本文为记录JS中常见的方法,您可以将其封装为你自己的工具函数,方便在任何项目中使用。如下方法为我工作期间遇到的实际需求整理得来,其中有些借鉴了他人的代码精华(距离时间有些久远,有些已经找不到原文了),如果您有更好的方法,欢迎留言讨论!篇幅有限,本文将会持续更新。
一、数组去重
1.Set()
适用场景:数组内的元素全部为基本数据类型(引用类型会失效)
let arr = [1, '2', 3, '2', false, false, true]
let newArr = [...new Set(arr)]
console.log(newArr)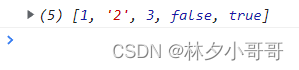
2.利用对象
适用场景:数组内的元素全部为对象,且有唯一值
数据源:
let arr = [{
id: 1,
name: 'zhangsan'
}, {
id: 2,
name: 'lisi'
}, {
id: 1,
name: 'zhangsan'
}]JS:
/**
* 数组去重
* @param Array {arr} 原始数组
* @param String {id} 数组元素的唯一标识,默认为id
*/
function arrDeduplication(arr, id = 'id') {
if (!(arr instanceof Array)) return arr
let obj = {}
let newArr = []
arr.forEach(k => {
if (!obj[k[id]]) {
obj[k[id]] = true //这里仅为标记此属性已经被添加了
newArr.push(k)
}
})
return newArr
}结果:
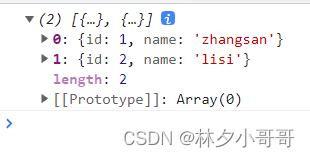
数组去重的方法有很多,这里仅列举常用且简单的
二、数组按固定长度分割
使用场景:例如:可滑动菜单,每页8个菜单,每个菜单根据权限动态渲染
数据源:
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]JS:
/**
* 数组按固定长度分割
* @param Array {arr} 原始数组
* @param Number {len} 长度
*/
function cutArray(arr, len) {
if (!(arr instanceof Array) || !len) return arr
let index = 0;
let newArr = [];
while (index < arr.length) {
newArr.push(arr.slice(index, index += len));
}
return newArr;
}
console.log(cutArray(arr, 5))结果:

三、数组排列组合
适用场景:商品sku
数据源:
let arr = [
['中杯', '大杯', '超大杯'], //份量
['加珍珠', '加椰果', '加西米露'] //小料
]
JS:
/**
* 数组排列组合
* @param Array {arr} 原始数组(二维数组)
*/
function doCombination(arr) {
var count = arr.length - 1; //数组长度(从0开始)
var tmp = [];
var totalArr = []; // 总数组
return doCombinationCallback(arr, 0); //从第一个开始
//js 没有静态数据,为了避免和外部数据混淆,需要使用闭包的形式
function doCombinationCallback(arr, curr_index) {
for (let val of arr[curr_index]) {
tmp[curr_index] = val; //以curr_index为索引,加入数组
//当前循环下标小于数组总长度,则需要继续调用方法
if (curr_index < count) {
doCombinationCallback(arr, curr_index + 1); //继续调用
} else {
totalArr.push(tmp); //(直接给push进去,push进去的不是值,而是值的地址)
}
//js 对象都是 地址引用(引用关系),每次都需要重新初始化,否则 totalArr的数据都会是最后一次的 tmp 数据;
let oldTmp = tmp;
tmp = [];
for (let index of oldTmp) {
tmp.push(index);
}
}
return totalArr;
}
}
console.log(doCombination(arr))结果:

四、数组排序
1.sort
字符串数据源:
let arr = ['张三', '李四', '安徒生', 'IKUN', 'FBI','Jay',
'vitas', 'jack', 'mary', '123', '3', '24']1.1 数字>汉字>字母 (数字按1-9,中文按拼音,英文按a-Z)
console.log(arr.sort((a, b) => a.localeCompare(b)))
数字数据源:
let arr = [1, 3, 4, 5, 16, 6, 32]1.2 数字从小到大排序
console.log(arr.sort((a, b) => a - b))
1.3 数字从大到小排序
console.log(arr.sort((a, b) => b - a))
1.4 按照给定规则数组排序
数据源:
let arr = [{
field: 'name',
value: 2
}, {
field: 'age',
value: 3
}, {
field: 'id',
value: 1
}, {
field: 'sex',
value: 4
}]排序规则数组:
// 排序规则数组
let order = ['id', 'name', 'job', 'age', 'city', 'sex']JS:
console.log(arr.sort((a, b) => {
return order.indexOf(a.field) - order.indexOf(b.field)
}))结果:
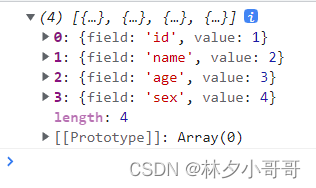
排序方法还有很多,例如:快速排序、冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序等
五、扁平化数组转树形结构(不用递归)
适用场景:将树结构转化为一维数组
来源:https://juejin.cn/post/6983904373508145189
数据源:
let arr = [{
id: 1,
name: '部门1',
pid: 0
},
{
id: 2,
name: '部门2',
pid: 1
},
{
id: 3,
name: '部门3',
pid: 1
},
{
id: 4,
name: '部门4',
pid: 3
},
{
id: 5,
name: '部门5',
pid: 4
},
]思路:
- 树结构首先需要考虑顶级目录,单个顶级目录的本质是一个对象,那么我们首先可以只考虑顶级目录,将所有的顶级目录找出来
- 有了顶级目录后,我们就需要考虑子目录了,我们可以在顶级目录上使用children来存放
- 区别顶级目录和子目录的方法是pid(父级id)和id,如果pid为0则是顶级目录,否则是子目录
- 子目录需要使用父级目录的id,也就是pid
- 由于是扁平化的数组,不考虑递归的话,我们可以借用对象引用来实现。将数组元素的id作为对象的键,数组元素做为值。然后在遍历对象的过程中,我们需要想办法让每一个值放到对应的位置
- 我们可以利用对象的浅拷贝来实现多层目录的修改
方法一:双循环
function arrayToTree(items) {
const result = []; // 存放结果集
const itemMap = {}; //
// 先将数组转成对象存储
for (const item of items) {
itemMap[item.id] = {
...item
}
}
for (const item of items) {
const id = item.id;
const pid = item.pid;
const treeItem = itemMap[id];
//pid === 0即当前为顶级目录
if (pid === 0) {
result.push(treeItem);
} else {
if (itemMap[pid]) {
itemMap[pid].children = itemMap[pid].children ? itemMap[pid].children : []
itemMap[pid].children.push(treeItem)
}
}
}
return result;
}方法二:单循环
function arrayToTree2(items) {
const result = []; // 存放结果集
const itemMap = {}; //
for (const item of items) {
const id = item.id;
const pid = item.pid;
if (!itemMap[id]) {
itemMap[id] = {
children: [],
}
}
itemMap[id] = {
...item,
children: itemMap[id]['children']
}
const treeItem = itemMap[id];
//pid === 0即当前为顶级目录
if (pid === 0) {
result.push(treeItem);
} else {
if (!itemMap[pid]) {
itemMap[pid] = {
children: [],
}
}
itemMap[pid].children.push(treeItem)
}
}
return result;
}结果:

代码分析:
1.首先,两种方法都是利用了对象引用来实现的,通过将元素的id作为键,元素本身作为值。
2.代码的关键都在“if(pid === 0)”之后,乍一看只是修改了itemMap的值,好像对最终返回的result没有影响,但我们仔细来看。函数中,在对itemMap的id属性进行赋值之后,其他的操作本质上只是改变了对象的引用,itemMap中的5个部门对象在内存中一直没有变,所以我们直接对这5个部门对象进行的修改,那么只要是引用它们的数据都会受影响。
3.所以我们可以直接修改itemMap上的属性,无需考虑嵌套关系。
六、日期
注意:在IOS16以下版本中,new Date()的参数中不支持传入“2022-03-27”这种格式,需要换为“2022/03/27”。以下方法未使用多参数类型,若使用TS,可以利用函数重载。
dateStr = dateStr.replace(/\-/g, '/')1.日期格式化
//年月日 时分秒
function formatDate(originVal) {
const dt = new Date(originVal)
const y = dt.getFullYear()
const m = (dt.getMonth() + 1 + '').padStart(2, '0')
const d = (dt.getDate() + '').padStart(2, '0')
const hh = (dt.getHours() + '').padStart(2, '0')
const mm = (dt.getMinutes() + '').padStart(2, '0')
const ss = (dt.getSeconds() + '').padStart(2, '0')
return `${y}-${m}-${d} ${hh}:${mm}:${ss}`
}
//年月日
function formatDate2(originVal) {
const dt = new Date(originVal)
const y = dt.getFullYear()
const m = (dt.getMonth() + 1 + '').padStart(2, '0')
const d = (dt.getDate() + '').padStart(2, '0')
return `${y}-${m}-${d}`
}2.前一天
//dateStr为当前日期
formatTime2(new Date(dateStr).getTime() - 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000)3.后一天
//dateStr为当前日期
formatTime2(new Date(dateStr).getTime() + 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000)七、节流防抖
来源:uview2
节流
节流的意思是,规定时间内,只触发一次。比如我们设定500ms,在这个时间内,无论点击按钮多少次,它都只会触发一次。具体场景可以是抢购时候,由于有无数人 快速点击按钮,如果每次点击都发送请求,就会给服务器造成巨大的压力,但是我们进行节流后,就会大大减少请求的次数。防抖
防抖的意思是,在连续的操作中,无论进行了多长时间,只有某一次的操作后在指定的时间内没有再操作,这一次才被判定有效。具体场景可以搜索框输入关键字过程中实时 请求服务器匹配搜索结果,如果不进行处理,那么就是输入框内容一直变化,导致一直发送请求。如果进行防抖处理,结果就是当我们输入内容完成后,一定时间(比如500ms)没有再 输入内容,这时再触发请求。
let timer; let
flag
/**
* 节流原理:在一定时间内,只能触发一次
*
* @param {Function} func 要执行的回调函数
* @param {Number} wait 延时的时间
* @param {Boolean} immediate 是否立即执行
* @return null
*/
function throttle(func, wait = 500, immediate = true) {
if (immediate) {
if (!flag) {
flag = true
// 如果是立即执行,则在wait毫秒内开始时执行
typeof func === 'function' && func()
timer = setTimeout(() => {
flag = false
}, wait)
}
} else if (!flag) {
flag = true
// 如果是非立即执行,则在wait毫秒内的结束处执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
flag = false
typeof func === 'function' && func()
}, wait)
}
}let timeout = null
/**
* 防抖原理:一定时间内,只有最后一次操作,再过wait毫秒后才执行函数
*
* @param {Function} func 要执行的回调函数
* @param {Number} wait 延时的时间
* @param {Boolean} immediate 是否立即执行
* @return null
*/
function debounce(func, wait = 500, immediate = false) {
// 清除定时器
if (timeout !== null) clearTimeout(timeout)
// 立即执行,此类情况一般用不到
if (immediate) {
const callNow = !timeout
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
timeout = null
}, wait)
if (callNow) typeof func === 'function' && func()
} else {
// 设置定时器,当最后一次操作后,timeout不会再被清除,所以在延时wait毫秒后执行func回调方法
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
typeof func === 'function' && func()
}, wait)
}
}八、深克隆
数据源:
let obj = {
a: 123,
b: 'zhangsan',
c: () => {
console.log('ccc')
},
d: [1, '2', {
name: 'linxi',
age: 18,
info: {
city: 'zz'
}
}],
e: null,
f: '',
g: false,
h: Symbol('h'),
i: undefined,
j: NaN
}1. JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())
适用场景:对象属性中没有函数、Symbol、undefined、NaN这4中类型
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)) 
2.完整版
function deepCopy(value) {
if (value instanceof Function) return value
else if (value instanceof Array) {
var newValue = []
for (let i = 0; i < value.length; ++i) newValue[i] = deepCopy(value[i])
return newValue
} else if (value instanceof Object) {
var newValue = {}
for (let i in value) newValue[i] = deepCopy(value[i])
return newValue
} else return value
}