内容来源:KhanAcademy-Internet101- IP Address and DNS
(原视频和字幕、评论为英文,下面中文内容为个人理解后,查阅网络资料所作翻译,仅供参考;部分中文定义源自百度百科)
1. 相关名词
ISP - Internet Service Provider 互联网服务提供商
当你用笔记本或者手机连上WiFi,WiFi会连接到ISP,而后ISP再将你与世界上数以亿计的设备连接在一起。
IP - Internet Protocol 网络协议
网络使用者众多,对网络制定标准才能尽量减少麻烦。有一个人们都认同的标准或者协议,一个事物才能传播起来并且有规则地去运行。
这个世界上的所有设备都有唯一的地址,网络上的地址只是数字。而每台电脑,或者说是每个需要连接网络的设备,其地址都称为IP地址。它们通过标准协议得到可以对设备进行识别的一串数字。
常用的网络协议有两种, IPv4和IPv6。
其中IPv4是旧的标准,目前使用最为广泛,其构成如下图所示:
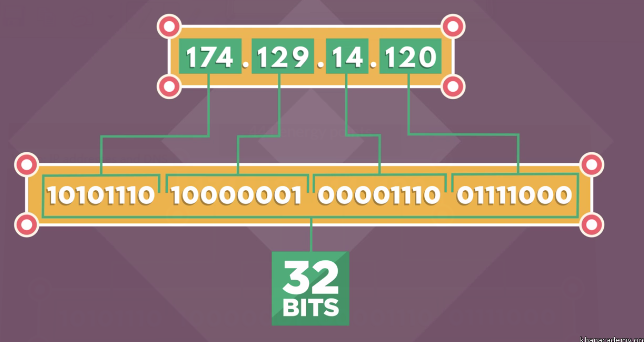
由4个字节组成。由于只有32位,所以能组合出的IP地址虽然很多,但是比较有限的。
另一种在缓慢普及的是IPv6,构成如下所示:
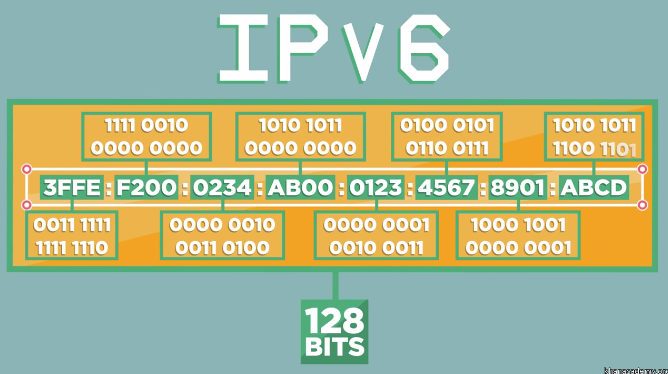
IPv6用了16字节的地址。其中一种标准表示即是图中所示的,由冒号分隔的8组4十六进制数位。
目前有超过80%的网络仍是通过IPv4连接的。
DNS - Domain Name System 域名系统
是互联网上IP地址和域名相互映射的一个分布式数据库。
举例来说,网址www.example.com对应的IP地址为153.104.63.227。
DNS其实就是将人类可读的地址转换成了电脑可识别的数值型IP地址。
DNS本身就是创造出来作为一个开放的公开通信的协议,也容易受到网络攻击。虽然DNS和IP地址之间存在一一对应的关系。但在使用网络的人们眼中,一般只有DNS可见,当其对应的IP地址被非法替换,那么实际会访问的地址就会随之变化。那么人们输入熟悉的网址出来的内容不再是原来的网址拥有者所提供的,甚至输入密码后信息采集将进入非法分子的数据库。
一般来说,判断访问的网站是不是真的,如果网址中有https,那么应该有对应的证书,这种情况是可以确定该网址的持有者的;若网址中有https,却无法获取其证书,那么可能该网站是假的;若网址中以http开头而非https开头,则无法确定该网址的持有者,也难以判断该网站的真实性。
DNS的运作方式可观看视频或参见视频后的第一个问答。
LAN - Local Area Network 局域网
是指在某一区域内由多台计算机互联成的计算机组。一般是方圆几千米以内。
NAT - Network Address Translation 网络地址转换
一个IETF标准,允许一个整体机构以一个公用IP地址出现在Internet上。
DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol 动态主机配置协议
是一个局域网的网络协议,使用UDP协议工作, 主要有两个用途:给内部网络或网络服务供应商自动分配IP地址,给用户或者内部网络管理员作为对所有计算机作中央管理的手段。
2. 为什么需要NAT和DHCP呢?
如前所说,IPv4能组合出来的IP地址是不够用的。既然不够用,那就没有办法每一个人都分配一个唯一的且永久的IP地址。
下面把几个回答翻译一下,看完就大致懂了。具体可能再看一下它们的定义和应用场景会更清楚。
第一个:
Every time when I connect to internet using a same computer, my IP address remains same or it changes?
每次我通过同一台电脑连接网络的时候,我的IP地址会保持不变还是会发生变化呢?
It depends on how the network is configured.
这要看网络是如何配置的。
Typically, when you hook a computer up to a network it will use DHCP to request an IP address from the DHCP server.
一般来说,当你将电脑联网时,它会使用DHCP去从DHCP服务器获取一个IP地址。
The DHCP server may lease out that IP address temporarily, or permanently. Often on a small local network the local part of the address would be permanent.
这个DHCP服务器可能会释放一个临时的IP地址,也有可能是永久的。通常在一个小的本地网络里,IP地址的本地部分会是永久的。
However, it is not unusual for an ISP (Internet Service Provider) to have a "pool" of IP addresses that they temporarily assign to clients.
然而,对于一个ISP来说,有一个IP地址池用于给客户端分配临时IP地址,也不是不寻常的事。
Many ISPs do this, because only a limited number of people will require an IP address at the same time, so they can have fewer IP addresses than clients and lease out the IP addresses as they are needed (this saves the ISP lots of money).
很多ISP都会这样做,因为在同一时间需要获取一个IP地址的人是比较有限的,所以通过这样的方式它们可以只拥有比客户端少的IP地址,但当客户端需要IP地址时都能去满足。一个IP地址是很昂贵的,这样的做法可以给ISP省很多钱。
The amount of time that you are leased out the IP address can vary widely.
而被分配一个IP地址等待的时间可以相差很远。
第二个:
I thought IP address was specific for a device. Why do websites have an IP address ? I'm confused now.
我以为每个设备会有特定的IP地址。为什么网址会有一个IP地址呢?我觉得有点困惑。
MAC addresses are specific to devices. Typically a network interface device will have a sticker or label with its MAC address on it.
MAC地址对设备来说是特定的。通常一个网络接口设备会有一个附着对应MAC地址的贴纸或标签。
IP addresses are not specific to devices.
但IP地址对于设备而言不是特定的。
Often, when you hook up a device to a network it requests an IP address to be assigned to it.
通常你将一个设备连到网络上的时候它会获取一个分配给它的IP地址。
The amount of time it is allowed to keep that IP address can vary (some networks may even choose to permanently assign a device an IP address ).
一个IP地址维持的时间可能会不同,有的网络甚至选择永久地把一个IP地址分配给一个设备。
It is even possible, through the use of Network Address Translation, for many devices to share the same IP address.
而通过网络地址转换甚至可以让许多设备共享相同的IP地址。
So why don't we just use MAC addresses for websites ?
那么为什么我们buyongMAC地址就好呢?
A MAC address is just for a single network interface device.
一个MAC地址只是属于一个单独的网络接口设备的。
If that device broke down and had to be replaced or the website want to use several different devices to balance the load of requests, a single MAC address wouldn't work.
如果这个设备坏掉了,需要被替换掉;或者有着网站需要好几台设备来平衡需求的负载,一个MAC地址可能就不太管用。
第三个:
How can you figure out what your computer's address is?
怎么知道自己电脑的IP地址是什么?
For Windows command prompt: use the command ipconfig
For Unix command prompt: use the command ifconfig
It will look something like this: X.X.X.X where X are numbers
得到的结果像是:X.X.X.X,这里的X指的是数字
If the IP address you find looks like 192.168.X.X (it starts with 192.168), then:
如果你看到IP地址是像192.168.X.X(192.168开头的),那么:
- You only found out your local IP address on your internal network.
- 你只是找到了在你内网上的本地IP地址。
- Your router is using NAT (network address translation), so that outside world only sees one IP address, but all your devices on your local network can use it
- 你的路由使用的是NAT,所以外部只能看到一个IP地址,但你本地网络上所有的网络都可以用这个IP地址来表示。
- To find the IP address that the outside world sees use https://www.whatismyip.com/(alternatively you can run the administrator tools for you router and it should tell you)
- 要看外部看到的IP地址是什么可以打开上面的网站,或者把路由的管理工具运行一下应该可以知道。
第四个:
if my hardware (say PC) is connected to a LAN will it have same IP address for local network and public network (internet) ?
如果我的硬件(比如说笔记本)连接着LAN,本地网络和外部网络(互联网)的IP地址会是一样的吗?
It depends.
这要看情况。
If you are not using Network address translation (NAT) then your external IP address will be the same as your local IP address.
如果你没有用NAT,那么你的外部IP地址会和本地的IP地址一样。
If you are using NAT (which most home networks with a router will be using) your router will present a single external IP address to the world, and your devices on your local network will have addresses between 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.255.255.
如果你在用着NAT(大多数用路由的家庭网络都会用),你的路由对世界展现的会是一个单一的外部IP地址,而连接在你本地网络的设备会有在192.168.0.0到192.168.255.255之间的IP地址。
NAT works by making up port numbers for each device on your local network.
NAT的运作是通过形成在你本地网络的每个设备的端口号实现的。
When one of your devices sends a packet to the internet, NAT will replace the source IP address with the external IP, and the source port with the port number it made up for that device.
当你的一台设备发送packet(packet可以网页浏览器的一幅图,也可以是一个程序的更新)到互联网,NAT会把源IP地址换为外部IP+该台设备对应的端口号。
When NAT receives a packet, it looks at the port number for the packet and then forwards it on to the device associated with that port number.
而当NAT收到packet时,它会识别packet目标的端口号,然后转发到该端口号对应的设备上。
(可以这么想,单一的IP地址是你们家地址,端口号是你们家每个人的名字,只要快递寄到你家,也写了收件人的名字,那快递员只要把快递送到你家就好了,你们可以自己把快递给收件人。这是另一个回答里所举的例子。)
Why do we use NAT ? Under the dominant standard IPv4 there are a limited number of IP addresses, and buying them is expensive.
为什么我们要用NAT?因为在占主导地位的IPv4标准下,只有有限的IP地址,它们又很贵。
NAT lets many devices share one IP address.
NAT可以让许多设备共享一个IP地址(降低成本)。
Under IPv6 (the newer standard, which is slowly spreading) there are so many IP addresses that every device can have its own IP address, which will make NAT, for the most part, unnecessary.
在IPv6(更新的标准,但缓慢的传播中)协议下,会有够多的IP地址来支持每台设备(视频里说甚至地球上的每颗沙子)都能够有一个自己的IP地址,NAT在这个协议下大部分情况则都是不必要的了。