一、分支结构
1、if
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 70;
if ( score < 60) {
System.out.println("不及格");
} else if (score >= 60 && score < 80) {
System.out.println("合格");
} else {
System.out.println("优秀");
}
}
2、switch
表达式类型只能是byte、short、int、char,JDK5开始支持枚举,JDK7开始支持String、不支持double、float、long
public static void main(String[] args) {
String weekday = "周三";
switch (weekday){
case "周一":
System.out.println("加班");
break;
case "周二":
System.out.println("解决bug");
break;
case "周三":
System.out.println("正常下班");
break;
default:
System.out.println("玩游戏");
}
}
二、循环结构
1、for循环
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("wielun");
}
}
2、while循环
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while(i < 3) {
System.out.println("wielun");
i++;
}
}
3、do-while循环
一定会先执行一次循环体
初始化语句;
do {
循环语句;
迭代语句;
} while (循环条件);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
do {
System.out.println("wielun");
i++;
} while (i < 3);
}
4、死循环
一直循环的执行下去,没有干预不会停止下来
// 三种不同做法
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (;;) {
System.out.println("wielun");
}
// 经典做法
while (true) {
System.out.println("wielun");
}
do {
System.out.println("wielun");
} while (true);
}
三、数组
1、数组定义
数组就是用来存储一批同种类型数据的内存区域
(1)静态初始化数组
定义数组的时候直接给数组赋值
// 完整格式
数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数组类型[]{元素1,元素2...};
int[] ages = new int[]{12,15,18};
(2)动态初始化数组
定义数组的时候只确定元素的类型和数组的长度,之后再存入具体数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] scores = new double[3];
// 赋值
scores[0] = 11.2;
System.out.println(scores[0]);
System.out.println(scores[1]);
}
结果:
11.2
0.0
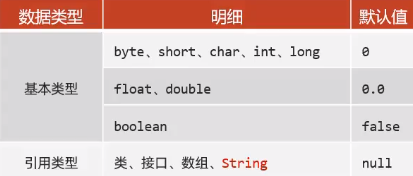
元素默认值规则:
2、数组的遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {12, 15, 18};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
四、方法
1、方法初体验
提高了代码的复用性,让程序的逻辑更清晰
public static void main(String[] args) {
int rs = sum(10,30);
System.out.println(rs);
}
public static int sum(int a,int b) {
int c = a + b;
return c;
}
2、方法的参数传递机制
(1)基本类型的参数传递
在传输实参给方法的形参的时候,并不是传输实参变量本身,而是传输实参变量中存储的值,这就是值传递
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
change(a);
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void change(int a) {
System.out.println(a);
a = 20;
System.out.println(a);
}
结果:
10
20
10
(2)引用类型的参数传递
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrs = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
change(arrs);
System.out.println(arrs[1]);
}
public static void change(int[] arrs) {
System.out.println("change1:" + arrs[1]);
arrs[1] = 22;
System.out.println("change2:" + arrs[1]);
}
结果:
change1:2
change2:22
22
3、方法重载
同一个类中,出现多个方法名称相同,但是形参列表是不同的,那么这些方法就是重载方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
fire();
fire("美国");
fire("美国",12);
}
public static void fire() {
System.out.println("fire1");
}
public static void fire(String location) {
System.out.println("fire2: " + location);
}
public static void fire(String location, int number) {
System.out.println("fire3: " + location + number);
}
结果:
fire1
fire2: 美国
fire3: 美国12