 引入Vuex
- 创建一个Store
- 将Store注入到Vue.js实例中
下面是一个示例:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
在这个示例中,我们首先引入了Vuex并将其安装到Vue.js中。然后,我们创建了一个Store,并将其注入到Vue.js实例中。在Store中,我们定义了一个state对象,其中包含了count属性,默认值为0。我们还定义了一个mutation,用于增加count的值。在Vue.js实例中,我们将Store注入到了组件中。
2. State
State是Vuex中最重要的概念之一。State是一个包含应用程序中所有状态的对象。我们可以在组件中使用$store.state来访问State中的属性。
下面是一个示例,展示了如何在组件中使用State:
<template>
<div>
<p>Count: {
{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<button @click="$store.commit('increment')">Increment</button>
</div>
</template>
在这个示例中,我们展示了如何在组件中访问State中的count属性。我们使用$store.state.count来访问count属性,并在模板中展示它。我们还定义了一个按钮,用于触发increment mutation。
3. Mutations
Mutation是Vuex中的另一个重要概念。Mutation是一个用于修改State的函数,它只能进行同步操作。在组件中,我们可以使用$store.commit来触发Mutation。
下面是一个示例,展示了如何定义和使用Mutation:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--
}
}
})
<template>
<div>
<p>Count: {
{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<button @click="$store.commit('increment')">Increment</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('decrement')">Decrement</button>
</div>
</template>
在这个示例中,我们定义了两个Mutation:increment和decrement。这些Mutation分别用于增加和减少count属性的值。在组件中,我们使用$store.commit来触发这些Mutation。
4. Getters
Getter是Vuex中的另一个概念,它可以帮助我们从State中派生出一些新的状态。Getter是一个函数,它接收State作为第一个参数,并返回一个新的派生状态。
下面是一个示例,展示了如何定义和使用Getter:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
}
}
})
<template>
<div>
<p>Count: {
{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<p>Double Count: {
{ $store.getters.doubleCount }}</p>
<button @click="$store.commit('increment')">Increment</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('decrement')">Decrement</button>
</div>
</template>
在这个示例中,我们定义了一个Getter:doubleCount。这个Getter返回State中count属性的两倍。在组件中,我们使用$store.getters.doubleCount来访问这个Getter。
5. Actions
Action是Vuex中的另一个重要概念。Action用于执行异步操作,例如发起一个API请求。Action是一个函数,它接收一个context对象作为第一个参数。context对象包含了State、Getter和Mutation等信息。
下面是一个示例,展示了如何定义和使用Action:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
}
},
actions: {
asyncIncrement(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
}
})
<template>
<div>
<p>Count: {
{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<p>Double Count: {
{ $store.getters.doubleCount }}</p>
<button @click="$store.commit('increment')">Increment</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('decrement')">Decrement</button>
<button @click="$store.dispatch('asyncIncrement')">Async Increment</button>
</div>
</template>
在这个示例中,我们定义了一个Action:asyncIncrement。这个Action使用setTimeout函数模拟了一个异步操作,并在1秒后触发increment mutation。在组件中,我们使用$store.dispatch来触发这个Action。
6. Modules
Module是Vuex中的另一个概念,它可以帮助我们更好地组织应用程序的状态。Module是一个包含State、Mutation、Getter和Action等信息的对象,它可以被其他模块引用。
下面是一个示例,展示了如何定义和使用Module:
const counterModule = {
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
}
},
actions: {
asyncIncrement(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
counter: counterModule
}
})
<template>
<div>
<p>Count: {
{ $store.state.counter.count }}</p>
<p>Double Count: {
{ $store.getters['counter/doubleCount'] }}</p>
<button @click="$store.commit('counter/increment')">Increment</button>
<button @click="$store.dispatch('counter/asyncIncrement')">Async Increment</button>
</div>
</template>
在这个示例中,我们定义了一个Module:counterModule。这个Module包含了一个State、一个Mutation、一个Getter和一个Action。我们还将这个Module添加到了Store中,使用模块名作为键。
在组件中,我们通过store.state.counter来访问counterModule中的State。我们使用store.getters['counter/doubleCount']来访问counterModule中的Getter。在调用Mutation和Action时,我们需要在模块名前加上前缀。
7. 总结
通过本教程,我们了解了Vuex的基本概念和使用方法。我们学习了State、Mutation、Getter、Action