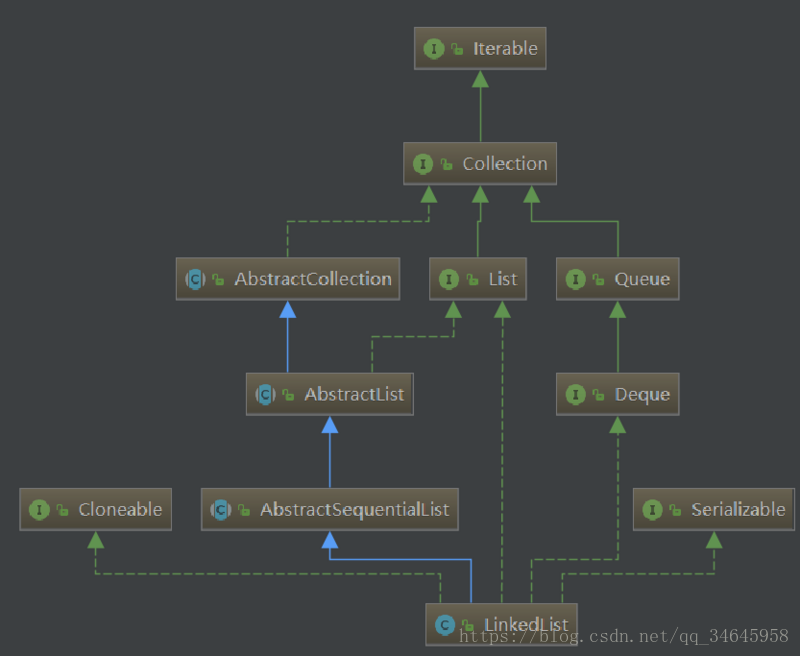
一.继承结构图
与Arraylist相比,没有实现randomAccess接口。但它实现了deque接口,底层就是数据结构中的链表
并且不是直接继承Abstractlist类,而是继承AbstractSequentialList类(这样它就不支持随机访问)
二.基本介绍
LinkedList是一个实现了list接口和Deque接口的双端链表
linkedlist不是线程安全的,如果想使得linkedlist变成线程安全的,可以使用collections类的synchronizedList方法去包装linkedlist对象
List list=Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));三.总结
1.linkedList获得头节点有哪些方法?获得头节点有哪些方法?
getFirst(),element(),peek(),peekFirst().其中getFirst和element在链表为空时会抛出nosuchElementException异常
而peek和peekfirst方法返回null(这两个方法的实现时完全一样的)
获得尾节点有peeklast()和getlast()方法,区别也是peeklast在链表为空时会返回null而不会报错
2.添加节点方法?
addfirst() addlast() offer() offerfirst() offerlast(),push()其中offer其实就是调用了addlast,push就是调用了addfirst
offerfirst和offerlast与前两者的区别就是这两个方法返回true,前两个方法返回void
3.删除节点的方法?
remove() removefirst() pop() poll() pollfirst() polllast()其中remove()和pop()其实就是调用了removefirst(),所以在链表为空时会抛出nosuchElementException
后面三个会在链表为空时返回null,不会抛出异常
4.由于Linkedlist是一个实现了Deque的的双端队列,多以linkedlist既可以当作queue又可以当作stack,用linkedList实现栈?
public class LinkedListStack<E>{
private LinkedList<E> linkedList;
public LinkedListStack(){
linkedList = new LinkedList<E>();
}
//压入数据
public void push(E e){
linkedList.push(e);
}
//弹出数据
public E pop(){
//在链表为空时会报异常
return linkedList.pop();
//在链表为空时返回null
//return linkedList.poll();
}
//检索栈顶数据(不弹出)
public E peek(){
return linkedList.peek();
}
}
public class LinkedListQueue<E> {
private LinkedList<E> linkedList;
public LinkedListQueue(){
linkedList = new LinkedList<E>();
}
//入队
public void enQueue(E e){
linkedList.addLast(e);
}
//出队
public void deQueue(){
//队列为空时抛出异常,等价于linkedList.removeFirst();
linkedList.pop();
//不会抛出异常
//linkedList.poll();
}
//打印队列
public void allItem(){
Iterator<E> iterator = linkedList.iterator();
if(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
queue.enQueue(1);
queue.enQueue(2);
queue.deQueue();
queue.allItem();
}
}
四.源码阅读
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
//当前链表中数据个数
transient int size = 0;
//linkedlist是双端链表结构,first指向链表头部,last指向链表尾部
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
//两个构造函数,一个用于构造空链表,另一个用已有的集合创建链表
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
//Node节点,存储节点的数据,前一个节点和后一个节点的引用
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
//添加元素在链表尾部
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//添加元素到指定位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//由于实现了deque接口,所以还有一系列添加节点的方法
addFirst(E e)方法
addLast(E e)方法
//offerfirst与addfirst的区别是该方法可以返回特定的返回值,addfirst返回void
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
//调用addfirst
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
offerLast(E e)方法(与addlast区别同上)
//获取某位置的元素
public E get(int index) {
//检查边界
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
//获得位置为0的头节点数据
(主要方法有:getfirst,element,peek,peekfirst)
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
//会在链表为空时抛出nosuchElementException异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
//peek和peekfirst会在链表为空时返回null而不会抛出异常
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
//获得位置size-1的尾节点数据
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
//返回第一个匹配的索引(可以看出linkedlist可以包含null元素)
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
//从头往后遍历
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
//从头往后遍历
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回最后一个匹配的索引
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
//从后向前遍历
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
//从后向前遍历
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
//检查链表是否包含了某个元素(实际上时调用了indexof方法)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
//删除某个对象(从前向后遍历,找到该元素后调用unlick方法)
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//如果删除对象为null
if (o == null) {
//从前向后遍历
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
//一旦匹配,调用unlink()方法和返回true
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
//从前向后遍历
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
//一旦匹配,调用unlink()方法和返回true
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;//得到后继节点
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;//得到前驱节点
//删除前驱指针
if (prev == null) {
first = next;如果删除的节点是头节点,令头节点指向该节点的后继节点
} else {
prev.next = next;//将前驱节点的后继节点指向后继节点
x.prev = null;
}
//删除后继指针
if (next == null) {
last = prev;//如果删除的节点是尾节点,令尾节点指向该节点的前驱节点
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;//得到后继节点
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;//得到前驱节点
//删除前驱指针
if (prev == null) {
first = next;如果删除的节点是头节点,令头节点指向该节点的后继节点
} else {
prev.next = next;//将前驱节点的后继节点指向后继节点
x.prev = null;
}
//删除后继指针
if (next == null) {
last = prev;//如果删除的节点是尾节点,令尾节点指向该节点的前驱节点
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;//得到后继节点
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;//得到前驱节点
//删除前驱指针
if (prev == null) {
first = next;如果删除的节点是头节点,令头节点指向该节点的后继节点
} else {
prev.next = next;//将前驱节点的后继节点指向后继节点
x.prev = null;
}
//删除后继指针
if (next == null) {
last = prev;//如果删除的节点是尾节点,令尾节点指向该节点的前驱节点
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;//得到后继节点
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;//得到前驱节点
//删除前驱指针
if (prev == null) {
first = next;如果删除的节点是头节点,令头节点指向该节点的后继节点
} else {
prev.next = next;//将前驱节点的后继节点指向后继节点
x.prev = null;
}
//删除后继指针
if (next == null) {
last = prev;//如果删除的节点是尾节点,令尾节点指向该节点的前驱节点
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}