流水线模式
流水线模式是一种软件设计模式,它提供了构建和执行一系列操作的能力。
此模式最好与插件模式结合使用,以便在应用程序启动时动态构建流水线。
顺序
流水线的最基本实现是一个简单的操作序列。
public interface IOperation<T>
{
void Invoke(T data);
}
可以调用操作的接口来处理数据。
public class Pipeline<T> : IOperation<T>
{
private readonly List<IOperation<T>> operations = new List<IOperation<T>>();
// add operation at the end of the pipeline
public void Register(IOperation<T> operation)
{
operations.Add(operation);
}
// invoke every operations
public void Invoke(T data)
{
foreach (var operation in operations) operation.Invoke(data);
}
}
流水线一个一个地处理每个操作。流水线类还实现了 IOperation 接口,因此它们可以组合在一起。
public class ReverseOperation : IOperation<string>
{
public void Invoke(string data) => Console.WriteLine($" The string is reversed : {data.Reverse()}");
}
该操作可以写在专用类中。
public class Operation<T> : IOperation<T>
{
private readonly Action<T> action;
public Operation(Action<T> action)
{
this.action = action;
}
public void Invoke(T data) => action(data);
}
或者使用包装器从lambda自动创建操作。
// build
var pipeline = new Pipeline<string>();
// lambda
pipeline.Register(new Operation<string>(str =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"The string {str} contains {str.Length} characters.");
}));
// class
pipeline.Register(new ReverseOperation());
// execute
pipeline.Invoke("apple");
应在调用流水线之前注册流水线操作。
断路器
您要添加到流水线中的第一个功能是添加断路器。
public interface IOperation<T>
{
bool Invoke(T data);
}
每个操作都会返回结果:失败或成功。
class Pipeline<T> : IOperation<T>
{
// invoke every operations
public bool Invoke(T data)
{
foreach (var operation in operations)
{
if (!operation.Invoke(data))
{
Console.WriteLine("Aborting pipeline..");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
如果操作失败,流水线执行应该停止。
异步
另一个要求可能是拥有一个可以处理异步操作的流水线。
public interface IOperation<T>
{
void SetNext(IOperation<T> next);
void Invoke(T data);
}
在完成数据处理后,每个操作现在都必须调用流水线中的下一个操作。
class Pipeline<T> : IOperation<T>
{
// not the best
private readonly List<IOperation<T>> operations = new List<IOperation<T>>();
private readonly IOperation<T> terminate;
public Pipeline()
{
terminate = new Operation<T>(data => {}); // not the best
}
void IOperation<T>.SetNext(IOperation<T> next)
{
terminate.SetNext(next);
}
// append an operation at the end of the pipeline
public void RegisterOperation(IOperation<T> operation)
{
// when the operation is finished, it will call terminate
operation.SetNext(terminate);
if (operations.Any())
{
// link the last registered operation with the newly registered one
operations.Last().SetNext(operation);
}
operations.Add(operation);
}
public void Invoke(T data)
{
var operation = operations.Any() ? operations.First() : terminate;
operation.Invoke(data);
}
}
流水线稍微复杂一点,因为它需要在注册新操作时设置下一个操作。另一种解决方案是使用构建器。
public class WriteOperation : IOperation<string>
{
private IOperation<string> next;
public void SetNext(IOperation<string> next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public void Invoke(string data)
{
Task.Run(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Writing data to the disk...");
Thread.Sleep(100); // just kidding !
Console.WriteLine("Data successfully written to the disk !");
next?.Invoke(data);
});
}
}
此操作是异步的,将在专用线程中运行,当时间到时,它将调用下一个操作以继续流水线。
class Operation<T> : IOperation<T>
{
private readonly Func<T, bool> action;
private IOperation<T> next;
public Operation(Func<T, bool> action)
{
this.action = action;
}
public Operation(Action<T> action)
{
this.action = data =>
{
action(data);
return true;
};
}
public void SetNext(IOperation<T> next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public void Invoke(T data)
{
if (action(data)) next.Invoke(data);
}
}
通用操作既可以与简单操作一起使用,也可以在使用函数时使用内置断路器。
// the main pipeline
var pipeline = new Pipeline<string>();
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new Operation<string>(data =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"Everyone likes {data} !");
return true;
}));
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new WriteOperation());
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new Operation<string>(data =>
{
if (data == "banana")
{
Console.WriteLine("This banana made the pipeline abort...");
return false;
}
return true;
}));
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new Operation<string>(data => Console.WriteLine("This operation should not be called !")));
// a verbose pipeline to wrap the main pipeline
var verbose = new Pipeline<string>();
verbose.RegisterOperation(new Operation<string>(data => Console.WriteLine("Beginning of the pipeline...")));
verbose.RegisterOperation(pipeline);
verbose.RegisterOperation(new Operation<string>(data => Console.WriteLine("End of the pipeline...")));
verbose.Invoke("banana");
Console.WriteLine("The pipeline is asynchronous, so we should have more messages after this one : ");
这个简单的例子使用了我们实现的几个特性。
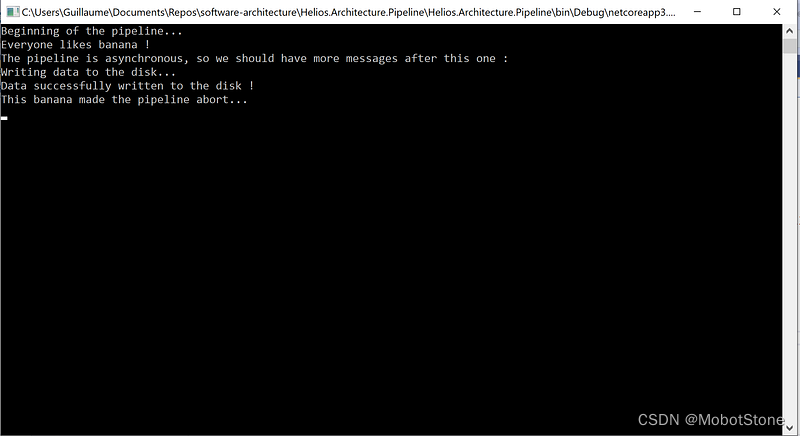
现在你知道如何让你的流水线异步了!
如果对之前的操作有另一个回调**,那就更好了,这样您就可以让结果逆流通过流水线。
插入
使用流水线设计模式的主要原因通常是需要能够添加插件,这些插件可以将操作附加到现有流水线或在其中挂钩操作。
public class Pipeline: IOperation
{
// exposes operations for hooking
public readonly LinkedList<IOperation> Operations = new LinkedList<IOperation>();
// add operation at the end of the pipeline
public void Register(IOperation operation)
{
Operations.AddLast(operation);
}
// invoke every operations
public void Invoke()
{
foreach (var operation in Operations) operation.Invoke();
}
}
流水线确实很基础,但这一次,操作暴露了。
class Application
{
internal abstract class Plugin
{
public abstract void Initialize(Application application);
}
private readonly List<Plugin> plugins = new List<Plugin>();
public readonly Pipeline Pipeline = new Pipeline();
public void RegisterPlugin(Plugin plugin)
{
plugins.Add(plugin);
}
public void Initialize()
{
Pipeline.Register(new Operation(() => Console.WriteLine("Step 1")));
Pipeline.Register(new Operation(() => Console.WriteLine("Step 2")));
Pipeline.Register(new Operation(() => Console.WriteLine("Step 3")));
foreach (var plugin in plugins) plugin.Initialize(this);
}
public void Run()
{
Pipeline.Invoke();
}
}
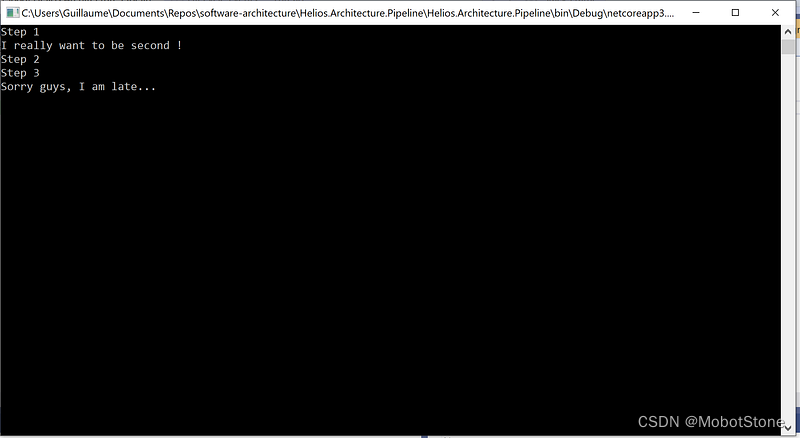
让我们来看一个带有流水线的简单应用程序,它只会在控制台中显示 3 个步骤。此应用程序还支持插件来修改流水线。
class HookPlugin : Application.Plugin
{
public override void Initialize(Application application)
{
var operations = application.Pipeline.Operations;
operations.AddAfter(operations.First, new Operation(() => Console.WriteLine("I really want to be second !")));
}
}
第一个插件将在流水线的第二个插槽中挂接另一个操作。
class LatePlugin : Application.Plugin
{
public override void Initialize(Application application)
{
application.Pipeline.Register(new Operation(() => Console.WriteLine("Sorry guys, I am late...")));
}
}
第二个插件将在流水线末尾附加一个新操作。
var application = new Application();
application.RegisterPlugin(new HookPlugin());
application.RegisterPlugin(new LatePlugin());
application.Initialize();
application.Run();
应用程序和插件放在一起,我们可以调用流水线。
批
另一个有用的功能是能够在与单个项目相同的流水线中处理批处理数据。
class BatchPipeline<T> : IOperation<T[]>
{
private readonly Pipeline<T> pipeline;
public BatchPipeline(Pipeline<T> pipeline)
{
this.pipeline = pipeline;
}
// invoke each operation on each item
public bool Invoke(T[] data)
{
// wrap items
var items = data.Select(item => new Result<T>(item)).ToArray();
foreach (var operation in pipeline.Operations)
{
// detects when every operation failed
var failed = true;
foreach (var item in items)
{
if(!item.Success) continue;
if (!operation.Invoke(item.Data)) item.Fail();
else failed = false;
}
// circuit breaker
if (failed) return false;
Console.WriteLine("----------------------");
}
return true;
}
}
批处理流水线包装流水线并调用每个项目的每个操作。
class Result<T>
{
public readonly T Data;
public bool Success { get; private set; } = true;
public void Fail() => Success = false;
public Result(T data)
{
Data = data;
}
}
每个项目都被包裹起来,所以我们可以记住断路器的结果。
public class CheckMagnitudeOperation : IOperation<int>
{
private readonly int threshold;
public CheckMagnitudeOperation(int magnitude)
{
threshold = (int) Math.Pow(10, magnitude);
}
public bool Invoke(int data)
{
if (data < threshold)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{data} < {threshold} -> ko");
return false;
}
Console.WriteLine($"{data} >= {threshold} -> ok");
return true;
}
}
此操作检查整数是否具有所需的数量级。
// base pipeline
var pipeline = new Pipeline<int>();
pipeline.Register(new CheckMagnitudeOperation(1));
pipeline.Register(new CheckMagnitudeOperation(2));
pipeline.Register(new CheckMagnitudeOperation(3));
pipeline.Register(new CheckMagnitudeOperation(4));
// batch pipeline
var batch = new BatchPipeline<int>(pipeline);
batch.Invoke(new []{ 12, 345, 6789 });
流水线将检查一批整数的数量级。
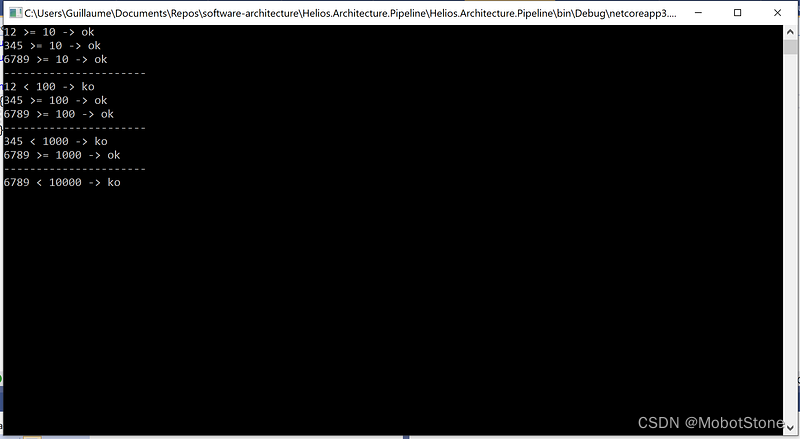 流水线只为没有失败的项目调用下一个操作。
流水线只为没有失败的项目调用下一个操作。
高性能流水线
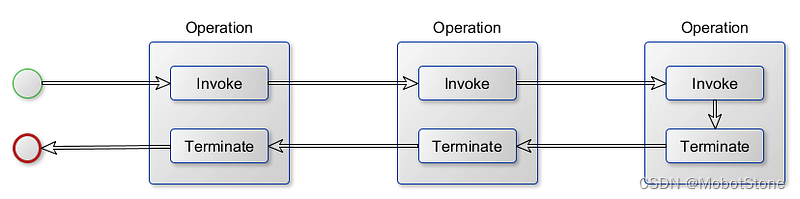
流水线设计模式也可以指更具体和以性能为导向的软件架构。
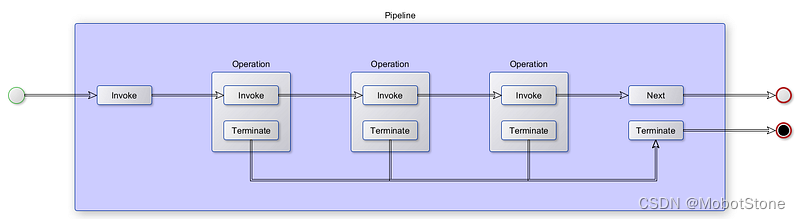
一些项目使用流水线通过在专用线程中运行流水线的每个操作来优化大量数据的处理。
abstract class Processor<T> : IOperation<T>
{
private readonly BlockingCollection<T> queue = new BlockingCollection<T>();
public IOperation<T> Next { private get; set; }
public IOperation<T> Terminate { private get; set; }
void IOperation<T>.Invoke(T data) => queue.Add(data);
protected Processor()
{
Task.Run(Run);
}
private void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Thread {GetType().Name} Started !");
while (true)
{
var data = queue.Take();
var operation = Process(data) ? Next : Terminate;
operation.Invoke(data);
Sleep(); // hack to have random output ;)
}
}
protected abstract bool Pr
每个线程都将从充当缓冲区的并发队列中消费和生成数据。
public interface IOperation<T>
{
IOperation<T> Next { set; }
IOperation<T> Terminate { set; }
void Invoke(T data);
}
这一次,我们将使用带有断路器的异步操作。
class Operation<T> : IOperation<T>
{
private readonly Func<T, bool> action;
public Operation(Func<T, bool> action)
{
this.action = action;
}
public IOperation<T> Next { private get; set; }
public IOperation<T> Terminate { private get; set; }
public void Invoke(T data)
{
var operation = action(data) ? Next : Terminate;
operation?.Invoke(data);
}
}
如果操作成功,它应该调用next,如果失败则终止。
class Pipeline<T> : IOperation<T>
{
private readonly List<IOperation<T>> operations = new List<IOperation<T>>();
public IOperation<T> Next { private get; set; }
public IOperation<T> Terminate { private get; set; }
private readonly IOperation<T> success;
private readonly IOperation<T> fail;
public Pipeline()
{
success = new Operation<T>(Success);
fail = new Operation<T>(Fail);
}
// append an operation at the end of the pipeline
public void RegisterOperation(IOperation<T> operation)
{
// when the operation is finished, it will call either call success or fail
operation.Next = success;
operation.Terminate = fail;
if (operations.Any())
{
// link the last registered operation with the newly registered one
operations.Last().Next = operation;
}
operations.Add(operation);
}
public void Invoke(T data)
{
var operation = operations.Any() ? operations.First() : fail;
operation.Invoke(data);
}
private bool Success(T data)
{
Continue(data);
return true;
}
private bool Fail(T data)
{
// we decide to bypass the circuit breaker
Continue(data);
return false;
}
private void Continue(T data)
{
Next?.Invoke(data);
}
}
流水线被设计成绕过断路器。Success或Fail,它总是会继续父流水线序列并调用下一个操作。
// build
var pipeline = new Pipeline<Order>();
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new CreateOrderProcessor());
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new PriceOrderProcessor());
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new PaymentOrderProcessor(User.Users.ToDictionary(user => user.Id, user => user.InitialBalance)));
pipeline.RegisterOperation(new DeliverOrderProcessor());
var monitor = new Pipeline<Order>();
monitor.RegisterOperation(pipeline);
monitor.RegisterOperation(new Operation<Order>(order =>
{
var report = order.Status == OrderStatus.Delivered ? "Success" : "Fail";
Console.WriteLine($"[IMPORTANT] Order {order.OrderId} Finished Processing : {report}");
return true;
}));
// process
foreach (var product in GetOrders()) monitor.Invoke(product);
这个场景有点复杂,所以我不会解释一切。这个想法是让不同的线程来处理传入的订单。订单处理完成后,我们会检查订单的状态。
class CreateOrderProcessor : Processor<Order>
{
private readonly List<Order> orders = new List<Order>();
protected override bool Process(Order order)
{
order.OrderId = orders.Count;
order.CreationTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
order.Status = OrderStatus.Created;
orders.Add(order);
Console.WriteLine($"Create Order {order.OrderId}");
return true;
}
}
每个订单处理器都隔离在一个专用线程中,因此您可以优化存储数据的方式并在不使用锁的情况下直接访问内存。
class PaymentOrderProcessor : Processor<Order>
{
protected override bool Process(Order order)
{
var balance = GetBalance(order.UserId);
var expected = balance - order.TotalPrice;
if (expected >= 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Payment User {order.UserId} Order {order.OrderId} : {order.TotalPrice} USD | Balance {balance} -> {expected}");
SetBalance(order.UserId, expected);
order.Status = OrderStatus.Payed;
return true;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Insufficient Balance : User {order.UserId} Balance {balance} USD | Order {order.OrderId} : {order.TotalPrice} USD");
order.Status = OrderStatus.Canceled;
return false;
}
}
}
支付订单处理器是唯一可以访问用户余额的线程。它可以获取或更新任何余额,而无需担心并发问题。
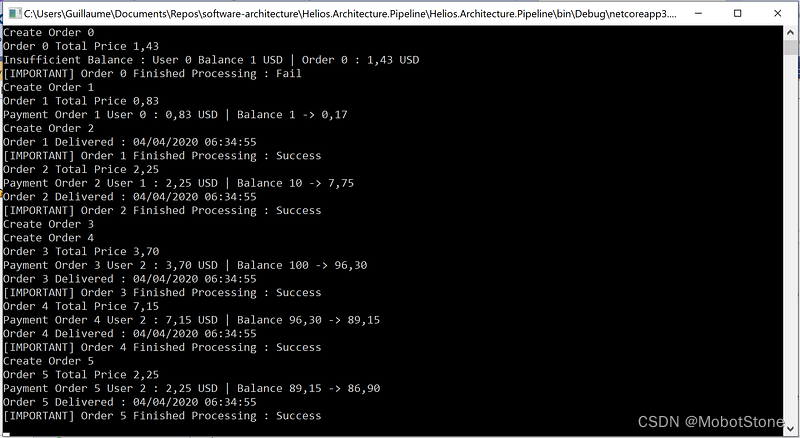
流水线正在尽可能快地处理操作序列。
结论
流水线设计模式有很多非常不同的实现方式,从简单的命令链到更复杂的工作流。